Advanced Tax Strategies For Inherited IRA's
Inherited IRA’s can be tricky. There are a lot of rules surrounding;
Establishment and required minimum distribution (“RMD”) deadlines
Options available to spouse and non-spouse beneficiaries
Strategies for deferring required minimum distributions
Special 60 day rollover rules for inherited IRA’s
Inherited IRA’s can be tricky. There are a lot of rules surrounding;
Establishment and required minimum distribution (“RMD”) deadlines
Options available to spouse and non-spouse beneficiaries
Strategies for deferring required minimum distributions
Special 60 day rollover rules for inherited IRA’s
Establishment Deadline
If the decedent passed away prior to December 31, 2019, as a non-spouse beneficiary you have until December 31st of the year following the decedent’s death to establish an inherited IRA, rollover the balance into that IRA, and begin taking RMD’s based your life expectancy. If you miss that deadline, you are locked into distribution the full balance with a 10 year period.
If the decedent passed away January 1, 2020 or later, with limited exceptions, the inherited IRA rollover option with the stretch option is no longer available to non-spouse beneficiaries.
RMD Deadline - Decedent Passed Away Prior to 12/31/19
If you successfully establish an inherited IRA by the December 31st deadline, if you are non-spouse beneficiary, you will be required to start taking a “required minimum distribution” based on your own life expectancy in the calendar year following the decedent’s date of death.
Here is the most common RMD mistake that is made. The beneficiary forgets to take an RMD from the IRA in the year that the decedent passes away. If someone passes away toward the beginning of the year, there is a high likelihood that they did not take the RMD out of their IRA for that year. They are required to do so and the RMD amount is based on what the decedent was required to take for that calendar year, not based on the life expectancy of the beneficiary. A lot of investment providers miss this and a lot of beneficiaries don’t know to ask this question. The penalty? A lovely 50% excise tax by the IRS on the amount that should have been taken.
Distribution Options Available To A Spouse
If you are the spouse of the decedent you have three distribution options available to you:
Take a cash distribution
Rollover the balance to your own IRA
Rollover the balance to an Inherited IRA
Cash distributions are treated the same whether you are a spouse or non-spouse beneficiary. You incur income tax on the amounts distributed but you do not incur the 10% early withdrawal penalty regardless of age because it’s considered a “death distribution”. For example, if the beneficiary is 50, normally if distributions are taken from a retirement account, they get hit with a 10% early withdrawal penalty for not being over the age of 59½. For death distributions to beneficiaries, that 10% penalty is waived.
#1 Mistake Made By Spouse Beneficiaries
This exemption of the 10% early withdrawal penalty leads me to the number one mistake that we see spouses make when choosing from the three distribution options listed above. The spouse has a distribution option that is not available to non-spouse beneficiaries which is the ability to rollover the balance to their own IRA. While this is typically viewed as the easiest option, in many cases, it is not the most ideal option. If the spouse is under 59½, they rollover the balance to their own IRA, if for whatever reason they need to access the funds in that IRA, they will get hit with income taxes AND the 10% early withdrawal penalty because it’s now considered an “early distribution” from their own IRA.
Myth: Spouse Beneficiaries Have To Take RMD’s From Inherited IRA’s
Most spouse beneficiaries make the mistake of thinking that by rolling over the balance to their own IRA instead of an Inherited IRA they can avoid the annual RMD requirement. However, unlike non-spouse beneficiaries which are required to take taxable distributions each year, if you are the spouse of the decedent you do not have to take RMD’s from the inherited IRA unless your spouse would have been age 70 ½ if they were still alive. Wait…..what?
Let me explain. Let’s say there is a husband age 50 and a wife age 45. The husband passes away and the wife is the sole beneficiary of his retirement accounts. If the wife rolls over the balance to an Inherited IRA, she will avoid taxes and penalties on the distribution, and she will not be required to take RMD’s from the inherited IRA for 20 years, which is the year that their deceased spouse would have turned age 70 ½. This gives the wife access to the IRA if needed prior to age 59 ½ without incurring the 10% penalty.
Wait, It Gets Better......
But wait, since the wife was 5 years young than the husband, wouldn’t she have to start taking RMD’s 5 years sooner than if she just rolled over the balance to her own IRA? If she keeps the balance in the Inherited IRA the answer is “Yes” but here is an IRA secret. At any time, a spouse beneficiary is allowed to rollover the balance in their inherited IRA to their own IRA. So in the example above, the wife in year 19 could rollover the balance in the inherited IRA to her own IRA and avoid having to take RMD’s until she reaches age 70½. The best of both worlds.
Spouse Beneficiary Over Age 59½
If the spouse beneficiary is over the age of 59½ or you know with 100% certainty that the spouse will not need to access the IRA assets prior to age 59 ½ then you can simplify this process and just have them rollover the balance to their own IRA. The 10% early withdrawal penalty will never be an issue.
Non-Spouse Beneficiary Options
As mentioned above, the distribution options available to non-spouse beneficiaries were greatly limited after the passing of the SECURE ACT by Congress on December 19, 2019. For most individuals that inherit retirement accounts after December 31, 2019, they will now be subject to the new "10 Year Rule" which requires non-spouse beneficiary to completely deplete the retirement account 10 years following the year of the decedents death.
For more on the this change and the options available to Non-Spouse beneficiaries in years 2020 and beyond, please read the article below:
60 Day Rollover Mistake
There is a 60 day rollover rule that allows the owner of an IRA to take a distribution from an IRA and if the money is deposited back into the IRA within 60 days, it’s like the distribution never happened. Each taxpayer is allowed one 60 day rollover in a 12 month period. Think of it as a 60 day interest free loan to yourself.
Inherited IRA’s are not eligible for 60 day rollovers. If money is distributed from the Inherited IRA, the rollover back into the IRA will be disallowed, and the individual will have to pay taxes on the amount distributed.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Big Changes For 401(k) Hardship Distributions
While it probably seems odd that there is a connection between the government passing a budget and your 401(k) plan, this year there was. On February 9, 2018, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 was passed into law which ended the government shutdown by raising the debt ceiling for the next two years. However, also buried in the new law were
While it probably seems odd that there is a connection between the government passing a budget and your 401(k) plan, this year there was. On February 9, 2018, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 was passed into law which ended the government shutdown by raising the debt ceiling for the next two years. However, also buried in the new law were changes to rules that govern hardship distributions in 401(k) plans.
What Is A Hardship Distribution?
A hardship distribution is an optional distribution feature within a 401(k) plan. In other words, your 401(k) plan may or may not allow them. To answer that question, you will have to reference the plan’s Summary Plan Description (SPD) which should be readily available to plan participants.
If your plan allows hardship distributions, they are one of the few in-service distribution options available to employees that are still working for the company. There are traditional in-service distributions which allow employees to take all or a portion of their account balance after reaching the age 59½. By contrast, hardship distributions are for employees that have experienced a “financial hardship”, are still employed by the company, and they are typically under the age of 59½.
Meeting The "Hardship" Requirement
First, you have to determine if your financial need qualifies as a "hardship". They typically include:
Unreimbursed medical expenses for you, your spouse, or dependents
Purchase of an employee's principal residence
Payment of college tuition and relative education costs such as room and board for the next 12 months for you, your spouse, dependents, or children who are no longer dependents.
Payment necessary to prevent eviction of you from your home, or foreclosure on the mortgage of your primary residence
For funeral expenses
Certain expenses for the repair of damage to the employee's principal residence
Second, there are rules that govern how much you can take out of the plan in the form of a hardship distribution and restrictions that are put in place after the hardship distribution is taken. Below is a list of the rules under the current law:
The withdrawal must not exceed the amount needed by you
You must first obtain all other distribution and loan options available in the plan
You cannot contribute to the 401(k) plan for six months following the withdrawal
Growth and investment gains are not eligible for distribution from specific sources
Changes To The Rules Starting In 2019
Plan sponsors need to be aware that starting in 2019 some of the rules surrounding hardship distributions are going to change in conjunction with the passing of the Budget Act of 2018. The reasons for taking a hardship distribution did not change. However, there were changes made to the rules associated with taking a hardship distribution starting in 2019. More specifically, of the four rules listed above, only one will remain.
No More "6 Month Rule"
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 eliminated the rule that prevents employees from making 401(k) contributions until 6 months after the date the hardship distribution was issued. The purpose of the 6 month wait was to deter employees from taking a hardship distribution. In addition, for employees that had to take a hardship it was a silent way of implying that “if things are bad enough financially that you have to take a distribution from your retirement account, you probably should not be making contributions to your 401(k) plan for the next few months.”
However, for employees that are covered by a 401(k) plan that offers an employer matching contribution, not being able to defer in the plan for 6 months also meant no employer matching contribution during that 6 month probationary period. Starting in 2019, employees will no longer have to worry about that limitation.
Loan First Rule Eliminated
Under the current 401(k) rules, if loans are available in the 401(k) plan, the plan participant was required to take the maximum loan amount before qualifying for a hardship distribution. That is no longer a requirement under the new law.
We are actually happy to see this requirement go away. It never really made sense to us. If you have an employee, who’s primary residence is going into foreclosure, why would you make them take a loan which then requires loan payments to be made via deductions from their paycheck? Doesn’t that put them in a worse financial position? Most of the time when a plan participant qualifies for a hardship, they need the money as soon as possible and having to go through the loan process first can delay the receipt of the money needed to remedy their financial hardship.
Earnings Are Now On The Table
Under the current 401(k) rules, if an employee requests a hardship distribution, the portion of their elective deferral source attributed to investment earnings was not eligible for withdrawal. Effective 2019, that rule has also changed. Both contributions and earnings will be eligible for a hardship withdrawal.
Still A Last Resort
We often refer to hardship distributions as the “option of last resort”. This is due to the taxes and penalties that are incurred in conjunction with hardship distributions. Unlike a 401(k) loan which does not trigger immediate taxation, hardship distributions are a taxable event. To make matters worse, if you are under the age of 59½, you are also subject to the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
For example, if you are under the age of 59½ and you take a $20,000 hardship distribution to make the down payment on a house, you will incur taxes and the 10% penalty on the $20,000 withdrawal. Let’s assume you are in the 24% federal tax bracket and 7% state tax bracket. That $20,000 distribution just cost you $8,200 in taxes.
Gross Distribution: $20,000
Fed Tax (24%): ($4,800)
State Tax (7%): ($1,400)
10% Penalty: ($2,000)
Net Amount: $11,800
There is also an opportunity cost for taking that money out of your retirement account. For example, let’s assume you are 30 years old and plan to retire at age 65. If you assume an 8% annual rate of return on your 401(K) investment that $20,000 really cost you $295,707. That’s what the $20,000 would have been worth, 35 years from now, compounded at 8% per year.
Plan Amendment Required
These changes to the hardship distribution rule will not be automatic. The plan sponsor of the 401(k) will need to amend the plan document to adopt these new rules otherwise the old hardship distribution rules will still apply. We recommend that companies reach out to their 401(k) providers to determine whether or not amending the plan to adopt the new hardship distribution rules makes sense for the company and your employees.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Marriage Penalty: Past and Present
Whether you're currently married or not, the new tax legislation may impact how the "Marriage Penalty" affects you. Never heard of such a thing? Let's take a look at a simple example and show how it may be different under the new tax regulation.
The Marriage Penalty: Past and Present
Whether you're currently married or not, the new tax legislation may impact how the "Marriage Penalty" affects you. Never heard of such a thing? Let's take a look at a simple example and show how it may be different under the new tax regulation.
The Past (kind of)
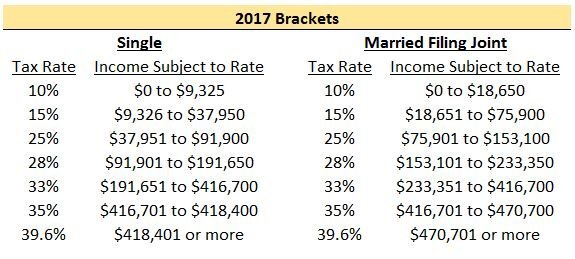
I say "kind of" because most people still have to file their 2017 tax return. Here is the 2017 tax table for Single Filers and Married Filing Joint Filers:
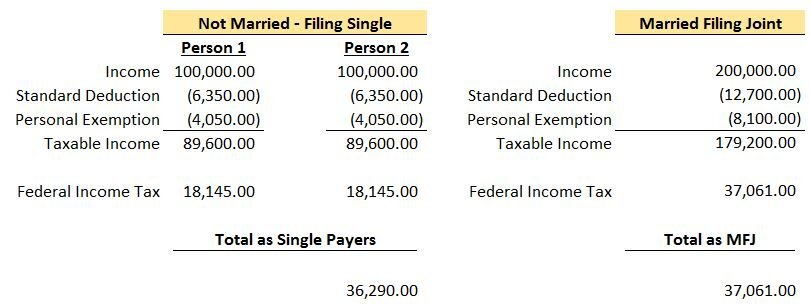
A reasonable person would think that the income subject to tax would simply double if you went from filing Single to Married Filing Joint. As you can see, this isn't the case once you are in the 25%+ tax bracket and it can mean big dollars! Let's take a look at a simple example where each person makes the same amount of money. We will also assume they will be taking the standard deduction in 2017.
Note: To calculate the “Federal Income Tax” amount above, you can use the IRS tables here 2017 1040 Tax Table Instructions. All of your income is not taxed at your top rate. For example, if your top income falls in the 25% tax bracket, as a single payer you will only pay 25% on income from $37,951 to $91,900. Everything below that range will be taxed at either 10% or 15%.
As you can see, because of the change in filing status, this couple owed a total of $771 more to the federal government. This is the “Marriage Penalty”. Typically as incomes rise, the dollar amount of the penalty becomes larger. For this couple, their top tax bracket went from 25% each when filing single to 28% filing joint.
The Present
Here is the 2018 tax table in the new tax legislation for Single Filers and Married Filing Joint Filers:
Upon review, you can see that the top income brackets are not doubled for Married Filing Joint. At 37%, a single person filing would reach the top rate at $500,001 while married filing joint would reach at $600,001. That being said, the “Marriage Penalty” appears to kick in at higher income levels compared to the past and therefore should impact less people. The income bracket for Married Filing Joint is doubled up until $400,000 of combined income compared to just $75,901 under the 2017 brackets.
Let’s take a look at the same couple in the example above.
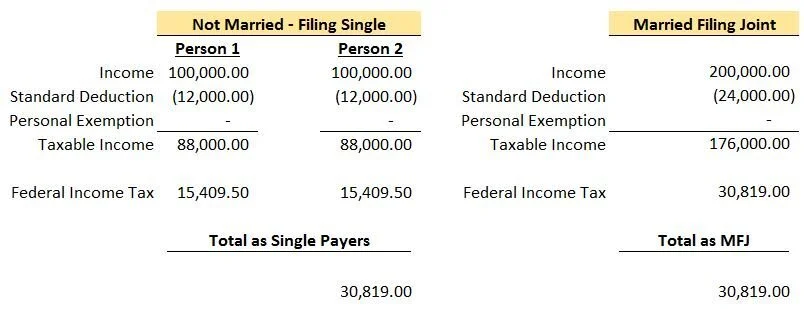
Due to the income brackets doubling from single to married filing joint for this couple, the “Marriage Penalty” they would have incurred in 2017 appears to go away. In this example, they would also pay less in federal taxes in both situations. This article is more focused on the impact on the “Marriage Penalty” but having a lower tax bill is always a plus.
Standard vs. Itemized Deductions
The tax brackets aren’t the only penalty. Another common tax increase people see when going from single to married filing joint are the deductions they lose. If I’m single and own a home, it is likely I will itemized because the sum of my property taxes, mortgage interest, and state income taxes exceed the standard deduction amount. Assume the couple in the example above is still not married but Person 1 owns a home and rather than taking the standard deduction, Person 1 itemizes for an amount of $15,000. For 2017, their total deductions will be $21,350 ($15,000 Person 1 plus $6,350 Person 2) and for 2018, their total deductions will be $27,000 ($15,000 Person 1 plus $12,000 Person 2).
Now they get married and have to choose whether to itemize or take the standard deduction.
2017: Assuming they live together in the same house, in 2017 they would still itemize because they have deductions of $15,000 for Person 1 and some additional items that Person 2 would bring to the table (i.e. their state income taxes). Say their total itemized deductions are $18,000 when married filing joint. They would still itemize because $18,000 is more than the Married Filing Joint standard deduction of $12,700. But now compare the $18,000 to the $21,350 they got filing single. They lose out on $3,350 of deductions. Usually, less deductions equals more taxes.
2018: Assuming they live together in the same house, in 2018 they would no longer itemize. Assuming their total itemized deductions are still $18,000, that is less than the $24,000 standard deduction they can take when married filing joint. $24,000 standard deduction in 2018 is still less than the $27,000 they got filing separately by $3,000. Again, less deductions usually means more taxes. The “Marriage Penalty” lives on!
A lot of people will still lose out on deductions in 2018 but the “Marriage Penalty” will hit less people because of the increase in the standard deduction. If Person 1 has itemized deductions of $10,000 in 2017, they would itemize if they filed single and possibly take the standard deduction of $12,700 filing joint. In 2018 however, Person 1 would take the standard deduction both as a single tax payer ($12,000) and married filing joint ($24,000) which takes away the “Marriage Penalty” related to the deduction.
The Why?
Why do tax brackets work this way? Like most taxes, I assume the idea was to generate more income for the government. Some may also argue that typical couples don't make the same salaries which seems like an archaic point of view.Was it all fixed with the new tax legislation? It doesn't appear so but it does look like less people will be struck by Cupid's Marriage Penalty.
About Rob.........
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Social Security Filing Strategies
Making the right decision of when to turn on your social security benefit is critical. The wrong decision could cost you tens of thousands of dollars over the long run. Given all the variables surrounding this decision, what might be the right decision for one person may be the wrong decision for another. This article will cover some of the key factors to
Making the right decision of when to turn on your social security benefit is critical. The wrong decision could cost you tens of thousands of dollars over the long run. Given all the variables surrounding this decision, what might be the right decision for one person may be the wrong decision for another. This article will cover some of the key factors to consider:
Normal Retirement Age
First, you have to determine your "Normal Retirement Age" (NRA). This is listed on your social security statement in the "Your Estimated Benefits" section. If you were born between 1955 – 1960, your NRA is between age 66 – 67. If you were born 1960 or later, your NRA is age 67. You can obtain a copy of your statement via the social security website.
Before Normal Retirement Age
You have the option to turn on social security prior to your normal retirement age. The earliest you can turn on social security is age 62. However, they reduce your social security benefit by approximately 7% per year for each year prior to your normal retirement age. See the chart below from USA Today which illustrates an individual with a normal retirement age of 66. If they turn on their social security benefit at age 62, they would only receive 75% of their full benefit. This reduction is a permanent reduction. It does not increase at a later date, outside of the small cost of living increases.
The big questions is: “If I start taking it age 62, at what age is the breakeven point?” Remember, if I turn on social security at 62 and my normal retirement age is 66, I have received 4 years of payments from social security. So at what age would I be kicking myself wishing that I had waited until normal retirement age to turn on my benefit. There are a few different ways to calculate this accounting for taxes, the rates of return on other retirement assets, inflations, etc. but in general it’s sometime between the ages of 78 and 82.
Since the breakeven point may be in your early 80’s, depending on your health, and the longevity in your family history, it may or may not make sense to turn on your benefit early. If we have a client that is in ok health but not great health and both of their parents passed way prior to age 85, then it may make sense to for them to turn on their social security benefit early. We also have clients that have pensions and turning on their social security benefit early makes the different between retiring now or have to work for 5+ more years. As long as the long-term projections work out ok, we may recommend that they turn on their social security benefit early so they can retire sooner.
Are You Still Working?
This is a critical question for anyone that is considering turning on their social security benefits early. Why? If you turn on your social security benefit prior to reaching normal retirement age, there is an “earned income” penalty if you earn over the threshold set by the IRS for that year. See the table listed below:
In 2016, for every $2 that you earned over the $15,720 threshold, your social security was reduced by $1. For example, let’s say I’m entitled to $1,000 per month ($12,000 per year) from social security at age 62 and in 2016 I had $25,000 in W2 income. That is $9,280 over the $15,720 threshold for 2016 so they would reduce my annual benefit by $4,640. Not only did I reduce my social security benefit permanently by taking my social security benefit prior to normal retirement age but now my $12,000 in annual social security payments they are going to reduce that by another $4,640 due to the earned income penalty. Ouch!!!
Once you reach your normal retirement age, this earned income penalty no longer applies and you can make as much as you want and they will not reduce your social security benefit.
Because of this, the general rule of thumb is if you are still working and your income is above the IRS earned income threshold for the year, you should hold off on turning on your social security benefits until you either reach your normal retirement age or your income drops below the threshold.
Should I Delay May Benefit Past Normal Retirement Age
As was illustrated in first table, if you delay your social security benefit past your normal retirement age, your benefit will increase by approximately 8% per year until you reach age 70. At age 70, your social security benefit is capped and you should elect to turn on your benefits.
So when does it make sense to wait? The most common situation is the one where you plan to continue working past your normal retirement age. It’s becoming more common that people are working until age 70. Not because they necessarily have too but because they want something to keep them busy and to keep their mind fresh. If you have enough income from employment to cover you expenses, in many cases, is does make sense to wait. Based on the current formula, your social security benefit will increase by 8% per year for each year you delay your benefit past normal retirement age. It’s almost like having an investment that is guaranteed to go up by 8% per year which does not exist.
Also, for high-income earners, a majority of their social security benefit will be taxable income. Why would you want to add more income to the picture during your highest tax years? It may very well make sense to delay the benefit and allow the social security benefit to increase.
Death Benefit
The social security death benefit also comes into play as well when trying to determine which strategy is the right one for you. For a married couple, when their spouse passes away they do not continue to receive both benefits. Instead, when the first spouse passes away, the surviving spouse will receive the “higher of the two” social security benefits for the rest of their life. Here is an example:
Spouse 1 SS Benefit: $2,000
Spouse 2 SS Benefit: $1,000
If Spouse 1 passes away first, Spouse 2 would bump up to the $2,000 monthly benefit and their $1,000 monthly benefit would end. Now let’s switch that around, let’s say Spouse 2 passes away first, Spouse 1 will continue to receive their $2,000 per month and the $1,000 benefit will end.
If social security is a large percentage of the income picture for a married couple, losing one of the social security payments could be detrimental to the surviving spouse. Due to this situation, it may make sense to have the spouse with the higher benefit delay receiving social security past normal retirement to further increase their permanent monthly benefit which in turn increases the death benefit for the surviving spouse.
Spousal Benefit
The “spousal benefit” can be a powerful filing strategy. If you are married, you have the option of turning on your benefit based on your earnings history or you are entitled to half of your spouse’s benefit, whichever benefit is higher. This situation is common when one spouse has a much higher income than the other spouse.
Here is an important note. To be eligible for the spousal benefit, you personally must have earned 40 social security “credits”. You receive 1 credit for each calendar quarter that you earn a specific amount. In 2016, the figure was $1,260. You can earn up to 4 credits each calendar year.
Another important note, under the new rules, you cannot elect your spousal benefit until your spouse has started receiving social security payments.
Here is where the timing of the social security benefits come into play. You can turn on your spousal benefit as early as 62 but similar to the benefit based on your own earnings history it will be reduce by approximately 7% per year for each year you start the benefit prior to normal retirement age. At your normal retirement age, you are entitled to receive your full spousal benefit.
What happens if you delay your spousal benefit past normal retirement age? Here is where the benefit calculation deviates from the norm. Typically when you delay benefits, you receive that 8% annual increase in the benefits up until age 70. The spousal benefit is based exclusively on the benefit amount due to your spouse at their normal retirement age. Even if your spouse delays their social security benefit past their normal retirement age, it does not increase the 50% spousal benefit.
Here is the strategy. If it’s determine that the spousal benefit will be elected as part of a married couple’s filing strategy, since delaying the start date of the benefits past normal retirement age will only increase the social security benefit for the higher income earning spouse and not the spousal benefit, in many cases, it does not make sense to delay the start date of the benefits past normal retirement age.
Divorce
For divorced couples, if you were married for at least 10 years, you can still elect the spousal benefit even though you are no longer married. But you must wait until your ex-spouse begins receiving their benefits before you can elect the spousal benefit.
Also, if you were married for at least 10 years, you are also entitled to the death benefit as their ex-spouse. When your ex-spouse passes away, you can notify the social security office, elect the death benefit, and you will receive their full social security benefit amount for the rest of your life instead of just 50% of their benefit resulting from the “spousal benefit” calculation.
Whether or not your ex-spouse remarries has no impact on your ability to elect the spousal benefit or death benefit based on their earnings history.
Consult A Financial Planner
Given all of the variables in the mix and the importance of this decision, we strongly recommend that you consult with a Certified Financial Planner® before making your social security benefit elections. While the interaction with a fee-based CFP® may cost you a few hundred dollars, making the wrong decision regarding your social security benefits could cost you thousands of dollars over your lifetime. You can also download a Financial Planner Budget Worksheet to give you that extra help when sorting out your finances and monthly budgeting.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Can I Use My 401K or IRA To Buy A House?
The most difficult part of buying a house is coming up with the down payment. This leads to the question, "Can I access cash in my retirement accounts to help toward the down payment on my house?". The short answer is in most cases, "Yes". The next important questions is "Is it a good idea to take a withdrawal from my retirement account for the down
The most difficult part of buying a house is coming up with the down payment. This leads to the question, "Can I access cash in my retirement accounts to help toward the down payment on my house?". The short answer is in most cases, "Yes". The next important questions is "Is it a good idea to take a withdrawal from my retirement account for the down payment given all of the taxes and penalties that I would have to pay?" This article aims to answer both of those questions and provide you with withdrawal strategies to help you avoid big tax consequences and early withdrawal penalties.
401(k) Withdrawal Options Are Not The Same As IRA's
First you have to acknowledge that different types of retirement accounts have different withdrawal options available. The withdrawal options for a down payment on a house from a 401(k) plan are not the same a the withdrawal options from a Traditional IRA. There is also a difference between Traditional IRA's and Roth IRA's.
401(k) Withdrawal Options
There may be loan or withdrawal options available through your employer sponsored retirement plan. I specifically say "may" because each company's retirement plan is different. You may have all or none of the options available to you that will be presented in this article. It all depends on how your company's 401(k) plan is designed. You can obtain information on your withdrawal options from the plan's Summary Plan Description also referred to as the "SPD".
Taking a 401(k) loan.............
The first option is a 401(k) loan. Some plans allow you to borrow 50% of your vested balance in the plan up to a maximum of $50,000 in a 12 month period. Taking a loan from your 401(k) does not trigger a taxable event and you are not hit with the 10% early withdrawal penalty for being under the age of 59.5. 401(k) loans, like other loans, change interest but you are paying that interest to your own account so it is essentially an interest free loan. Typically 401(k) loans have a maximum duration of 5 years but if the loan is being used toward the purchase of a primary residence, the duration of the loan amortization schedule can be extended beyond 5 years if the plan's loan specifications allow this feature.
Note of caution, when you take a 401(k) loan, loan payments begin immediately after the loan check is received. As a result, your take home pay will be reduced by the amount of the loan payments. Make sure you are able to afford both the 401(k) loan payment and the new mortgage payment before considering this option.
The other withdrawal option within a 401(k) plan, if the plan allows, is a hardship distribution. As financial planners, we strongly recommend against hardship distributions for purposes of accumulating the cash needed for a down payment on your new house. Even though a hardship distribution gives you access to your 401(k) balance while you are still working, you will get hit with taxes and penalties on the amount withdrawn from the plan. Unlike IRA's which waive the 10% early withdrawal penalty for first time homebuyers, this exception is not available in 401(k) plans. When you total up the tax bill and the 10% early withdrawal penalty, the cost of this withdrawal option far outweighs the benefits.
If You Have A Roth IRA.......Read This.....
Roth IRA's can be one of the most advantageous retirement accounts to access for the down payment on a new house. With Roth IRA's, you make after tax contributions to the account, and as long as the account has been in existence for 5 years and you are over the age of 59� all of the earnings are withdrawn from the account 100% tax free. If you withdraw the investment earnings out of the Roth IRA before meeting this criteria, the earnings are taxed as ordinary income and a 10% early withdrawal penalty is assessed on the earnings portion of the account.
What very few people know is if you are under the age of 59� you have the option to withdraw just your after-tax contributions and leave the earnings in your Roth IRA. By doing so, you are able to access cash without taxation or penalty and the earnings portion of your Roth IRA will continue to grow and can be distributed tax free in retirement.
The $10,000 Exclusion From Traditional IRA's.......
Typically if you withdraw money out of your Traditional IRA prior to age 59� you have to pay ordinary income tax and a 10% early withdrawal penalty on the distribution. There are a few exceptions and one of them is the "first time homebuyer" exception. If you are purchasing your first house, you are allowed to withdrawal up to $10,000 from your Traditional IRA and avoid the 10% early withdrawal penalty. You will still have to pay ordinary income tax on the withdrawal but you will avoid the early withdrawal penalty. The $10,000 limit is an individual limit so if you and your spouse both have a traditional IRA, you could potentially withdrawal up to $20,000 penalty free.
Helping your child to buy a house..........
Here is a little known fact. You do not have to be the homebuyer. You can qualify for the early withdrawal exemption if you are helping your spouse, child, grandchild, or parent to buy their first house.
Be careful of the timing rules..........
There is a very important timing rule associated with this exception. The closing must take place within 120 day of the date that the withdrawal is taken from the IRA. If the closing happens after that 120 day window, the full 10% early withdrawal penalty will be assessed. There is also a special rollover rule for the first time homebuyer exemption which provides you with additional time to undo the withdrawal if need be. Typically with IRA's you are only allowed 60 days to put the money back into the IRA to avoid taxation and penalty on the IRA withdrawal. This is called a "60 Day Rollover". However, if you can prove that the money was distributed from the IRA with the intent to be used for a first time home purchase but a delay or cancellation of the closing brought you beyond the 60 day rollover window, the IRS provides first time homebuyers with a 120 window to complete the rollover to avoid tax and penalties on the withdrawal.
Don't Forget About The 60 Day Rollover Option
Another IRA withdrawal strategy that is used as a “bridge solution” is a “60 Day Rollover”. The 60 Day Rollover option is available to anyone with an IRA that has not completed a 60 day rollover within the past 12 months. If you are under the age of 59.5 and take a withdrawal from your IRA but you put the money back into the IRA within 60 days, it’s like the withdrawal never happened. We call it a “bridge solution” because you have to have the cash to put the money back into your IRA within 60 days to avoid the taxes and penalty. We frequently see this solution used when a client is simultaneously buying and selling a house. It’s often the intent that the seller plans to use the proceeds from the sale of their current house for the down payment on their new house. Unfortunately due to the complexity of the closing process, sometimes the closing on the new house will happen prior to the closing on the current house. This puts the homeowner in a cash strapped position because they don’t have the cash to close on the new house.
As long as the closing date on the house that you are selling happens within the 60 day window, you would be able to take a withdrawal from your IRA, use the cash from the IRA withdrawal for the closing on their new house, and then return the money to your IRA within the 60 day period from the house you sold. Unlike the “first time homebuyer” exemption which carries a $10,000 limit, the 60 day rollover does not have a dollar limit.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Avoid These 1099 “Employee” Pitfalls
As financial planners we are seeing more and more individuals, especially in the software development and technology space, hired by companies as “1099 employees”. “1099 employees” is an ironic statement because if a company is paying you via a 1099 technically you are not an “employee” you are a self-employed sub-contractor. It’s like having
As financial planners we are seeing more and more individuals, especially in the software development and technology space, hired by companies as “1099 employees”. “1099 employees” is an ironic statement because if a company is paying you via a 1099 technically you are not an “employee” you are a self-employed sub-contractor. It’s like having your own separate company and the company that you work for is your “client”.
There are advantages to the employer to pay you as a 1099 sub-contractor as opposed to a W2 employee. When you are a W2 employee they may have to provide you with health benefits, the company has to pay payroll taxes on your wages, there may be paid time off, you may qualify for unemployment benefits if you are fired, eligibility for retirement plans, they have to put you on payroll, pay works compensation insurance, and more. Basically companies have a lot of expenses associated with you being a W2 employee that does not show up in your paycheck.
To avoid all of these added expenses the employer may decide to pay you as a 1099 “employee”. Remember, if you are a 1099 employee you are “self-employed”. Here are the most common mistakes that we see new 1099 employees make:
Making estimated tax payments throughout the year
This is the most common error. When you are a W2 employee, it’s the responsibility of the employer to withhold federal and state income tax from your paycheck. When you are a 1099 sub-contractor, you are not an employee, so they do not withhold taxes from your compensation…………that is now YOUR RESPONSIBILITY. Most 1099 individuals have to make what is called “estimated tax payments” four times a year which are based on either your estimated income for the year or 110% of the previous year’s income. Best advice……..if 1099 income is new for you, setup a consultation with an accountant. They will walk you through tax withholding requirements, tax deductions, tax filing forms, etc. It’s very difficult to get everything right using Turbo Tax when you are a self-employed individual.
Tracking mileage and expenses throughout the year
Since you are self-employed you need to keep track of your expenses including mileage which can be used as deductions against your income when you file your tax return. Again, we recommend that you meet with a tax professional to determine what you do and do not need to track throughout the year.
The tax return is prepared incorrectly
No one wants a love letter from the IRS. Those letters usually come with taxes due, penalties, and a “guilty until proven innocent” approach. There may be additional “schedules” that you need to file with your tax return now that you are self-employed. The tax schedules detail your self-employment income, deductions, estimated tax payments, and other material items.
Important rule, do not cut corners by reducing the gross amount of your 1099 income. This is a big red flag that is easy for the IRS to catch. The company that issued the 1099 to you usually reports that 1099 payment to the IRS with your social security number or the Tax ID number of your self-employment entity. The IRS through an automated system can run your social security number or tax ID to cross check the 1099 payment and 1099 income to make sure it was reported.
Legal protection
As a 1099 sub-contractor, you have to consider the liability that could arise from the services that you are providing to your “client” (your employer). As a self-employed individual, the company that you “work for” could sue you for any number of reasons and if you are operating the business under your social security number (which most are) your personal assets could be at risk if a lawsuit arises. Advice, talk to an attorney that is knowledgeable in business law to discuss whether or not setting up a corporate entity makes sense for your self-employment income to better protect yourself.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.