The Marriage Penalty: Past and Present
Whether you're currently married or not, the new tax legislation may impact how the "Marriage Penalty" affects you. Never heard of such a thing? Let's take a look at a simple example and show how it may be different under the new tax regulation.
The Marriage Penalty: Past and Present
Whether you're currently married or not, the new tax legislation may impact how the "Marriage Penalty" affects you. Never heard of such a thing? Let's take a look at a simple example and show how it may be different under the new tax regulation.
The Past (kind of)
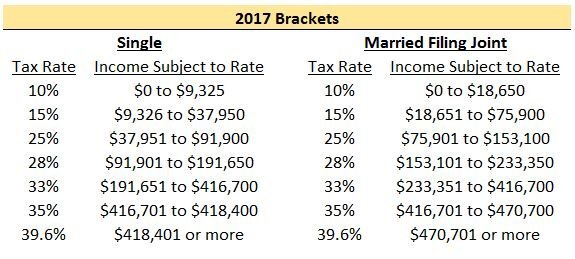
I say "kind of" because most people still have to file their 2017 tax return. Here is the 2017 tax table for Single Filers and Married Filing Joint Filers:
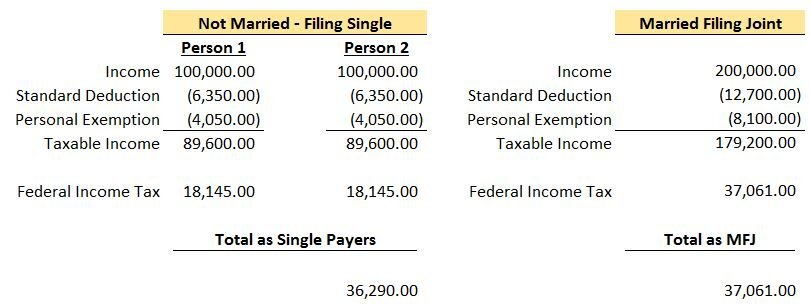
A reasonable person would think that the income subject to tax would simply double if you went from filing Single to Married Filing Joint. As you can see, this isn't the case once you are in the 25%+ tax bracket and it can mean big dollars! Let's take a look at a simple example where each person makes the same amount of money. We will also assume they will be taking the standard deduction in 2017.
Note: To calculate the “Federal Income Tax” amount above, you can use the IRS tables here 2017 1040 Tax Table Instructions. All of your income is not taxed at your top rate. For example, if your top income falls in the 25% tax bracket, as a single payer you will only pay 25% on income from $37,951 to $91,900. Everything below that range will be taxed at either 10% or 15%.
As you can see, because of the change in filing status, this couple owed a total of $771 more to the federal government. This is the “Marriage Penalty”. Typically as incomes rise, the dollar amount of the penalty becomes larger. For this couple, their top tax bracket went from 25% each when filing single to 28% filing joint.
The Present
Here is the 2018 tax table in the new tax legislation for Single Filers and Married Filing Joint Filers:
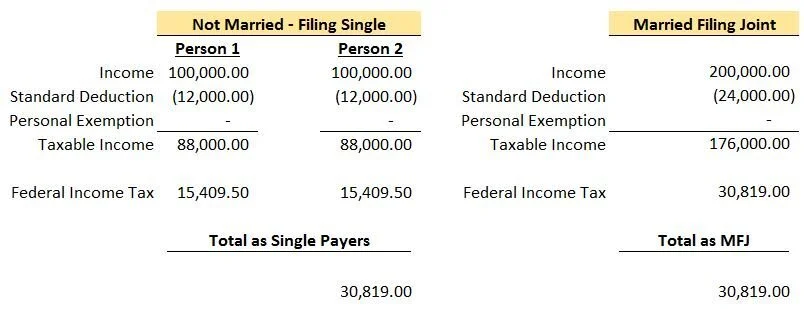
Upon review, you can see that the top income brackets are not doubled for Married Filing Joint. At 37%, a single person filing would reach the top rate at $500,001 while married filing joint would reach at $600,001. That being said, the “Marriage Penalty” appears to kick in at higher income levels compared to the past and therefore should impact less people. The income bracket for Married Filing Joint is doubled up until $400,000 of combined income compared to just $75,901 under the 2017 brackets.
Let’s take a look at the same couple in the example above.
Due to the income brackets doubling from single to married filing joint for this couple, the “Marriage Penalty” they would have incurred in 2017 appears to go away. In this example, they would also pay less in federal taxes in both situations. This article is more focused on the impact on the “Marriage Penalty” but having a lower tax bill is always a plus.
Standard vs. Itemized Deductions
The tax brackets aren’t the only penalty. Another common tax increase people see when going from single to married filing joint are the deductions they lose. If I’m single and own a home, it is likely I will itemized because the sum of my property taxes, mortgage interest, and state income taxes exceed the standard deduction amount. Assume the couple in the example above is still not married but Person 1 owns a home and rather than taking the standard deduction, Person 1 itemizes for an amount of $15,000. For 2017, their total deductions will be $21,350 ($15,000 Person 1 plus $6,350 Person 2) and for 2018, their total deductions will be $27,000 ($15,000 Person 1 plus $12,000 Person 2).
Now they get married and have to choose whether to itemize or take the standard deduction.
2017: Assuming they live together in the same house, in 2017 they would still itemize because they have deductions of $15,000 for Person 1 and some additional items that Person 2 would bring to the table (i.e. their state income taxes). Say their total itemized deductions are $18,000 when married filing joint. They would still itemize because $18,000 is more than the Married Filing Joint standard deduction of $12,700. But now compare the $18,000 to the $21,350 they got filing single. They lose out on $3,350 of deductions. Usually, less deductions equals more taxes.
2018: Assuming they live together in the same house, in 2018 they would no longer itemize. Assuming their total itemized deductions are still $18,000, that is less than the $24,000 standard deduction they can take when married filing joint. $24,000 standard deduction in 2018 is still less than the $27,000 they got filing separately by $3,000. Again, less deductions usually means more taxes. The “Marriage Penalty” lives on!
A lot of people will still lose out on deductions in 2018 but the “Marriage Penalty” will hit less people because of the increase in the standard deduction. If Person 1 has itemized deductions of $10,000 in 2017, they would itemize if they filed single and possibly take the standard deduction of $12,700 filing joint. In 2018 however, Person 1 would take the standard deduction both as a single tax payer ($12,000) and married filing joint ($24,000) which takes away the “Marriage Penalty” related to the deduction.
The Why?
Why do tax brackets work this way? Like most taxes, I assume the idea was to generate more income for the government. Some may also argue that typical couples don't make the same salaries which seems like an archaic point of view.Was it all fixed with the new tax legislation? It doesn't appear so but it does look like less people will be struck by Cupid's Marriage Penalty.
About Rob.........
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Changes to 2016 Tax Filing Deadlines
In 2015, a bill was passed that changed tax filing deadlines for certain IRS forms that will impact a lot of filers. Not only is it important to know the changes so you can prepare and file your return timely but to understand why the changes were made.
In 2015, a bill was passed that changed tax filing deadlines for certain IRS forms that will impact a lot of filers. Not only is it important to know the changes so you can prepare and file your return timely but to understand why the changes were made.
Summary of Changes
IRS Form Business Type Previous Deadline New Deadline
1065 Partnership April 15 March 15
1120C Corporation March 15 April 15
NOTE: The dates in the chart above are for companies with years ending 12/31. If a company has a different fiscal year, Partnerships will now file by the 15th day of the third month following year end and C Corporations will now file by the 15th day of the fourth month following year end.
Why the Changes?
The most practical reason for the change to filing deadlines is that individuals with partnership interests will now have a better opportunity to file their individual returns (Form 1040) without extending. Form K-1 provides information related to the activity of a Partnership at the level of each individual partner. For example, if I own 50% of a Partnership, my K-1 would show 50% of the income (or loss) generated, certain deductions, and any other activity needed for me to file my Form 1040. The issue with the previous Partnership return deadline of April 15th is that it coincided with the individual deadline. This resulted in partners of the company not receiving their K-1’s with sufficient time to file their personal return by April 15th. With Partnerships now having a deadline of March 15th, this will give individuals a month to receive their K-1 and file their personal return without having to extend.
The deadline for Form 1120, which is filed by C Corporations, was also changed with this bill. Where the Form 1065 deadline was cut back by a month, the Form 1120 was extended a month. C Corporations, for tax purposes, are treated similar to individuals whereas they pay taxes directly when they file their return. Partnerships are not taxed directly, rather the income or loss is passed through to each individual partner who recognizes the tax ramifications on their personal return. For this reason, the deadline for Form 1120 being extended a month has little impact, if any, on individuals. The change gives C Corporations more time to file without having to extend the return.
S Corporations are another common business type. The deadlines for S Corporation returns (Form 1120S) were not changed with this bill. S Corporations are similar to Partnerships in that K-1’s are distributed to owners and the income or loss generated is passed through to the individuals return. That being said, Form 1120S already has a due date of March 15th, the same as the new Partnership deadline.
Extension Deadlines
IRS Form Business Type Deadline
1040 Individual October 15
1065 Partnership September 15
1120 C Corporation September 15
1120S S Corporation September 15
Extension deadlines were not immediately changed with the passing of the bill. Although Partnerships previously had the same filing deadline as individuals, the deadline with the filing of an extension was a month before. This was necessary because if a Partnership did not have to file an extended return until October 15th, individuals with partnership interests wouldn’t have a choice but to file delinquent.
The one change to the extension chart above set to take place in 2026 is the C Corporation extension being changed to October 15th.
Summary
Overall, the changes appear to have improved the filing calendar. This may be a big adjustment for Partnerships that are used to the April 15th deadline as they will have one less month to get organized and file. For this reason, you may see an increase in 2016 Partnership extensions.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.