Do You Have To Pay Tax On Your Social Security Benefits?
I have some unfortunate news. If you look at your most recent paycheck, you are going to see a guy by the name of “FICA” subtracting money from your take-home pay. Part of that FICA tax is sent to the Social Security system, which entitles you to receive Social Security payments when you retire. The unfortunate news is that, even though it was a tax that you paid while you were working, when you go to receive your payments from Social Security, most retirees will have to pay some form of Income Tax on it. So, it’s a tax you pay on a tax? Pretty much!
In this article, I will be covering:
· The percent of your Social Security benefit that will be taxable
· The tax rate that you pay on your Social Security benefits
· The Social Security earned income penalty
· State income tax exceptions
· Withholding taxes from your Social Security payments
What percent of your Social Security benefit is taxable?
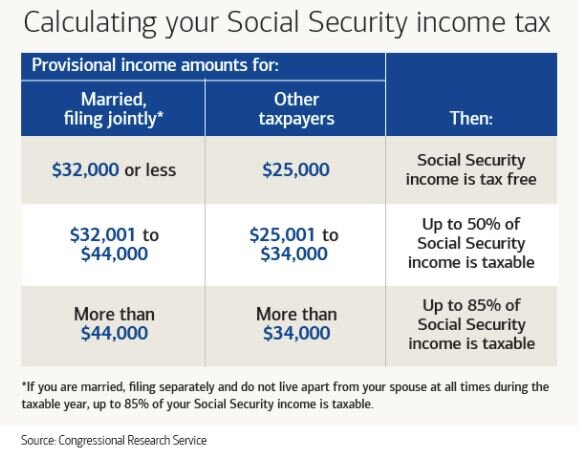
First, let’s start off with how much of your Social Security will be considered taxable income. It ranges from 0% to 85% of the amount received. Where you fall in that range will depend on the amount of income that you have each year. Here is the table for 2021:
But, here’s the kicker. 50% of your Social Security benefit that you receive counts towards the income numbers that are listed in the table above to arrive at your “combined Income” amount. Here is the formula:
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) + nontaxable interest + 50% of your SS Benefit = Combined Income
If you are a single tax filer, and you are receiving $30,000 in Social Security benefits, you are already starting at a combined income level of $15,000 before you add in any of your other income from employment, pensions, pre-tax distributions from retirement accounts, investment income, or rental income.
As you will see in the table, if your combined income for a single filer is below $25,000, or a joint filer below $32,000, you will not have to pay any tax on your Social Security benefit. Taxpayers above those thresholds will have to pay some form of tax on their Social Security benefits. But, I have a small amount of good news: no one has to pay tax on 100% of their benefit, because the highest percentage is 85%. Therefore, everyone at a minimum receives 15% of their benefit tax free.
NOTE: The IRS does not index the combined income amounts in the table above for inflation, meaning that even though an individual’s Social Security and wages tends to increase over time, the dollar amounts listed in the table stay the same from year to year. This has caused more and more taxpayers to have to pay tax on a larger portion of their Social Security benefit over time.
Tax Rate on Social Security Benefits
Your Social Security benefits are taxed as ordinary income. There are no special tax rates for Social Security like capital gains rates for investment income. Social Security is taxed at the federal level but may or may not be taxed at the state level. Currently there are 37 states in the U.S. that do not tax Social Security benefits. There are 4 states that tax it at the same level as the federal government and there are 13 states that partially tax the benefit. Here is table:
Withholding Taxes From Your Social Security Benefit
For taxpayers that know that will have to pay tax on their Social Security benefit, it is usually a good idea to have Social Security withholding taxes taken directly from your Social Security payments. Otherwise, you will have to issue checks for estimated tax payments throughout the year which can be a headache. They only provide you with four federal tax withholding options:
· 7%
· 10%
· 12%
· 22%
These percentages are applied to the full amount of your Social Security benefit, not to just the 50% or 85% that is taxable. Just something to consider when selecting your withholding elections.
To make a withholding election, you have to complete Form W-4V (Voluntary Withholding Request). Once you have completed the form, which only has 7 lines, you can mail it or drop it off at the closest Social Security Administration office.
Social Security Earned Income Penalty
If you elect to turn on your Social Security benefit prior to your Normal Retirement Age (NRA) AND you plan to keep working, you have to be aware of the Social Security earned income penalty. Your Normal Retirement Age is the age that you are entitled to receive your full Social Security benefit, and it’s based on your date of birth.
The earned income penalty ONLY applies to taxpayers that turn on their Social Security prior to their normal retirement age. Once you have reached your normal retirement age, this penalty does not apply.
Basically, the IRS limits how much you are allowed to make each year if you elect to turn on your Social Security early. If you earn over those amounts, you may have to pay all or a portion of the Social Security benefit back to the government. In the Chart below “FRA” stands for “Fully retirement age”, which is the same as “Normal Retirement Age” (NRA). Also note that for married couples, the earned income numbers below apply to your personal earnings, and do not take into consideration your spouse’s income.
INCOME UNDER $18,960: If you earned income is below $18,960, no penalty, you get to keep your full social security benefit
INCOME OVER $18,960: You lose $1 of your social security benefit for every $2 you earn over the threshold. Example:
· You turn on your social security at age 63
· Your social security benefit is $20,000 per year
· You make $40,000 per year in wages
Since you made $40,000 in wages, you are $21,040 over the $18,960 limit:
$21,040 x 50% ($1 reduction for every $2 earned) = $10,520 penalty.
The following year, your $20,000 Social Security benefit would be reduced by $10,520 for the assessment of the earned income penalty. Ouch!!
As a general rule of thumb, if you plan on working prior to your Social Security normal retirement age, and your wages will be in excess of the $18,960 limit, it usually make sense to wait to turn on your Social Security benefit until your wages are below the threshold or you reach normal retirement age.
NOTE: You will see in the middle row of the table “In the calendar year FRA is reached”. In the year that you reach your full retirement age for social security the wage threshold his higher and the penalty is lower (a $1 penalty for every $3 over the threshold).
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
DISCLOSURE: This material is for informational purposes only. Neither American Portfolios nor its Representatives provide tax, legal or accounting advice. Please consult your own tax, legal or accounting professional before making any decisions. Any opinions expressed in this forum are not the opinion or view of American Portfolios Financial Services, Inc. and have not been reviewed by the firm for completeness or accuracy. These opinions are subject to change at any time without notice. Any comments or postings are provided for informational purposes only and do not constitute an offer or a recommendation to buy or sell securities or other financial instruments. Readers should conduct their own review and exercise judgment prior to investing. Investments are not guaranteed, involve risk and may result in a loss of principal. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Investments are not suitable for all types of investors. Investment advisory services offered through Greenbush Financial Group, LLC. Greenbush Financial Group, LLC is a Registered Investment Advisor. Securities offered through American Portfolio Financial Services, Inc (APFS). Member FINRA/SIPC. Greenbush Financial Group, LLC is not affiliated with APFS. APFS is not affiliated with any other named business entity. There is no guarantee that a diversified portfolio will enhance overall returns or outperform a non-diversified portfolio. Diversification does not ensure against market risk. The opinions voiced in this material are for general information only and are not intended to provide specific advice or recommendations for any individual. To determine which investments may be appropriate for you, consult your financial advisor prior to investing. All performance referenced is historical and is no guarantee of future results. All indices are unmanaged and cannot be invested into directly. Guarantees apply to certain insurance and annuity products (not securities, variable or investment advisory products) and are subject to product terms, exclusions and limitations and the insurer's claims-paying ability and financial strength. Before investing, consider the investment objectives, risks, charges, and expenses of the annuity and its investment options. Please submit using the same generated coversheet for this submission number. Potential investors of 529 plans may get more favorable tax benefits from 529 plans sponsored by their own state. Consult your tax professional for how 529 tax treatments and account fees would apply to your particular situation. To determine which college saving option is right for you, please consult your tax and accounting advisors. Neither APFS nor its affiliates or financial professionals provide tax, legal or accounting advice. Please carefully consider investment objectives, risks, charges, and expenses before investing. For this and other information about municipal fund securities, please obtain an offering statement and read it carefully before you invest. Investments in 529 college savings plans are neither FDIC insured nor guaranteed and may lose value.
How Do Social Security Survivor Benefits Work?
Social Security payments can sometimes be a significant portion of a couple’s retirement income. If your spouse passes away unexpectedly, it can have a dramatic impact on your financial wellbeing in retirement. This is especially
Social Security payments can sometimes be a significant portion of a couple’s retirement income. If your spouse passes away unexpectedly, it can have a dramatic impact on your financial wellbeing in retirement. This is especially true if there was a big income difference between you and your spouse. In this article we will review:
Who is eligible to receive the Social Security Survivor Benefit
How the benefit is calculated
Electing to take the benefit early vs. delaying the benefit
Filing strategies that allow the surviving spouse to receive more from Social Security
Social Security Earned Income Penalty
Social Security filing strategies that married couples should consider to preserve the Survivor Benefit
Divorce: 2 Ex-spouses & 1 Current Spouse: All receiving the same Survivor Benefit
How Much Social Security Does A Surviving Spouse Receive?
When your spouse passes away, as the surviving spouse, you are entitled to receive the higher of the two benefits. You do not continue to collect both benefits simultaneously.
Example: Jim is age 80 and he is collecting a Social Security benefit of $2,500 per month. His wife Sarah is 79 and is collecting $2,000 per month for her Social Security benefit.
If Jim passes away first, Sarah would begin to receive $2,500 per month, but her $2,000 per month benefit would end.
If Sarah passes away first, Jim would continue to receive his $2,500 per month because his benefit was the higher of the two, and Sarah’s Social Security payments would end.
Married For 9 Month
To be eligible for the Social Security Survivor Benefit as the spouse, you have to have been married for at least nine months prior to your spouse passing away. If the marriage was shorter than that, you are not entitled to the Social Security Survivor Benefit.
Increasing Your Spouse’s Survivor Benefit
Due to this higher of the two rule, as financial planners we work this into the Social Security filing strategy for our clients. Before we get into the strategy, let’s do a quick review of your filing options and how it impacts your Social Security benefit.
Normal Retirement Age
Each of us has a Normal Retirement Age for Social Security which is based on our date of birth. The Normal Retirement Age is the age that you are entitled to your full Social Security benefit:
Should You Turn On The Benefit Early?
For your own personal Social Security benefit, once you reach age 62, you have the option to turn on your Social Security benefit early. However, if you elect to turn on your Social Security benefit prior to Normal Retirement Age, your monthly benefit is permanently reduced by approximately 6% per year for each year you take it early. So, if your normal retirement age is 67 and you file for Social Security at age 62, you only receive 70% of your full benefit and that is a permanent reduction.
On the flip side, if you delay filing for Social Security past your normal retirement age, your Social Security benefit increases by about 8% per year until you reach age 70.
There is no benefit to delaying Social Security past age 70.
How This Factors Into The Survivor Benefit
The decision of when you turn on your Social Security benefit will ultimately impact the Social Security Survivor Benefit that is available to your spouse should you pass away first. Remember, it’s the higher of the two. When there is a large gap between the amount that you and your spouse will receive from Social Security, it’s not uncommon for us to recommend that the higher income earner should delay filing for Social Security as long as possible. By delaying the start date, it increases the monthly amount that higher income earning spouse receives, which in turn preserves a higher monthly survivor benefit regardless of which spouse passes away first.
Example: Matt and Sarah are married, they are both 62, they retired last year, and they are trying to decide if they should turn on their Social Security benefit now, waiting until Normal Retirement Age, or delay it until age 70. Matt’s Social Security benefit at age 67 would be $2,700 per month. Sarah Social Security benefit at age 67 would be $2,000 per month.
They need $7,000 per month to meet their expenses. If Matt and Sarah both took their Social Security benefits at age 62, Matt’s benefit would be reduced to $1,890 per month and Sarah’s benefit would be reduced to $1,400 per month. At age 75, Matt passes away from a heart attack. Sarah’s Social Security benefit would increase to the amount that Matt was receiving, $1,890, and Sarah’s benefit of $1,400 per month would end. Since Sarah’s monthly expenses are still close to $7,000 per month, with the loss of the second Social Security benefit, she would have to withdraw $5,110 per month from another source to meet the $7,000 in monthly expenses. That’s $61,320 per year!!
Let’s compare that scenario to Matt waiting to file for his Social Security benefit until age 70 and Sarah turning on her Social Security benefit at age 62. By turning on Sarah’s benefit at age 62, it provides them with some additional income to meet expense, but when Matt turns 70, he will now receive $3,348 per month from Social Security. If Matt passes away at age 75, Sarah now receives Matt’s $3,348 per month from Social Security and her lower benefit ends. However, since the Social Security payments are higher than the previous example, now Sarah only needs to withdraw $3,652 per month from her personal savings to meet her expenses. That equals $43,824 per year.
If Sarah lives to age 90, by Matt making the decision to delay his Social Security Benefit to age 70, that saved Sarah an additional $262,400 that she otherwise would have had to withdraw from her personal savings over that 15 year period.
Age 60 - Surviving Spouse Benefit
As mentioned above, with your personal Social Security retirement benefits, you have the option to turn on your Social Security payments as early as age 62 at a reduced amount. In contrast, if your spouse predeceases you, you are allowed to turn on the Social Security Survivor Benefit as early as age 60.
Similar to turning on your personal Social Security benefit at age 62, if you elect to receive the Social Security Survivor Benefit prior to reaching your normal retirement age, Social Security reduces the benefit by approximately 6% per year, for each year that you start receiving the benefit prior to your normal retirement age.
Advance Filing Strategy
There is an advanced filing strategy associated with the Survivor Benefit. Social Security allows you to turn on the Survivor Benefit which is based on your spouse’s earnings history and defer your personal benefit until a future date. This allows your benefit to continue to grow even though you are currently receiving payments from Social Security. When you turn age 70, you can switch over to your own benefit which is at its maximum dollar threshold. But you would only do this, if your benefit was higher than the survivor benefit.
Example: Mike and Lisa are married and are both entitled to receive $2,000 per month from Social Security at age 67. Mike passes away unexpectedly at age 50. When Lisa turns 60, she will have to option to turn on the Social Security Survivor Benefit based on Mike’s earnings history at a reduced amount of $1,160 per month. In the meantime, Lisa can allow her personal Social Security benefit to continue to grow, and at age 70, Sarah can switch from the Surviving Spouse Benefit of $1,160 over to her personal benefit of $2,480 per month.
Beware of the Social Security Earned Income Penalty
If you are considering turning on your Social Security benefits prior to your normal retirement age, you must be aware of the Social Security earned income penalty. This is true for both your own personal Social Security benefits and the benefits you may receive as the surviving spouse. In 2020, if you are receiving Social Security benefits prior to your normal retirement age and you have earned income over $18,240 for that calendar year, not only are you receiving the benefit at a permanently reduced amount but Social Security assesses a penalty at the end of the year which is equal to $1 for every $2 of income over that threshold.
Example: Jackie decides to turn on her Social Security Survivor Benefits at age 60 in the amount of $1,000 per month. She is still working and will receive $40,000 in W-2 income. Based on the formula, of the $12,000 in Social Security payments that Jackie received, Social Security would assess a $10,880 penalty against that amount. So she basically loses it all to the penalty.
For clarification purposes, when Social Security levies the earned income penalty, they do not require you to issue them a check for the dollar amount of the penalty; instead, they deduct the amount that is due to them from your future Social Security payments. This usually happens shortly after you file your tax return for the previous year because the IRS uses your tax return to determine if the earned income penalty applies.
For this reason, there is a general rule of thumb that if you have not reached your normal retirement age for Social Security and you anticipate receiving income during the year well above the $18,240 threshold, it typically does not make sense to turn on the Social Security benefits early. It just ends up creating more taxable income for you, and you end up losing most or all of the money the next year when Social Security assesses the earned income penalty against your future benefits.
Once you reach normal retirement age, this earned income penalty no longer applies. You can turn on Social Security benefits and make as much as you want without a penalty.
Divorce
We find that many ex-spouses are not aware that they are also entitled to the Social Security Survivor Benefit if they were married to the decedent for more than 10 years prior to the divorce. Meaning if your ex-spouse passes away and you were married more than 10 years, if the monthly benefit that they were receiving from Social Security is higher than yours, you go back to Social Security, file under the Survivor Benefit, and your benefit will increase to their amount.
The only way you lose this option is if you remarry prior to age 60. However, if you get remarried after age 60, it does not jeopardize your ability to claim the Survivor Benefit based on your ex-spouse’s earnings history.
If your ex-spouse was remarried at the time they passed away, you are still entitled to receive the Survivor Benefit. In addition, their current spouse will also be able to claim the Survivor Benefit simultaneously and it does not reduced the amount that you receive as the ex-spouse.
There was even a case where an individual was divorced twice, both marriages lasted more than 10 years, and he was remarried at the time he passed away. After his passing, the two ex-spouses and the current spouse were all eligible to receive the full Social Security Survivor Benefit based on his earnings history.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Social Security Filing Strategies
Making the right decision of when to turn on your social security benefit is critical. The wrong decision could cost you tens of thousands of dollars over the long run. Given all the variables surrounding this decision, what might be the right decision for one person may be the wrong decision for another. This article will cover some of the key factors to
Making the right decision of when to turn on your social security benefit is critical. The wrong decision could cost you tens of thousands of dollars over the long run. Given all the variables surrounding this decision, what might be the right decision for one person may be the wrong decision for another. This article will cover some of the key factors to consider:
Normal Retirement Age
First, you have to determine your "Normal Retirement Age" (NRA). This is listed on your social security statement in the "Your Estimated Benefits" section. If you were born between 1955 – 1960, your NRA is between age 66 – 67. If you were born 1960 or later, your NRA is age 67. You can obtain a copy of your statement via the social security website.
Before Normal Retirement Age
You have the option to turn on social security prior to your normal retirement age. The earliest you can turn on social security is age 62. However, they reduce your social security benefit by approximately 7% per year for each year prior to your normal retirement age. See the chart below from USA Today which illustrates an individual with a normal retirement age of 66. If they turn on their social security benefit at age 62, they would only receive 75% of their full benefit. This reduction is a permanent reduction. It does not increase at a later date, outside of the small cost of living increases.
The big questions is: “If I start taking it age 62, at what age is the breakeven point?” Remember, if I turn on social security at 62 and my normal retirement age is 66, I have received 4 years of payments from social security. So at what age would I be kicking myself wishing that I had waited until normal retirement age to turn on my benefit. There are a few different ways to calculate this accounting for taxes, the rates of return on other retirement assets, inflations, etc. but in general it’s sometime between the ages of 78 and 82.
Since the breakeven point may be in your early 80’s, depending on your health, and the longevity in your family history, it may or may not make sense to turn on your benefit early. If we have a client that is in ok health but not great health and both of their parents passed way prior to age 85, then it may make sense to for them to turn on their social security benefit early. We also have clients that have pensions and turning on their social security benefit early makes the different between retiring now or have to work for 5+ more years. As long as the long-term projections work out ok, we may recommend that they turn on their social security benefit early so they can retire sooner.
Are You Still Working?
This is a critical question for anyone that is considering turning on their social security benefits early. Why? If you turn on your social security benefit prior to reaching normal retirement age, there is an “earned income” penalty if you earn over the threshold set by the IRS for that year. See the table listed below:
In 2016, for every $2 that you earned over the $15,720 threshold, your social security was reduced by $1. For example, let’s say I’m entitled to $1,000 per month ($12,000 per year) from social security at age 62 and in 2016 I had $25,000 in W2 income. That is $9,280 over the $15,720 threshold for 2016 so they would reduce my annual benefit by $4,640. Not only did I reduce my social security benefit permanently by taking my social security benefit prior to normal retirement age but now my $12,000 in annual social security payments they are going to reduce that by another $4,640 due to the earned income penalty. Ouch!!!
Once you reach your normal retirement age, this earned income penalty no longer applies and you can make as much as you want and they will not reduce your social security benefit.
Because of this, the general rule of thumb is if you are still working and your income is above the IRS earned income threshold for the year, you should hold off on turning on your social security benefits until you either reach your normal retirement age or your income drops below the threshold.
Should I Delay May Benefit Past Normal Retirement Age
As was illustrated in first table, if you delay your social security benefit past your normal retirement age, your benefit will increase by approximately 8% per year until you reach age 70. At age 70, your social security benefit is capped and you should elect to turn on your benefits.
So when does it make sense to wait? The most common situation is the one where you plan to continue working past your normal retirement age. It’s becoming more common that people are working until age 70. Not because they necessarily have too but because they want something to keep them busy and to keep their mind fresh. If you have enough income from employment to cover you expenses, in many cases, is does make sense to wait. Based on the current formula, your social security benefit will increase by 8% per year for each year you delay your benefit past normal retirement age. It’s almost like having an investment that is guaranteed to go up by 8% per year which does not exist.
Also, for high-income earners, a majority of their social security benefit will be taxable income. Why would you want to add more income to the picture during your highest tax years? It may very well make sense to delay the benefit and allow the social security benefit to increase.
Death Benefit
The social security death benefit also comes into play as well when trying to determine which strategy is the right one for you. For a married couple, when their spouse passes away they do not continue to receive both benefits. Instead, when the first spouse passes away, the surviving spouse will receive the “higher of the two” social security benefits for the rest of their life. Here is an example:
Spouse 1 SS Benefit: $2,000
Spouse 2 SS Benefit: $1,000
If Spouse 1 passes away first, Spouse 2 would bump up to the $2,000 monthly benefit and their $1,000 monthly benefit would end. Now let’s switch that around, let’s say Spouse 2 passes away first, Spouse 1 will continue to receive their $2,000 per month and the $1,000 benefit will end.
If social security is a large percentage of the income picture for a married couple, losing one of the social security payments could be detrimental to the surviving spouse. Due to this situation, it may make sense to have the spouse with the higher benefit delay receiving social security past normal retirement to further increase their permanent monthly benefit which in turn increases the death benefit for the surviving spouse.
Spousal Benefit
The “spousal benefit” can be a powerful filing strategy. If you are married, you have the option of turning on your benefit based on your earnings history or you are entitled to half of your spouse’s benefit, whichever benefit is higher. This situation is common when one spouse has a much higher income than the other spouse.
Here is an important note. To be eligible for the spousal benefit, you personally must have earned 40 social security “credits”. You receive 1 credit for each calendar quarter that you earn a specific amount. In 2016, the figure was $1,260. You can earn up to 4 credits each calendar year.
Another important note, under the new rules, you cannot elect your spousal benefit until your spouse has started receiving social security payments.
Here is where the timing of the social security benefits come into play. You can turn on your spousal benefit as early as 62 but similar to the benefit based on your own earnings history it will be reduce by approximately 7% per year for each year you start the benefit prior to normal retirement age. At your normal retirement age, you are entitled to receive your full spousal benefit.
What happens if you delay your spousal benefit past normal retirement age? Here is where the benefit calculation deviates from the norm. Typically when you delay benefits, you receive that 8% annual increase in the benefits up until age 70. The spousal benefit is based exclusively on the benefit amount due to your spouse at their normal retirement age. Even if your spouse delays their social security benefit past their normal retirement age, it does not increase the 50% spousal benefit.
Here is the strategy. If it’s determine that the spousal benefit will be elected as part of a married couple’s filing strategy, since delaying the start date of the benefits past normal retirement age will only increase the social security benefit for the higher income earning spouse and not the spousal benefit, in many cases, it does not make sense to delay the start date of the benefits past normal retirement age.
Divorce
For divorced couples, if you were married for at least 10 years, you can still elect the spousal benefit even though you are no longer married. But you must wait until your ex-spouse begins receiving their benefits before you can elect the spousal benefit.
Also, if you were married for at least 10 years, you are also entitled to the death benefit as their ex-spouse. When your ex-spouse passes away, you can notify the social security office, elect the death benefit, and you will receive their full social security benefit amount for the rest of your life instead of just 50% of their benefit resulting from the “spousal benefit” calculation.
Whether or not your ex-spouse remarries has no impact on your ability to elect the spousal benefit or death benefit based on their earnings history.
Consult A Financial Planner
Given all of the variables in the mix and the importance of this decision, we strongly recommend that you consult with a Certified Financial Planner® before making your social security benefit elections. While the interaction with a fee-based CFP® may cost you a few hundred dollars, making the wrong decision regarding your social security benefits could cost you thousands of dollars over your lifetime. You can also download a Financial Planner Budget Worksheet to give you that extra help when sorting out your finances and monthly budgeting.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.