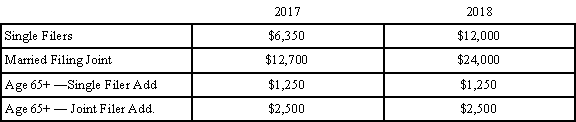How Much Will The Value Of Your House Drop Under The New Tax Law?
It's not a secret to anyone at this point that the new tax bill is going to inflict some pain on the U.S. housing market in 2018. The questions that most homeowners and real estate investors are asking is: "How much are home prices likely to decrease within the next year due to the tax changes?" The new $10,000 limitation on SALT deductions, the lower
It's not a secret to anyone at this point that the new tax bill is going to inflict some pain on the U.S. housing market in 2018. The questions that most homeowners and real estate investors are asking is: "How much are home prices likely to decrease within the next year due to the tax changes?" The new $10,000 limitation on SALT deductions, the lower deduction cap mortgages interest, and the higher standard deduction are all lining up to take a bite out of real estate prices. The size of the bite will largely depend on where you live and the value of your house.
3 Bites That Will Hurt
The Trump tax reform made three significant changes to the tax laws that will impact housing prices:
Capped state and local tax ("SALT") deductions at $10,000 (includes property taxes)
Lowered the deduction cap on the first $750,000 of a mortgage
Doubled the standard deduction
The New Standard Deduction
There is a reason why I'm starting this analysis with the doubling of the standard deduction in 2018. For many households in the U.S., the doubling of the standard deduction will make the cap on the SALT deductions irrelevant. Let me explain. Below is a comparison of the standard deduction limits in 2017 versus 2018:
In 2018, a married couple filing a joint tax return would need over $24,000 in itemized deductions to justify not taking the standard deduction and calling it a day. For a married couple, both W-2 employees, $7,000 in property taxes, $9,000 in state income taxes, if those are their only itemized deductions, then it will most likely makes sense for them to take the $24,000 standard deduction. So the $10,000 cap on property taxes and state income taxes becomes irrelevant because it’s an itemized deduction. This will be a big change for many U.S. households. In 2017, that same family may have itemized because their property and state taxes exceeded the $12,700 standard deduction threshold.
For taxpayers age 65 and older, the new tax law kept the additional standard deduction amounts: $1,250 for single filers and $2,500 for married filing joint which are over and above the normal limits.
$10,000 Cap On State & Local Taxes
Starting in 2018, taxpayers are limited to a $10,000 deduction for a combination of their property taxes, school taxes, and state & local income tax. For states that have both high property taxes and high income taxes like New York, New Jersey, and California, homeowners will most likely be looking at a larger decrease in the value of their homes versus states like Florida that have lower property taxes and no state income taxes. The houses with the higher dollar value may experience a larger drop in price.
If you live in a $200,000 house, the property / school taxes are $5,000, and you decided to sell your house, the family looking to buy your house may already be planning on taking the $24,000 standard deduction at that income level, so the new tax cap would not really decrease the “value” of the house to the potential buyer.
On the flip side, if you own a $600,000 house, your property/school taxes are $18,000, and you are looking to sell your house, the new $10,000 cap will most likely have a negative impact on the value of your house. As you might assume, the individuals and families with the higher incomes that could afford to purchase a $600,000 house will naturally be the homeowners that will continue to itemize their deduction in 2018. So owning that $600K house in 2018 comes at an additional annual cost to the buyer because they lose $8,000 in property tax deductions. For individuals and families in the top federal tax bracket (37%), the cost to live in that house just went up by $3,120 per year. I have personally already had two clients call me that just purchased a house in 2017 with property taxes above the $10,000 cap and they said “I might not have purchased this big of a house if I knew I was not going to be able to deduct all of the property taxes”.
$750,000 Deduction Cap On Mortgages
Prior to 2018, taxpayers could only deduct interest on the first $1,000,000 of a mortgage. For all new mortgages, beginning in 2018, the cap was reduced from $1,000,000 to $750,000. The new tax law grandfathered the $1M cap for mortgages that were already in existence prior to December 31, 2017. Obviously this change will only impact very high income earning individuals and families living in houses valued at $1M+ but it still may have a negative impact on the prices of those big houses. I say "may" because if you can afford a $3M condo in Manhattan, you may not care that you lost a $7,500 tax deduction.
It Depends Where You Live
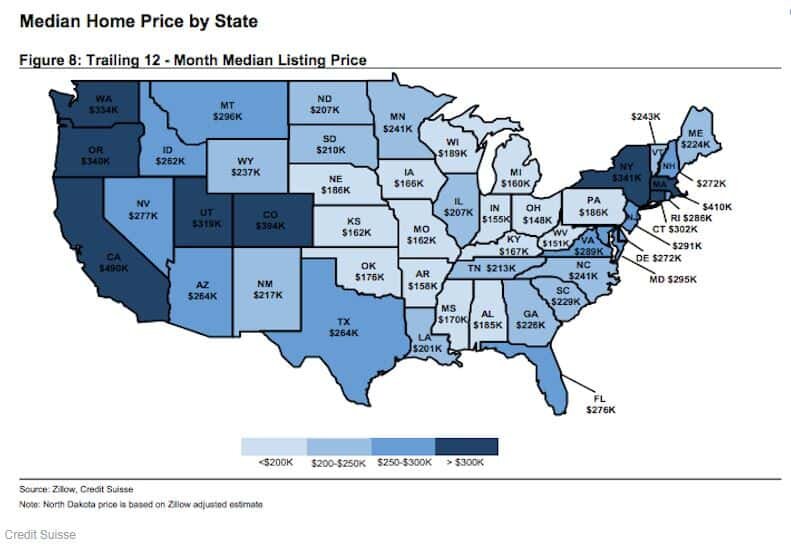
Given these changes to tax law, it seems likely that the states with higher property taxes and higher home values will be the most vulnerable to price adjustments. Below is a map, from Zillow and Credit Suisse, showing the median home price by state:
Let's also locate the states that have a high concentration of mortgages over $500,000. As mentioned above, this may put price pressure on homeowners trying to sell houses above the new $750,000 mortgage interest deduction threshold:
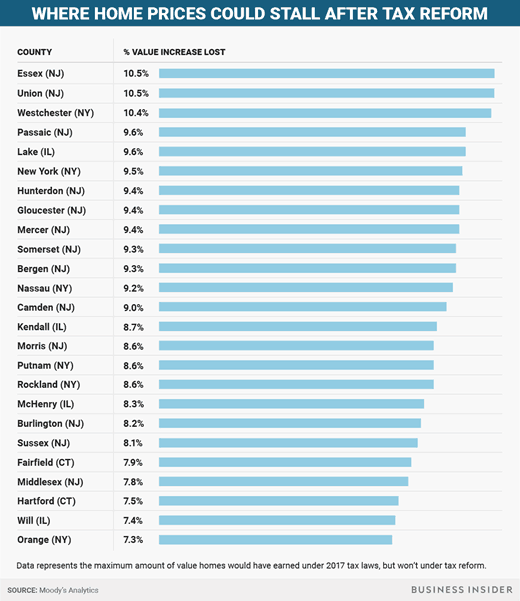
And the "Non-Winners" are New York, California, and New Jersey. Moody's published a list of the 25 counties that are expect to lose the largest percentage of value. Note, that only six of those counties are located outside of New York or New Jersey:
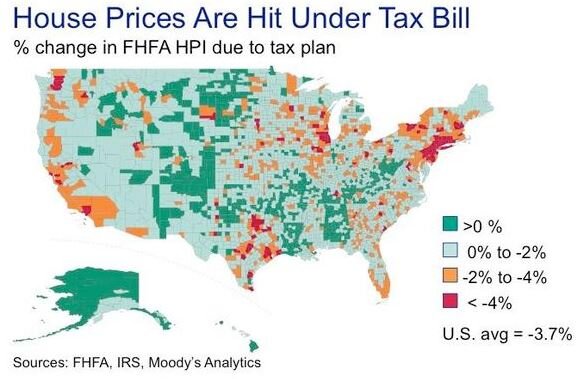
To bring it all together, Moody's and FHFA published the illustration below showing the percentage change in the Federal Housing Finance Agency – House Price Index as a result of the new tax bill:
It's safe to assume that geographically, the negative impact that the new tax rules will have on the U.S. house market will occur in concentrated pockets as opposed to a widespread reduction in housing prices across the country.
Do Not Move To Alaska Just Yet!!
Before you show the chart above to your family at dinner tonight with a “Go Alaska” hat on, I urge you to read on. (Disclosure, I have nothing against Alaska. I was born in Fairbanks, Alaska) If you live in one of the “red spots” on the heat map above or in one of the counties in the list of “where home prices could stall after tax reform”, the charts above do not necessarily mean that at the end of 2018 your house is going to be worth 5% less than it was at the beginning of 2018. Moody’s has done the comparison of the tax bill passing versus no tax bill. If prior to the tax bill being passed it was estimated in 2018 that homes in your area were going to increase in value by 5% and the heat map above shows a 4% drop as a result of tax reform, then that means instead the value of your home growing by 5% it may only grow by 1%.
As with any forecast, it’s anyone’s guess at this point how the math will actually work itself out but in general I think it will be more positive than the consensus expects.
House Values Under $250,000 – Status Quo
Given the changes to the tax law, if you live in a house that is valued under $250,000, regardless of where you live, the downward pressure on the price of your house as a result of tax reform should be minimal. Why? Most buyers in this range will most likely be electing the standard deduction anyways so the new $10,000 cap on SALT deductions should have little to no impact. This should even be true for states that have high property taxes because the homeowners would need over $24,000 in itemized deductions before the $10,000 cap would potentially hurt them tax wise.
The Sandwich: House Values $250,000 - $750,000
The homeowners at the highest risk of a reduction in the value of their house are located in what I call “The Sandwich”. They have a house that is valued somewhere between $250,000 – $750,000 and they live in a high property tax state. While Congress touts that the doubling of the standard deduction is a “fix all” for all of the tax deductions that have been taken away, it’s unfortunately not. There are a number of individuals and families that are in the income range customarily associated with buying a $250K – $750K house that may actually pay more in taxes under the new rules.
Taxpayers in this group are also moving from their “starter house” in their first “big house”. Unlike the super wealthy that may care less about paying an extra $5,000 in taxes per year, for an upper middle class family that has kids, that is saving for college, and contributing to 401(k) plans, the loss of that tax benefit may mean they can’t take a family vacation if they buy that bigger house. Less buyers in the market for houses in this “Sandwich” range translates to lower prices.
How much lower? Probably nothing dramatic in the short term because the U.S. economy is doing so well. When the economy is growing, people feel secure in their jobs, wages are going up, workers are getting bonuses, and that provides them with the additional income needed to make that larger mortgage payment and pay a little more in taxes.
My concern would be for someone that is planning to purchase a house and then sell within the next 5 years. If the economy goes into a recession, people start losing their jobs, and the U.S. consumer starts look for more ways to stretch their dollars, the homeowners that stretched themselves to buy the bigger house based on the big bonus that they received when the economy was humming are at a big risk of losing their house. In addition, there may be fewer buyers in the market because families may not want to waste money on property taxes that they can’t deduct.
The Millionaire Club: House Values $750,000+
It would seem that houses in the $750,000+ range have the most lose to for two reasons. First, homeowners in this category pay the highest property taxes and they are typically not electing the standard deduction at this income level. Second, home buyers at this price point would also be negatively impacted by the lower $750,000 cap on the mortgage interest deduction.
But I doubt this will be the case. Why? There is only so much lake front property. If you make over $5M per year and you fall in love with a lake house in upstate New York that has a $1.5M price tag, while you could try to find a similar lake house in a more tax friendly state, if you make $5M per year, what’s another $15,000 in expenses for buy your first choice.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
How Rental Income Will Be Taxed In Years 2019+
Tax reform will change the way rental income is taxed to landlords beginning in 2018. Under current law, rental income is classified as "passive income" and that income simply passes through to the owner's personal tax return and they pay ordinary income tax on it. Beginning in 2018, rental income will be eligible to receive the same preferential tax
Tax reform will change the way rental income is taxed to landlords beginning in 2018. Under current law, rental income is classified as "passive income" and that income simply passes through to the owner's personal tax return and they pay ordinary income tax on it. Beginning in 2018, rental income will be eligible to receive the same preferential tax treatment as the "qualified business income" (QBI) for small business owners.
20% Deduction
Starting in 2018, taxpayers with qualified business income (including rental income), may be eligible to take a tax deduction up to 20% of their QBI. Determining whether or not you will be eligible to capture the full 20% deduction on your rental income will be based on your total taxable income for year. The taxable income thresholds are as follows:Single filers: $157,500Married filing joint: $315,000"Total taxable income" is not your AGI (adjusted gross income) and it's not just income from your real estate business or self-employment activities. It's your total taxable income less some deductions. The IRS has yet to provide us with full guidance on the definition of "total taxable income". For example, let's assume you have three rental properties owned by an LLC and you net $50,000 in income from the LLC each year. But your wife is a lawyer that makes $350,000 per year. Your total taxable income for the year would be $400,000 landing you above the $315,000 threshold.
Below The Income Threshold
If your total taxable income is below the income thresholds listed above, the calculation is very easy. Take your total QBI and multiply it by 20% and that's your tax deduction.
Above The Income Threshold
If your total taxable income is above the thresholds, the calculation gets more complex. If you exceed the income thresholds, your deduction is the LESSER of:
20% of QBI
The GREATER OF:
50% of W-2 wages paid to employees
25% of W-2 wages paid to employees PLUS 2.5% of the unadjusted asset basis
The best way to explain the calculation is by using an example. Assume the following:
I bought a commercial building 3 years ago for $1,000,000
I have already captured $100,000 in depreciation on the building
After expenses, I net $150,000 in income each year
The LLC that owns the property has no employees
I'm married
I own a separate small business that makes $400,000 in income
Since I'm over the $315,000 total taxable income threshold for a married couple filing joint, I will calculate my deduction as follows:The LESSER of:
20% of QBI = $30,000 ($150,000 x 20%)
The GREATER of:
50% of W-2 wage paid to employees = $0 (no employees)
25% of W-2 wages page to employees plus 2.5% of unadjusted basis
(25% of wages = $0) + (2.5% of unadjusted basis = $25,000) = $25KIn this example, my deduction would be limited to $25,000. Here are a few special notes about the calculation listed above. In the 11th hour, Congress added the "2.5% of unadjusted basis" to the calculation. Without it, it would have left most landlords with a $0 deduction. Why? Real estate owners typically do not have W-2 employees, so 50% of W-2 wages would equal $0. Some larger real estate investors have "property management companies" but they are usually set up as a separate entity. In which case, the W-2 income of the property management company would not be included in the calculation for the QBI deduction. If you are someone who owns a property or properties and is need of a Property management company to help you with organizing and operating your property, then doing research in your general area to find a real estate company that can help you with that is important.Another special note, 2.5% is based on an unadjusted basis and it's not reduced by depreciation. However, the tangible property has to be subject to depreciation on the last day of the year to be eligible for the deduction. Meaning, even though the 2.5% is not reduced for the amount of depreciation already taken on the property, the property must still be in the "depreciation period" on the last day of the year to be eligible for the QBI deduction.Tony Nitti, a writer for Forbes, also makes the following key points:
The depreciable period starts on the date the property is placed in service and ends on the LATER of:
- 10 years, or- The last day of the last full year in the asset's "regular" (not ADS) depreciation periodMeaning, if you purchase a non-residential rental building that is depreciated over 39 years, the owner can continue to capture the depreciation on the building but that will not impact the 2.5% unadjusted basis number for the full 39 years of the depreciation period.
Any asset that was fully depreciated prior to 2018, unless it was placed in service after 2008, will not count toward the basis.
Shareholders or partners may only take into consideration for purposes of applying the limitation 2.5% his or her allocable share of the basis of the property. So if the total basis of commercial property is $1,000,000 and you are a 20% owner, you basis limitation is $1,000,000 x 20% x 2.5% = $5,000
Phase-In Of The Threshold
The questions I usually get next is: "If I'm married and our total taxable income is $320,000 which is only $5,000 over the threshold, do I automatically have to use the more complex calculation?" The special calculation "phases in" over the following total taxable income thresholds:Single filers: $157,500 - $207,500Married filing joint: $315,000 - $415,000I won't get into the special phase-in calculation because it's more complex than the special "above the income threshold" calculation that we already walked through but just know that it will be a blend of the straight 20% deduction and the W-2 & 2.5% adjusted basis calculation.
Qualified Trade or Business Requirement
In August 2018, the IRS came out with further clarification of how the QBI deduction would apply to real estate. In order to qualify for the QBI deduction for real estate income, your real estate holdings have to qualify as a "trade or business". The definition of a trade or business for QBI purposes deviates slightly from the traditional IRS definition. There is a safe harbor that states if you spend more than 250 hours a year working on that business it will qualify for the deduction.There are a few items to consider in the 250 hour calculation. So called "drive bys" where the owner is spending time driving by their properties to check on them does not count toward the 250 hours. If you have a property management company, the hours that they spend managing your propoerty can be credited toward your 250 hour requirement. However, the property management company has to provide you with proper documentation to qualify for those credited hours.
Consult Your Accountant
I'm a Certified Financial Planner®, not an accountant. I wrote this article to give real estate investors a broad view of what tax reform may have instore for them in 2018. If you own rental property, you should be actively consulting with our accountant through the year. As the IRS continues to release guidance regarding the QBI deduction throughout 2018, you will want to make sure that your real estate holdings are positioned properly to take full advantage of the new tax rules.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.