How Pension Income and Retirement Account Withdrawals Can Impact Unemployment Benefits
How Pension Income and Retirement Account Withdrawals Can Impact Unemployment Benefits As the economy continues to slow, unemployment claims continue to rise at historic rates.
How Pension Income and Retirement Account Withdrawals Can Impact Unemployment Benefits
As the economy continues to slow, unemployment claims continue to rise at historic rates. Due to this expected increase in unemployment, the CARES Act included provisions for Coronavirus related distributions which give people access to retirement dollars with more favorable tax treatment. Details on these distributions can be found here. With retirement dollars becoming more accessible with the CARES Act, a common question we are receiving is “Will a retirement distribution impact my Unemployment Benefits?”.
Unemployment Benefits vary from state to state and therefore the answer to this question can be different depending on the state you reside in. This article will focus on New York State Unemployment Benefits, but a lot of the items discussed may be applied similarly in other states.
The answer to this question also depends on the type of retirement account you are receiving money from so we will touch on the most common.
Note: Typically, to qualify for unemployment insurance benefits, you must have been paid minimum wage during the “base period”. Base period is defined as the first four quarters of the last five calendar quarters prior to the calendar quarter which the claim is effective. “Base period employer” is any employer that paid the claimant during the base period.
Pension Reduction
Money received from a pension that a base period employer contributed to will result in a dollar for dollar reduction in your unemployment benefit. Even if you partially contributed to the pension, 100% of the amount received will result in an unemployment benefit reduction.
If you were the sole contributor to the pension, then the unemployment benefit should not be impacted.
Even if you are retired from a job and receiving a pension, you may still qualify for unemployment benefits if you are actively seeking employment.
Qualified Retirement Plans (examples; 401(k), 403(b))
If the account you are accessing is from a base period employer, a withdrawal from a qualified retirement plan could result in a reduction in your unemployment benefit. It is common for retirement plans to include some type of match or profit-sharing element which would qualify as an employer contribution. Accounts which include employer contributions may result in a reduction of your unemployment benefit.
We recommend you contact the unemployment claims center to determine how these distributions would impact your benefit amount before taking them.
IRA
No unemployment benefit rate reduction will occur if the distribution is from a qualified IRA.Knowing there is no reduction caused by qualified IRA withdrawals, a common practice is rolling money from a qualified retirement plan into an IRA and then accessing it as needed. Once you are no longer at the employer, you are often able to take a distribution from the plan. Rolling it into an IRA and accessing the money from that account rather than directly from the retirement plan could result in a higher unemployment benefit.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Warning To All Employees: Review The Tax Withholding In Your Paycheck Otherwise A Big Tax Bill May Be Waiting For You
As a result of tax reform, the IRS released the new income tax withholding tables in January and your employer probably entered those new withholding amounts into the payroll system in February. It was estimated that about 90% of taxpayers would see an increase in their take home pay once the new withholding tables were implemented.
As a result of tax reform, the IRS released the new income tax withholding tables in January and your employer probably entered those new withholding amounts into the payroll system in February. It was estimated that about 90% of taxpayers would see an increase in their take home pay once the new withholding tables were implemented. While lower tax rates and more money in your paycheck sounds like a good thing, it may come back to bite you when you file your taxes.
The Tax Withholding Guessing Game
Knowing the correct amount to withhold for federal and state income taxes from your paycheck is a bit of a guessing game. Withhold too little throughout the year and when you file your taxes you have a tax bill waiting for you equal to the amount of the shortfall. Withhold too much and you will receive a big tax refund but that also means you gave the government an interest free loan for the year.
There are two items that tell your employer how much to withhold for federal income tax from your paycheck:
Income Tax Withholding Tables
Form W-4
The IRS provides your employer with the Income Tax Withholding Tables. On the other hand, you as the employee, complete the Form W-4 which tells your employer how much to withhold for taxes based on the “number of allowances” that you claim on the form.
What Is A W-4 Form?
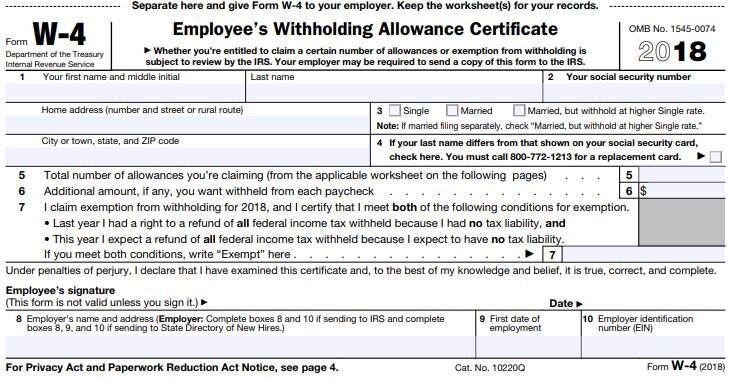
The W-4 form is one of the many forms that HR had you complete when you were first hired by the company. Here is what it looks like:
Section 3 of this form tells your employer which withholding table to use:
Single
Married
Married, but withhold at higher Single Rate
Section 5 tells your employer how many "allowances" you are claiming. Allowance is just another word for "dependents". The more allowances your claim, the lower the tax withholding in your paycheck because it assumes that you will have less "taxable income" because in the past you received a deduction for each dependent. This is where the main problem lies. Due to the changes in the tax laws, the tax deduction for personal exemptions was eliminated. This may adversely affect some taxpayers the were claiming a high number of allowances on their W-4 form because even though the number of their dependents did not change, their taxable income may be higher in 2018 because the deduction for personal exemptions no longer exists.
Even though everyone should review their Form W-4 form this year, employees that claimed allowances on their W-4 form are at the highest risk of either under withholding or over withholding taxes from their paychecks in 2018 due to the changes in the tax laws.
How Much Should I Withhold From My Paycheck For Taxes?
So how do you go about calculating that right amount to withhold from your paycheck for taxes to avoid an unfortunate tax surprise when you file your taxes for 2018? There are two methods:
Ask your accountant
Use the online IRS Withholding Calculator
The easiest and most accurate method is to ask your personal accountant when you meet with them to complete your 2017 tax return. Bring them your most recent pay stub and a blank Form W-4. Based on the changes in the tax laws, they can assist you in the proper completion of your W-4 Form based on your estimated tax liability for the year.If you complete your own taxes, I would highly recommend visiting the updated IRS Withholding Calculator. The IRS calculator will ask you a series of questions, such as:
How many dependents you plan to claim in 2018
Are you over the age of 65
The number of children that qualify for the dependent care credit
The number of children that will qualify for the new child tax credit
Estimated gross wages
How much fed income tax has already been withheld year to date
Payroll frequency
At the end of the process it will provide you with your personal results based on the data that you entered. It will provide you with guidance as to how to complete your Form W-4 including the number of allowances to claim and if applicable, the additional amount that you should instruct your employer to withhold from your paycheck for federal income taxes. Additional withholding requests are listed in Section 6 of the Form W-4.
Avoid Disaster
Having this conversation with your accountant and/or using the new IRS Withholding Calculator will help you to avoid a big tax disaster in 2018. Unfortunately, many employees may not learn about this until it's too late. Employees that are used to getting a tax refund may find out in the spring of next year that they owe thousands of dollars to the IRS because the combination of the new tax tables and the changes in the tax law that caused them to inadvertently under withhold federal income taxes throughout the year.
Action Item!!
Take action now. The longer you wait to run this calculation or to have this conversation with your accountant, the larger the adjustment may be to your paycheck. It's easier to make these adjustments now when you have nine months left in the year as opposed to waiting until November.I would strongly recommend that you share this article with your spouse, children in the work force, and co-workers to help them avoid this little known problem. The media will probably not catch wind of this issue until employees start filing their tax returns for 2018 and they find out that there is a tax bill waiting for them.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
How Does A Simple IRA Plan Work?
Not every company with employees should have a 401(k) plan. In many cases, a Simple IRA plan may be the best fit for a small business. These plans carry the following benefits
Not every company with employees should have a 401(k) plan. In many cases, a Simple IRA plan may be the best fit for a small business. These plans carry the following benefits
No TPA fees
Easy to setup & operate
Employee attraction and retention tool
Pre-tax contributions for the owners to lower their tax liability
Your company
To be eligible to sponsor a Simple IRA, your company must have less than 100 employees. The contribution limits to these plans are about half that of a 401(k) plan but it still may be the right fit for you company. Here are some of the most common statements that we hear from the owners of the business that would lead you to considering a Simple IRA plan over a 401(k) plan:
"I want to put a retirement plans in place for my employees that has very low fees and is easy to operate."
"We are a start-up, we don't have a lot of money to contribute to the plan as the owners, but we want to put a plan in place to attract and retain employees."
"I plan on contributing $15,000 per year to the plan, even if I sponsored a plan that allowed me to contribute more I wouldn't because I'm socking all of the profits back into the business"
"I have a SEP IRA now but I just hired my first employee. I need to setup a different type of plan since SEP IRA's are 100% employer funded"
Establishment Deadline
The deadline to establish a Simple IRA plan is October 1st. Once you have cross over that date, you would have to wait until the following calendar year to set the plan.
Eligibility
The eligibility requirements for a Simple IRA are different than a SEP IRA or 401(k) plans. Unlike these other plan "1 Year of Service" = $5,000 of compensation earned in a calendar year. If you want to only cover "full-time" employees with your retirement plan, you may need to consider a 401(k) plan which has the 1 year and 1000 hours requirement to obtain a year of service. The most restrictive "wait time" that you can put into place is 2 years. Meaning an employee must obtain 2 years of service before they are eligible to start contributing to the plan. You can also be more lenient that 2 years, such as immediate entry or a 1-year wait, but 2 years is the most restrictive it can be.
Types of Contributions
Like a 401(k) plan, Simple IRA have both employee deferral contributions and employer contributions.
Employee Deferrals
Eligible employees are allowed to make pre-tax contributions to their Simple IRA accounts. The contribution limits are less than a traditional 401(k). Below is a tale comparing the 2021 contribution limits of a Simple IRA vs a 401(k) Plan:
There are not Roth deferrals allows in Simple IRA plans.
Employer Contributions
Unlike other employer sponsored retirement plans, employer contributions are mandatory each year to a Simple IRA plan. The company must choose between two pre-set employer contribution formulas:
2% Non-elective
3$ Matching contribution
With the 2% non-elective contribution, the company must contribute 2% of each eligible employee’s compensation to the plan whether they contribute to the plan or not.
For the 3% matching contribution, it’s a dollar for dollar match up to 3% of compensation that they employee contributes to the plan. The match formula is more popular than the 2% non-elective contribution because the company only must contribute if the employee contributes.
Special 1% Rule
With the employer matching contribution there is also a special rule. In 2 out of any 5 consecutive years, the company can lower the employer match to as low as 1% of pay. We will often see start-up company's take advantage of this rule by putting a 1% employer match in place for the first 2 years of the plan to minimize costs and then they are committed to making the 3% match for years 3, 4, and 5.
100% Vesting
All employer contributions to Simple IRA plans are 100% vested. The company is not allowed to attach a "vesting schedule" to the contributions.
Important Compliance Requirements
Make sure you have a 5304 Simple Form in your files for each year you sponsor the Simple IRA plan. If you are audited by the IRS or DOL, they will ask for these forms. You need to distribute this form to all of your employee each year between Nov 1st and Dec 1st for the upcoming plan year. The documents notifies your employees that:
A retirement plan exists
Plan eligibility requirement
Employer contribution formula
Who they submit their deferral elections to within the company
If you do not have this form on file, the IRS will assume that you have immediate eligibility for your Simple IRA plan, meaning that all of your employees are due employer contributions since day one of employment. Even employee that used to work for you and have since terminated employment. It’s an ugly situation.
Make sure the company is timely when submitting the employee deferrals to the Simple IRA plan. Since you are withholding money from employees pay for the salary deferrals the IRS want you to send that money to their Simple IRA accounts “as soon as administratively feasible”. The suggested time phrase is within a week of the deduction in payroll. But you must be consistent with the timing of your remittances to your Simple IRA plan. If you typically submit contributions to your Simple IRA provider 5 days after a payroll run but one week you randomly submit it 2 days after the payroll run, 2 days just became the rule and all of the other deferral remittances are “late”. The company will be assessed penalties for all of the late deferral remittances. So be consistent.
Cannot Terminate Mid-Year
Unlike other retirement plans, you cannot terminate a Simple IRA plan mid-year. Simple IRA plan termination are most common when a company started with a Simple IRA, has grown in employee head count, and now wishes to put a 401(k) plan in place. You must wait until after December 31st to terminate the Simple IRA plan and implement the new 401(k) plan.
Special 2 Year Rule
If you replace your Simple IRA with a 401(k) plan, the balances in the Simple IRA can usually be rolled over into the new 401(k) if the employee elects to do so. However, be very careful of the special Simple IRA 2 Year Distribution Rule. If you process any type of distribution from a Simple IRA, within a two-year period of the employee depositing their first dollar to the account, and the employee is under 59½, they are hit with a 25% IRS penalty. THIS ALSO APPLIES TO DIRECT ROLLOVERS. Normally when you process a direct rollover from one retirement plan to another, no taxes or penalties are assessed. That is not the case in Simple IRA plan so be care of this rule. If you decide to switch from a Simple IRA to a 401(k), make sure you run a list of all the employees that maintain a balance in the Simple IRA plan to determine which employees are subject to the 2-year withdrawal restriction.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Fiduciary Rule: Exposing Your 401(K) Advisor’s Secrets
It’s here. On June 9, 2017, the long awaited Fiduciary Rule for 401(k) plans will arrive. What secrets does your 401(k) advisor have?
It’s here. On June 9, 2017, the long awaited Fiduciary Rule for 401(k) plans will arrive. The wirehouse and broker-dealer community within the investment industry has fought this new rule every step of the way. Why? Because their secrets are about to be exposed. Fee gouging in these 401(k) plans has spiraled out of control and it has gone on for way too long. While the Fiduciary Rule was designed to better protect plan participants within these employer sponsored retirement plans, the response from the broker-dealer community, in an effort to protect themselves, may actually drive the fees in 401(k) plans higher than they are now.
If your company sponsors an employer sponsored retirement plan and your investment advisor is a broker with one of the main stream wirehouse or broker dealers then they may be approaching you within the next few months regarding a “platform change” for your 401(k) plan. Best advice, start asking questions before you sign anything!! The brokerage community is going to try to gift wrap this change and present this as a value added service to their current 401(k) clients when the reality is this change is being forced onto the brokerage community and they are at great risk at losing their 401(k) clients to independent registered investment advisory firms that have served as co-fiduciaries to their plans along.
The Fiduciary Rule requires all investment advisors that handle 401(k) plans to act in the best interest of their clients. Up until now may brokers were not held to this standard. As long as they delivered the appropriate disclosure documents to the client, the regulations did not require them to act in their client’s best interest. Crazy right? Well that’s all about to change and the response of the brokerage community will shock you.
I will preface this article by stating that there have been a variety of responses by the broker-dealer community to this new regulation. While we cannot reasonably gather information on every broker-dealers response to the Fiduciary Rule, this article will provide information on how many of the brokerage firms are responding to the new legislation given our independent research.
SECRET #1:
Many of the brokerage dealers are restricting what 401(k) platforms their brokers can use. If the broker currently has 401(k) clients that maintain a plan with a 401(k) platform outside of their new “approved list”, they are forcing them to move the plan to a pre-approved platform or the broker will be required to resign as the advisor to the plan. Even though your current 401(k) platform may be better than the new proposed platform, the broker may attempt to move your plan so they can keep the plan assets. How is this remotely in your employee’s best interest? But it’s happening. We have been told that some of these 401(k) providers end up on the “pre-approve list” because they are willing to share fees with the broker dealer. If you don’t share fees, you don’t make the list. Really ugly stuff!!
SECRET #2:
Because these wirehouses and broker-dealers know that their brokers are not “experts” in 401(k) plans, many of the brokerage firms are requiring their 401(k) plans to add a third-party fiduciary service which usually results in higher plan fees. The question to ask is “if you were so concerned about our fiduciary liability why did you wait until now to present this third party fiduciary service?” They are doing this to protect themselves, not the client. Also, many of these third party fiduciary services could standardize the investment menu and take the control of the investment menu away from the broker. Which begs the question, what are you paying the broker for?
SECRET #3:
Some broker-dealers are responding to the Fiduciary Rule by forcing their brokers to move all their 401(k) plans to a “fee based platform” versus a commission based platform. The plan participants may have paid commissions on investments when they were purchased within their 401(k) account and now could be forced out of those investments and locked into a fee based fee structure after they already paid a commission on their balance. This situation will be common for 401(k) plans that are comprised primarily of self-directed brokerage accounts. Make sure you ask the advisor about the impact of the fee structure change and any deferred sales charges that may be imposed due to the platform change.
SECRET #4:
The plan fees are often times buried. The 401(k) industry has gotten very good at hiding fees. They talk in percentages and basis points but rarely talk in hard dollars. One percent does not sound like a lot but if you have a $2 million dollar 401(k) plan that equals $20,000 in fees coming out of the plans assets every year. Most of the fees are buried in the mutual fund expense ratios and you basically have to be an investment expert to figure out how much you are paying. This has continued to go on because very rarely do companies write a check for their 401(k) fees. Most plans debit plan assets for their plan fees but the fees are real.
With all of these changes taking place, now is the perfect time to take a good hard look at your company’s employer sponsored retirement plan. If your current investment advisor approaches you with a recommended “platform change” that is a red flag. Start asking a lot of questions and it may be a good time to put your plan out to bid to see if you can negotiate a better overall solution for you and your employees.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Traditional vs. Roth IRA’s: Differences, Pros, and Cons
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRA’s) are one of the most popular retirement vehicles available for savers and the purpose of this article is to give a general idea of how IRA’s work, explain the differences between Traditional and Roth IRA’s, and provide some pros and cons of each. In January 2015, The Investment Company Institute put out a research
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRA’s) are one of the most popular retirement vehicles available for savers and the purpose of this article is to give a general idea of how IRA’s work, explain the differences between Traditional and Roth IRA’s, and provide some pros and cons of each. In January 2015, The Investment Company Institute put out a research report with some interesting statistics regarding IRA’s which can be found at the following link, ICI Research Perspective. The article states, “In mid-2014, 41.5 million, or 33.7 percent of U.S. households owned at least one type of IRA”. At first I was slightly shocked and asked myself the following question: “If IRA’s are the most important investment vehicle and source of income for most retirees, how do only one third of U.S. households own one?” Then when I took a step back and considered how money gets deposited into these retirement vehicles this figure begins making more sense.
Yes, a lot of American’s will contribute to IRA’s throughout their lifetime whether it is to save for retirement throughout one’s lifetime or each year when the CPA gives you the tax bill and you ask “What can I do to pay less?” When thinking about IRA’s in this way, one third of American’s owning IRA’s is a scary figure and leads one to believe more than half the country is not saving for retirement. This is not necessarily the case. 401(k) plans and other employer sponsored defined contribution plans have become very popular over the last 20 years and rather than individuals opening their own personal IRA’s, they are saving for retirement through their employer sponsored plan.
Employees with access to these employer plans save throughout their working years and then, when they retire, the money in the company retirement account will be rolled into IRA’s. If the money is rolled directly from the company sponsored plan into an IRA, there is likely no tax or penalty as it is going from one retirement account to another. People roll the balance into IRA’s for a number of reasons. These reasons include the point that there is likely more flexibility with IRA’s regarding distributions compared to the company plan, more investment options available, and the retiree would like the money to be managed by an advisor. The IRA’s allow people to draw on their savings to pay for expenses throughout retirement in a way to supplement income that they are no longer receiving through a paycheck.
The process may seem simple but there are important strategies and decisions involved with IRA’s. One of those items is deciding whether a Traditional, Roth or both types of IRA’s are best for you. In this article we will breakdown Traditional and Roth IRA’s which should illustrate why deciding the appropriate vehicle to use can be a very important piece of retirement planning.
Why are they used?
Both Traditional and Roth IRA’s have multiple uses but the most common for each is retirement savings. People will save throughout their lifetime with the goal of having enough money to last in retirement. These savings are what people are referring to when they ask questions like “What is my number?” Savers will contribute to retirement accounts with the intent to earn money through investing. Tax benefits and potential growth is why people will use retirement accounts over regular savings accounts. Retirees have to cover expenses in retirement which are likely greater than the social security checks they receive. Money is pulled from retirement accounts to cover the expenses above what is covered by social security. People are living longer than they have in the past which means the answer to “What is my number?” is becoming larger since the money must last over a greater period.
How much can I contribute?
For both Traditional and Roth IRA’s, the limit in 2021 for individuals under 50 is the lesser of $6,000 or 100% of MAGI and those 50 or older is the lesser of $7,000 or 100% of MAGI. More limit information can be found on the IRS website Retirement Topics - IRA Contribution Limits
What are the important differences between Traditional and Roth?
Taxation
Traditional (Pre-Tax) IRA: Typically people are more familiar with Traditional IRA’s as they’ve been around longer and allow individuals to take income off the table and lower their tax bill while saving. Each year a person contributes to a Pre-Tax IRA, they deduct the contribution amount from the income they received in that tax year. The IRS allows this because they want to encourage people to save for retirement. Not only are people decreasing their tax bill in the year they make the contribution, the earnings of Pre-Tax IRA’s are not taxed until the money is withdrawn from the account. This allows the account to earn more as money is not being taken out for taxes during the accumulation phase. For example, if I have $100 in my account and the account earns 10% this year, I will have $10 of earnings. Since that money is not taxed, my account value will be $110. That $110 will increase more in the following year if the account grows another 10% compared to if taxes were taken out of the gain. When the money is used during retirement, the individual will be taxed on the amount distributed at ordinary income tax rates because the money was never taxed before. A person’s tax rate during retirement is likely to be lower than while they are working because total income for the year will most likely be less. If the account owner takes a distribution prior to 59 ½ (normal retirement age), there will be penalties assessed.
Roth (After-Tax) IRA: The Roth IRA was established by the Taxpayer Relief Act of 1997. Unlike the Traditional IRA, contributions to a Roth IRA are made with money that has already been subject to income tax. The money gets placed in these accounts with the intent of earning interest and then when the money is taken during retirement, there is no taxes due as long as the account has met certain requirements (i.e. has been established for at least 5 years). These accounts are very beneficial to people who are younger or will not need the money for a significant number of years because no tax is paid on all the earnings that the account generates. For example, if I contribute $100 to a Roth IRA and the account becomes $200 in 15 years, I will never pay taxes on the $100 gain the account generated. If the account owner takes a distribution prior to 59 ½ (normal retirement age), there will be penalties assessed on the earnings taken.
Eligibility
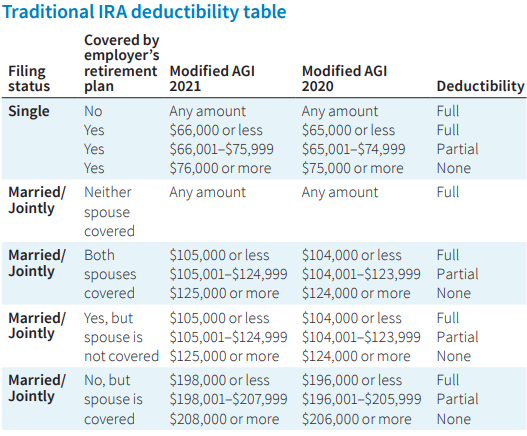
Traditional IRA: Due to the benefits the IRS allows with Traditional IRA’s, there are restrictions on who can contribute and receive the tax benefit for these accounts. Below is a chart that shows who is eligible to deduct contributions to a Traditional IRA:
There are also Required Minimum Distributions (RMD’s) associated with Pre-Tax dollars in IRA’s and therefore people cannot contribute to these accounts after the age of 70 ½. Once the account owner turns 70 ½, the IRS forces the individual to start taking distributions each year because the money has never been taxed and the government needs to start receiving revenue from the account. If RMD’s are not taken timely, there will be penalties assessed.
Roth IRA: As long as an individual has earned income, there are only income limitations on who can contribute to Roth IRA’s. The limitations for 2021 are as follows:
There are a number of strategies to get money into Roth IRA’s as a financial planning strategy. This method is explained in our article Backdoor Roth IRA Contribution Strategy.
Investment Strategies
Investment strategies are different for everyone as individuals have different risk tolerances, time horizons, and purposes for these accounts.
That being said, Roth IRA’s are often times invested more aggressively because they are likely the last investment someone touches during retirement or passes on to heirs. A longer time horizon allows one to be more aggressive if the circumstances permit. Accounts that are more aggressive will likely generate higher returns over longer periods. Remember, Roth accounts are meant to generate income that will never be taxed, so in most cases that account should be working for the saver as long as possible. If money is passed onto heirs, the Roth accounts are incredibly valuable as the individual who inherits the account can continue earning interest tax free.
Choosing the correct IRA is an important decision and is often times more complex than people think. Even if you are 30 years from retiring, it is important to consider the benefits of each and consult with a professional for advice.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.