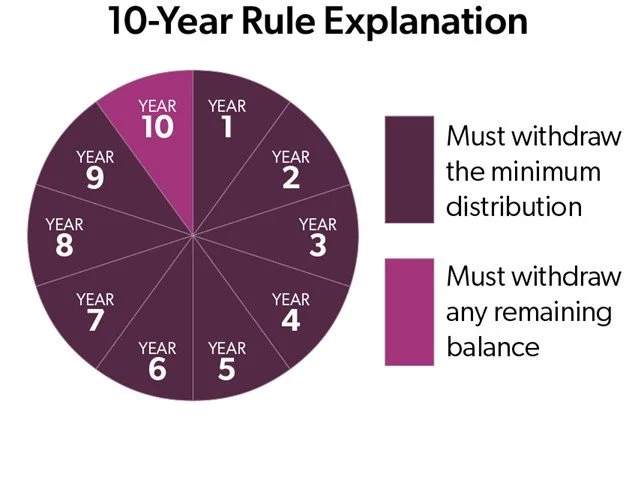
Attention Non-Spouse 10-Year Beneficiaries: 2030 Is Rapidly Approaching
If you inherited an IRA or other retirement account from a non-spouse after December 31, 2019, the SECURE Act’s 10-year rule may create a major tax event in 2030. Many beneficiaries don’t realize how much the account can grow during the 10-year window—potentially forcing large taxable withdrawals if they wait until the final year. In this article, we explain how the 10-year rule works, why 2030 is a high-risk tax year, and planning strategies that can reduce the tax hit long before the deadline arrives.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
If you inherited an IRA or other retirement account from a non-spouse after December 31, 2019, the clock is ticking—and for many families, the tax consequences are coming into sharper focus.
The SECURE Act, which went into effect in 2020, dramatically changed how non-spouse beneficiaries must handle inherited retirement accounts. While these rules may have seemed far off at the time, 2030 is now just around the corner for those who inherited accounts in the first year of the new law.
In this article, we’ll cover:
How the SECURE Act’s 10-year rule works
Why 2030 could trigger significant tax liabilities
How market growth has quietly made the problem bigger
Practical tax-planning strategies to consider now
Why waiting until the last year can be costly
A Quick Refresher: What Changed Under the SECURE Act?
Prior to 2020, most non-spouse beneficiaries could “stretch” distributions from an inherited IRA over their lifetime. This allowed smaller required distributions and, in many cases, never required the account to be fully depleted.
That all changed with the SECURE Act.
For most non-spouse beneficiaries:
The inherited retirement account must be fully depleted within 10 years
The rule applies to anyone who passed away after December 31, 2019
All pre-tax dollars distributed during that period are taxable income
From the IRS’s perspective, this rule change was a revenue raiser—it ensures that inherited retirement assets become taxable within a defined window.
Why 2030 Is Such a Big Deal
For individuals who inherited a retirement account from someone who passed away in 2020, the 10-year clock runs out at the end of 2030.
That means:
Only five tax years remain (2026–2030) before the final distribution year
Any remaining balance must be distributed—and taxed—by the end of year 10
Large balances could result in substantial one-year tax spikes
Many beneficiaries have only been taking small distributions or the minimum required amounts. While that may have felt prudent at the time, it can create a tax bombshell in the final year if the account balance is still large.
RMD Rules Add Another Layer of Complexity
Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) rules under the SECURE Act depend on whether the original account owner was already taking RMDs when they passed away.
Some beneficiaries were required to take annual RMDs
Others were not required to take annual distributions—but still must empty the account by year 10
Regardless of which category you fall into, the key issue remains the same:
Waiting too long often concentrates taxable income into fewer years.
Market Growth Has Made the Problem Bigger
Ironically, strong market performance over the past several years has amplified the issue.
For individual that have a large allocation to stocks within their inherited IRA, since the market returns have been so strong over the past few years, they may have seen the balance in their inherited IRA increase despite taking RMDs from the account each year.
This is great from a wealth-building perspective, but it also means:
Larger balances remain late in the 10-year window
Larger forced distributions
Larger tax bills await
In short, investment success can unintentionally worsen the tax outcome if distributions aren’t coordinated with a broader tax plan.
Why Smoothing Income Often Makes Sense
For many non-spouse beneficiaries, the goal should be tax smoothing—intentionally spreading distributions over the remaining years to avoid one massive taxable event in year 10.
This often means:
Taking more than the minimum each year
Coordinating distributions with your current income level
Evaluating how many years remain in your 10-year window
The sooner this planning happens, the more flexibility you typically have.
One Common Strategy: Offset Taxes With 401(K) Contributions
One tax-planning strategy we often explore with clients involves maximizing employer-sponsored retirement plan contributions.
Here’s a simplified example:
A 50-year-old employee is contributing $15,000 to their 401(k)
In 2026, they may be eligible to contribute up to $32,500
That’s an additional $17,500 of potential pre-tax deferrals
A possible strategy:
Take a $17,500 distribution from the inherited IRA (taxable)
Increase payroll deferrals so more income flows into the 401(k) pre-tax
Use the inherited IRA distribution to supplement take-home pay
Result:
Taxable income from the inherited IRA distribution is fully offset by pre-tax retirement contributions, while also shifting assets into the inherited IRA owner's personal 401(k) account, which does not have a 10-year distribution restriction.
A Critical Caveat for 2026
High-income earners should be aware that starting in 2026, certain catch-up contributions for those over age 50 may be required to be made as Roth contributions. Roth deferrals do not provide an immediate tax deduction, which could limit the effectiveness of this strategy.
When Waiting Can Make Sense
Not every situation calls for accelerating distributions.
For individuals who plan to retire before the 10-year period ends, delaying distributions may be intentional and strategic. Once paychecks stop:
Ordinary income may drop significantly
Larger inherited IRA distributions could fall into lower tax brackets
This can be a very effective approach—but only when planned in advance.
The Real Warning Sign to Watch For
This article isn’t about fear—it’s about awareness.
If you:
Inherited a retirement account after 2019
Have only been taking small distributions or RMDs
Haven’t mapped out the remaining years of your 10-year window
There’s a real risk that a large, avoidable tax liability is waiting at the end of the road.
Final Thoughts
The SECURE Act permanently changed the landscape for non-spouse beneficiaries, and 2030 is approaching faster than many realize. Thoughtful, proactive tax planning—especially in the final years of the 10-year period—can make a meaningful difference in outcomes.
Now is the time to:
Count the remaining years
Project future tax exposure
Coordinate investment, distribution, Medicare premium, and tax strategies
Advanced planning today can help turn a looming tax problem into a manageable—and sometimes even strategic—opportunity.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Trump Accounts For Minor Children Explained: A New Wealth-Building Opportunity
Trump Accounts are a new retirement savings vehicle created under the 2025 tax reform that allow parents, grandparents, and even employers to contribute up to $5,000 per year for a minor child — even if the child has no earned income. In this article, we explain how Trump Accounts work, contribution limits, tax rules, planning opportunities, and the key considerations to understand before opening one.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
Over the past several months, we’ve received a lot of questions from parents and grandparents about the new Trump Accounts created under the 2025 tax reform. Most of those questions fall into a few clear categories:
How do Trump Accounts get set up?
Who can fund them, and how much can be contributed?
What makes them different from traditional or Roth IRAs?
And most importantly—are they really worth it?
What’s driving so much interest is that these accounts can be a tremendous long-term wealth-building opportunity for children and grandchildren. Unlike traditional or Roth IRAs, which require earned income to contribute, Trump Accounts allow up to $5,000 per year in contributions even if the child has no income at all. That creates decades of potential tax-deferred compounding.
That said, Trump Accounts also come with a unique set of rules, especially while the account owner is a minor. In this article, we’ll break down how Trump Accounts work, how they’re funded, how they interact with other retirement accounts, and where the real planning opportunities—and responsibilities—exist.
What Is a Trump Account?
A Trump Account is a new type of retirement account designed specifically for minors, created as part of the One Big Beautiful Bill Act of 2025. Conceptually, it is built on the framework of a traditional IRA, but with special rules that apply from birth through age 17.
The goal of these accounts is simple: to jump-start retirement savings as early as possible, even before a child has their first job.
Contribution Limits and Funding Rules
Annual Contribution Limits
Total annual contributions are limited to $5,000 per year
Of that amount, up to $2,500 may come from an employer
These limits apply beginning in 2026 and will be indexed for inflation in future years
Who Can Contribute?
Trump Accounts can receive contributions from several sources:
Parents, grandparents, or other individuals (after-tax)
Employers (pre-tax)
Government or charitable entities (pre-tax)
A one-time $1,000 federal government contribution for eligible children
Importantly, individual contributions are made with after-tax dollars, meaning they create “basis” in the account, while employer and government contributions are pre-tax.
The $1,000 Government Contribution
As part of a pilot program, the federal government will contribute $1,000 to a Trump Account for children born between 2025 and 2028, provided the parent or guardian opts in.
Key points:
The contribution is pre-tax
It does not count toward the $5,000 annual limit
Parents must actively elect the contribution—it is not automatic
This is essentially “free money,” and for many families, that alone may justify opening the account.
How Trump Accounts Can Be Invested
Trump Accounts have very strict investment rules:
Accounts must be established with initial trustees selected by the U.S. Treasury
Individuals may have only one Trump Account
Investments are limited to unleveraged mutual funds or ETFs
The investments must track a qualified index of primarily U.S. equities
Holding cash is virtually not allowed
Total investment fees cannot exceed 0.10%
At this time, the list of approved custodians has not yet been released, and is expected sometime in 2026.
How and When Trump Accounts Are Set Up
Trump Accounts cannot be opened with a traditional custodian yet.
Here’s what we know about the setup process:
Accounts become operational starting July 4, 2026
All accounts must initially be opened using U.S. Treasury–approved trustees
A new IRS Form 4547 and an online application at trumpaccounts.gov are expected to launch in mid-2026
To establish the accounts Form 4547 or the special application can be submitted prior to the July 4, 2026 program launch date
That same process will be used to request the $1,000 government contribution
Once established, families can begin making annual contributions.
Special Rule for Working Minors
One of the most powerful planning features applies to minors who do have earned income.
If a child earns income:
They can contribute to a Trump Account
They can also contribute to a traditional IRA or Roth IRA
The contribution limits do not reduce or affect one another
In other words, a working minor can fund both account types in the same year, creating even more long-term compounding potential.
Roth Conversion Opportunity After Age 18
Once the account owner turns 18, Trump Accounts largely revert to standard traditional IRA rules.
This is where advanced planning opportunities emerge:
It can then be converted to a Roth IRA
Once converted, future growth and qualified withdrawals may be tax-free
However, there’s an important catch.
Tracking Basis Is Critical
Individual contributions were made with after-tax dollars
Employer and government contributions are pre-tax
Investment growth is pre-tax
This creates a mixed-tax account, requiring careful basis tracking over time. If records aren’t maintained, the IRS may treat withdrawals as fully taxable.
Beware of Kiddie Tax: Roth conversions trigger a taxable event for any pre-tax contributions or earnings held within the Trump Account. Conversions and distributions from IRAs are considered unearned income of the minor child, which can trigger the Kiddie tax, making the taxable distribution amount subject to tax at the parent’s tax rate instead of the child’s.
Employer Contributions Are Allowed
Employers are permitted to contribute to Trump Accounts:
Contributions are pre-tax
They may be made for the employee or the employee’s dependent child
Employer contributions count toward the $5,000 annual limit (up to $2,500)
This opens the door for unique employer-based benefits and planning strategies.
How Trump Account Distributions Work After Age 18
Once a child reaches age 18, Trump Accounts undergo an important transition. While these accounts are designed for minors, the distribution rules after age 18 closely resemble those of a traditional IRA, which introduces both flexibility and responsibility.
Understanding how distributions work at this stage is critical, because mistakes can create unnecessary taxes or penalties.
No Distributions Before Age 18
First, it’s important to note that Trump Accounts do not allow distributions prior to age 18. Until then, the account is strictly a long-term retirement vehicle.
Once the account owner reaches the year they turn 18, distributions become available—but that does not mean they are penalty-free.
Traditional IRA Rules Apply After Age 18
Beginning in the year the child turns 18, the Trump Account is treated much like a traditional IRA for tax purposes. That means:
Distributions are generally taxable
Early withdrawals may be subject to a 10% penalty
The account follows pro-rata taxation rules if it contains both after-tax and pre-tax money
How Distributions Are Taxed
Trump Accounts typically hold two types of money:
After-tax contributions (from parents, grandparents, or others)
Pre-tax dollars, which include:
Employer contributions
Government contributions (including the $1,000 pilot contribution)
All investment growth
When a distribution is taken, the IRS does not allow the account owner to choose which dollars come out. Instead, each withdrawal is treated as a proportional mix of taxable and non-taxable funds.
Example (Simplified)
If 25% of the account consists of after-tax contributions, then:
25% of any distribution is tax-free
75% is taxable as ordinary income
This makes accurate recordkeeping essential, since the after-tax portion (known as “basis”) must be documented to avoid overpaying taxes.
Early Withdrawal Penalties Still Apply
Although distributions are allowed after age 18, they are not automatically penalty-free.
Withdrawals before age 59½ generally incur a 10% early withdrawal penalty
Certain exceptions may apply, such as:
Qualified higher education expenses
Limited first-time home purchase expenses
Certain structured payment arrangements
Absent one of these exceptions, both income taxes and penalties may apply.
Rollovers and Roth Conversions Instead of Distributions
Rather than taking cash distributions, many families will focus on rollovers and Roth conversions, which are allowed once the account owner turns 18.
At that point:
The Trump Account can be rolled into a traditional IRA
It may then be converted to a Roth IRA
A Roth conversion is taxable on the pre-tax portion of the account, but once completed, future growth and qualified withdrawals can be tax-free.
This strategy can be especially powerful if conversions are done during low-income years, though taxes still must be paid—ideally using funds outside the account to avoid penalties.
Final Thoughts
Trump Accounts represent a powerful but complex planning tool. For families focused on long-term retirement wealth for children or grandchildren, they offer an early start that was never possible before. However, the rules around taxation, investment limitations, and recordkeeping mean these accounts should be used strategically, not blindly.
As always, thoughtful planning—and understanding how these accounts fit into the bigger financial picture—makes all the difference.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Do children need earned income to have a Trump Account?
No. Earned income is not required.
2. Are contributions tax-deductible?
Individual contributions are not deductible. Employer and government contributions are pre-tax.
3. Can grandparents contribute?
Yes, as long as total annual limits are respected.
4. Can a child have more than one Trump Account?
No. Only one account per individual is allowed.
5. When can withdrawals be taken?
Distributions follow traditional IRA rules and generally are penalty-free after age 59½.
6. Are Roth conversions allowed?
Yes, starting at age 18 once the account follows IRA rules.
7. Are these accounts required to invest in stocks?
Yes. Investments must track qualified U.S. equity indexes.
8. Is the $1,000 government contribution automatic?
No. Parents must opt in using the IRS process.
Can You Give Money to Your Grandkids Tax-Free? Here’s What the IRS Says
The IRS allows grandparents to give up to $19,000 per grandchild in 2025 without filing a gift tax return, and up to $13.99 million over their lifetime before any tax applies. Gifts are rarely taxable for recipients — but understanding Form 709, 529 plan rules, and tuition exemptions can help families transfer wealth efficiently and avoid IRS issues.
Many grandparents want to help their grandchildren financially—whether it’s for education, a first home, or simply to transfer wealth during their lifetime. But the question often arises: will my grandkids owe taxes on those gifts? In most cases, the answer is no—the recipient of a gift doesn’t pay taxes. Instead, the giver may need to file a gift tax return if the gift exceeds the annual exclusion amount. Here’s how the IRS actually handles gifts to grandchildren, what forms apply, and how to avoid unnecessary taxes or filing headaches.
Who Pays the Tax on a Gift?
Under IRS rules, the person making the gift (the donor) is responsible for any gift tax—not the person receiving it. This means if a grandparent gives money, investments, or property to a grandchild, the child typically doesn’t report or owe anything.
However, there are thresholds to know:
Annual gift tax exclusion (2025): $19,000 per recipient
Lifetime gift and estate tax exemption (2025): $13.99 million per person
If a grandparent gives less than $19,000 to any one grandchild during the year, no filing or tax applies. Gifts above that limit simply require Form 709, but gift tax is only owed once total lifetime gifts exceed the $13.99 million exemption.
Studies show that fewer than 1% of Americans ever owe gift tax—most gifts fall well below these thresholds.
What Counts as a Gift
The IRS defines a gift as any transfer where full value isn’t received in return. Common examples include:
Cash gifts or checks
Paying a grandchild’s tuition or medical bills directly
Contributing to a 529 plan
Transferring stocks or real estate below market value
Tuition and Medical Exceptions
Certain payments don’t count toward the annual gift limit if you pay the institution directly:
Tuition paid straight to a college or private school
Medical expenses paid directly to a hospital or provider
These payments are excluded from both the annual and lifetime gift limits, making them powerful estate-planning tools for grandparents who want to help without triggering IRS reporting.
Gifting Through a 529 Plan
A popular way to help grandchildren is through 529 college savings plans. Contributions are treated as gifts for tax purposes, but there’s a special election that allows grandparents to “front-load” five years’ worth of annual exclusions.
In 2025, you can contribute up to $95,000 per grandchild ($19,000 × 5) without using any lifetime exemption.
Married couples can jointly contribute up to $190,000 per grandchild with the same rule.
This allows for significant education funding while keeping assets out of the grandparent’s taxable estate.
What the IRS Actually Looks At
When reviewing gifts, the IRS primarily focuses on:
Value and documentation – was the transfer properly valued and recorded?
Ownership control – did the grandparent truly give up control of the asset?
Direct vs. indirect payments – paying tuition directly to a school is excluded; writing a check to the grandchild is not.
Cumulative totals – large gifts across multiple years can push a donor closer to their lifetime exemption.
It’s rare for the IRS to flag or audit small gifts, but clear documentation and Form 709 filings for larger transfers help prevent confusion or estate complications later.
Tax-Free Ways to Support Grandkids
There are several strategies to help grandchildren financially without ever triggering gift tax concerns:
Pay tuition or medical bills directly to the provider
Make annual $19,000 gifts to as many recipients as desired
Fund 529 plans using the 5-year front-loading rule
Use custodial accounts (UGMA/UTMA) for small transfers
Contribute to Roth IRAs for working grandchildren (earned income required)
Each of these options lets you transfer wealth efficiently while minimizing tax reporting.
When a Gift Tax Return Is Required
A federal gift tax return (Form 709) is required when:
You give more than $19,000 to one individual in a single year (2025 limit)
You give property or assets that exceed the annual limit in fair market value
You elect to spread a 529 plan contribution over five years
Filing doesn’t mean you owe tax—it simply allows the IRS to track your lifetime exemption usage. Most taxpayers never actually pay gift tax; they only report it for record-keeping purposes.
FAQs: Gifting to Grandchildren
Q: Do my grandchildren have to report a cash gift on their tax return?
A: No. Gifts are not considered taxable income to the recipient and don’t need to be reported.
Q: How much can I give my grandchild without filing a gift tax return?
A: You can give up to $19,000 per grandchild in 2025 without any filing requirement.
Q: What happens if I exceed the $19,000 limit?
A: You’ll file Form 709, but you likely won’t owe any gift tax unless you’ve already used your $13.99 million lifetime exemption.
Q: Do 529 plan contributions count as gifts?
A: Yes, but you can elect to treat large contributions as if they were made evenly over five years to stay within the annual exclusion limits.
Q: Can I pay my grandchild’s college tuition tax-free?
A: Yes, as long as the payment goes directly to the educational institution, it doesn’t count toward the annual exclusion.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Retirement Tax Traps and Penalties: 5 Gotchas That Catch People Off Guard
Even the most disciplined retirees can be caught off guard by hidden tax traps and penalties. Our analysis highlights five of the biggest “retirement gotchas” — including Social Security taxes, Medicare IRMAA surcharges, RMD penalties, the widow’s penalty, and state-level tax surprises. Learn how to anticipate these costs and plan smarter to preserve more of your retirement income.
Even the most disciplined savers can be blindsided in retirement by unexpected taxes, penalties, and benefit reductions that derail a carefully built plan. These “retirement gotchas” often appear subtle during your working years but can cost tens of thousands once you stop earning a paycheck.
Here are five of the biggest surprises retirees face—and how to avoid them before it’s too late.
1. The Tax Torpedo from Social Security
Many retirees are surprised to learn that Social Security isn’t always tax-free. Depending on your income, up to 85% of your benefit can be taxed.
The IRS uses something called “provisional income,” which includes half your Social Security benefit plus all other taxable income and tax-free municipal bond interest.
For individuals, taxes begin when provisional income exceeds $25,000.
For married couples, it starts at $32,000.
A well-intentioned IRA withdrawal or capital gain can push you over these thresholds—causing a sudden jump in taxes. Strategic Roth conversions and careful withdrawal sequencing can help smooth this out over time.
2. Higher Medicare Premiums (IRMAA)
The Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount (IRMAA) is one of the most overlooked retirement costs. Once your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeds certain limits, your Medicare Part B and D premiums increase—often by thousands of dollars per year.
For 2025, IRMAA surcharges begin when MAGI exceeds roughly $103,000 for single filers or $206,000 for married couples. The catch? Medicare looks back two years at your income. A Roth conversion, property sale, or large one-time distribution can unexpectedly trigger higher premiums two years later.
Proactive tax planning can prevent crossing these thresholds unintentionally.
3. Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
Once you reach age 73, the IRS requires you to start withdrawing from pre-tax retirement accounts each year—whether you need the money or not. These RMDs are taxed as ordinary income and can increase your tax bracket, raise Medicare premiums, and reduce your eligibility for certain deductions.
The biggest mistake is waiting until your 70s to plan for them. Roth conversions in your 60s can reduce future RMDs, and charitable giving through Qualified Charitable Distributions (QCDs) can offset the tax impact once they begin.
4. The Widow’s Penalty
When one spouse passes away, the surviving spouse’s tax brackets and standard deduction are cut in half—but income sources often don’t decrease proportionally. Social Security may drop by one benefit, but RMDs, pensions, and investment income remain largely the same.
The result is a higher effective tax rate for the survivor. This “widow’s penalty” can last for years, especially when combined with RMDs and Medicare surcharges. Couples can reduce the long-term impact through lifetime Roth conversions, strategic asset titling, and beneficiary planning.
5. State Taxes and Hidden Relocation Costs
Many retirees move to lower-tax states hoping to stretch their income, but state-level taxes can be tricky. Some states tax pension and IRA withdrawals, others tax Social Security, and a few impose taxes on out-of-state income or estates.
Additionally, higher property taxes, insurance premiums, and healthcare costs can offset income tax savings. A comprehensive cost-of-living comparison is essential before relocating.
Our analysis at Greenbush Financial Group often reveals that the “best” retirement state depends more on quality of life, healthcare access and total cost of living than on income tax rates alone.
How to Avoid These Retirement Surprises
Most retirement gotchas come down to timing and coordination—especially between taxes, Social Security, and healthcare. A few key steps can make a major difference:
Run retirement income projections that include taxes and IRMAA thresholds.
Consider partial Roth conversions before RMD age.
Sequence withdrawals intentionally between taxable, tax-deferred, and Roth accounts.
Evaluate the long-term impact of home state taxes before moving.
Review beneficiary and trust structures regularly.
The earlier you identify potential traps, the easier they are to fix while you still control your income and withdrawals.
The Bottom Line
Retirement is more complex than simply replacing a paycheck. The interplay between taxes, healthcare, and income sources can turn small decisions into costly mistakes. By spotting these gotchas early, you can preserve more of your wealth and enjoy a smoother, more predictable retirement.
Our advisors at Greenbush Financial Group can help you identify your biggest risk areas and design a plan to minimize the tax and income surprises most retirees never see coming.
FAQs: Retirement Planning Surprises
Q: Are Social Security benefits always taxed?
A: No. But depending on your income, up to 85% of your benefits may be taxable.
Q: How can I avoid higher Medicare premiums?
A: Manage your income below IRMAA thresholds through strategic Roth conversions and tax-efficient withdrawals.
Q: What happens if I miss an RMD?
A: You could face a 25% penalty on the amount not withdrawn, reduced to 10% if corrected quickly.
Q: Why do widows and widowers pay more in taxes?
A: Filing status changes from joint to single, cutting brackets and deductions in half while much of the income remains.
Q: Are all retirement states tax-friendly?
A: No. Some states tax retirement income or have higher overall costs despite no income tax.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
The Advantages of Using Appreciated Securities to Fund a Donor-Advised Fund
Many people fund their donor-advised funds with cash, but gifting appreciated securities can be a smarter move. By donating stocks, mutual funds, or ETFs instead of cash, you can avoid capital gains tax and still claim a charitable deduction for the asset’s full market value. Our analysis at Greenbush Financial Group explains how this strategy can create a double tax benefit and help you give more efficiently.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
Many individuals fund their donor-advised funds (DAFs) with cash — but they may be missing out on a major tax-saving opportunity. By gifting appreciated securities (such as stocks, mutual funds, or ETFs) from a brokerage account instead of cash, taxpayers can avoid capital gains taxes and still receive a charitable deduction for the fair market value of the gift.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Why donor-advised funds have grown in popularity
The pros and cons of funding a DAF with cash
How gifting appreciated securities can create a double tax benefit
Charitable deduction limitations to keep in mind when using this strategy
The Rise in Popularity of Donor-Advised Funds
Donor-advised funds have become one of the most popular charitable giving vehicles in recent years. Much of this growth is tied to changes in the tax code — particularly the increase in the standard deduction.
Since charitable contributions are itemized deductions, taxpayers must itemize in order to claim them. But with the standard deduction now so high, fewer taxpayers itemize their deductions at all.
For example:
In 2025, the standard deduction for a married couple is $31,500.
Let’s say that a couple pays $10,000 in property taxes and donates $10,000 to charity.
Their total itemized deductions would be $20,000, which is still below the $31,500 standard deduction — meaning they’d receive no additional tax benefit for their $10,000 charitable gift.
That’s where donor-advised funds come in.
If this same couple plans to give $10,000 per year to charity for the next five years (totaling $50,000), they could “bunch” those future gifts into one year by contributing $50,000 to a donor-advised fund today. This larger, one-time contribution would push their itemized deductions well above the standard deduction threshold, allowing them to capture a significant tax benefit in the current year.
Another advantage is flexibility — the funds in a donor-advised account can be invested and distributed to charities over many years. It’s a way to pre-fund future giving while taking advantage of a larger immediate tax deduction.
Funding with Cash
It’s perfectly fine to fund a donor-advised fund with cash, especially if your goal is simply to capture a large charitable deduction in a single tax year.
Cash contributions are straightforward and qualify for a deduction of up to 60% of your adjusted gross income (AGI). But while this approach helps you maximize deductions, there may be an even more tax-efficient way to give — especially if you own highly appreciated investments in a taxable brokerage or trust account.
Using Appreciated Securities to Make Donor-Advised Fund Contributions
A potentially superior strategy is to contribute appreciated securities instead of cash. Doing so provides a double tax benefit:
Avoid paying capital gains tax on the unrealized appreciation of the asset.
Receive a charitable deduction for the fair market value of the donated securities.
Here’s an example:
Suppose you bought Google stock for $5,000, and it’s now worth $50,000.
If you sell the stock and then donate the $50,000 cash to your donor-advised fund, you’d owe capital gains tax on the $45,000 gain.
Alternatively, if you donate the stock directly to your donor-advised fund, you:
Avoid paying tax on that $45,000 unrealized gain, and
Still receive a $50,000 charitable deduction for the fair market value of the stock.
After the transfer, if you’d still like to own Google stock, you can repurchase it within your brokerage account — effectively resetting your cost basis to the current market value. This approach can help manage future capital gains exposure while supporting your charitable goals.
Charitable Deduction Limitations: Cash vs. Appreciated Securities
Whether you donate cash or appreciated securities, it’s important to understand the IRS limits on charitable deductions relative to your income. These limitations are based on a percentage of your adjusted gross income (AGI) and vary depending on the type of asset you donate:
This means if you donate appreciated securities worth more than 30% of your AGI, the excess amount can’t be deducted in the current year — but it can be carried forward for up to five additional years until fully utilized.
Being mindful of these limits ensures that your charitable giving strategy is both tax-efficient and compliant.
Final Thoughts
Using appreciated securities to fund a donor-advised fund can be one of the most effective ways to maximize your charitable impact and minimize taxes. By avoiding capital gains tax on appreciated assets and receiving a deduction for their full fair market value, you can create a powerful, ongoing giving strategy that benefits both your finances and your favorite causes.
Before implementing this strategy, it’s wise to work with your financial advisor or CPA to confirm eligibility, ensure proper documentation, and coordinate timing for optimal tax efficiency.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why is donating appreciated securities to a donor-advised fund more tax-efficient than giving cash?
Donating appreciated securities allows you to avoid paying capital gains tax on the investment’s appreciation while still receiving a charitable deduction for its fair market value.
How does a donor-advised fund help maximize charitable deductions?
A donor-advised fund (DAF) allows you to “bunch” multiple years of charitable contributions into a single tax year, pushing your itemized deductions above the standard deduction threshold. This strategy can help you capture a larger tax benefit in the current year while retaining flexibility to distribute funds to charities over time.
What are the IRS deduction limits for donating appreciated securities versus cash?
Cash donations to public charities or donor-advised funds are generally deductible up to 60% of your adjusted gross income (AGI), while donations of appreciated securities are limited to 30% of AGI. Any unused deductions can typically be carried forward for up to five years.
Can I repurchase the same securities after donating them to a donor-advised fund?
Yes. After donating appreciated securities, you can repurchase the same investment within your brokerage account. This effectively resets your cost basis to the current market value, helping manage future capital gains exposure while maintaining your investment position.
Who might benefit most from using appreciated securities to fund a donor-advised fund?
This strategy is especially beneficial for investors with highly appreciated assets in taxable accounts who want to support charitable causes while reducing taxes. It can also help high-income earners manage taxable income in peak earning years.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when donating appreciated securities?
Common pitfalls include selling the securities before donating them (which triggers capital gains tax) or failing to meet IRS substantiation requirements for non-cash gifts. Working with a financial advisor or CPA ensures proper execution and documentation.
Planning for Healthcare Costs in Retirement: Why Medicare Isn’t Enough
Healthcare often becomes one of the largest and most underestimated retirement expenses. From Medicare premiums to prescription drugs and long-term care, this article from Greenbush Financial Group explains why healthcare planning is critical—and how to prepare before and after age 65.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
When most people picture retirement, they imagine travel, hobbies, and more free time—not skyrocketing healthcare bills. Yet, one of the biggest financial surprises retirees face is how much they’ll actually spend on medical expenses.
Many retirees dramatically underestimate their healthcare costs in retirement, even though this is the stage of life when most people access the healthcare system the most. While it’s common to pay off your mortgage leading up to retirement, it’s not uncommon for healthcare costs to replace your mortgage payment in retirement.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Why Medicare isn’t free—and what parts you’ll still need to pay for.
What to consider if you retire before age 65 and don’t yet qualify for Medicare.
The difference between Medicare Advantage and Medicare Supplement plans.
How prescription drug costs can take retirees by surprise.
The reality of long-term care expenses and how to plan for them.
Planning for Healthcare Before Age 65
For those who plan to retire before age 65, healthcare planning becomes significantly more complicated—and expensive. Since Medicare doesn’t begin until age 65, retirees need to bridge the coverage gap between when they stop working and when Medicare starts.
If your former employer offers retiree health coverage, that’s a tremendous benefit. However, it’s critical to understand exactly what that coverage includes:
Does it cover just the employee, or both the employee and their spouse?
What portion of the premium does the employer pay, and how much is the retiree responsible for?
What out-of-pocket costs (deductibles, copays, coinsurance) remain?
If you don’t have retiree health coverage, you’ll need to explore other options:
COBRA coverage through your former employer can extend your workplace insurance for up to 18 months, but it’s often very expensive since you’re paying the full premium plus administrative fees.
ACA marketplace plans (available through your state’s health insurance exchange) may be an alternative, but premiums and deductibles can vary widely depending on your age, income, and coverage level.
In many cases, healthcare costs for retirees under 65 can be substantially higher than both Medicare premiums and the coverage they had while working. This makes it especially important to build early healthcare costs into your retirement budget if you plan to leave the workforce before age 65.
Medicare Is Not Free
At age 65, most retirees become eligible for Medicare, which provides a valuable foundation of healthcare coverage. But it’s a common misconception that Medicare is free—it’s not.
Here’s how it breaks down:
Part A (Hospital Insurance): Usually free if you’ve paid into Social Security for at least 10 years.
Part B (Medical Insurance): Covers doctor visits, outpatient care, and other services—but it has a monthly premium based on your income.
Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Also carries a monthly premium that varies by plan and income level.
Example:
Let’s say you and your spouse both enroll in Medicare at 65 and each qualify for the base Part B and Part D premiums.
In 2025, the standard Part B premium is approximately $185 per month per person.
A basic Part D plan might average around $36 per month per person.
Together, that’s about $220 per person, or $440 per month for a couple—just for basic Medicare coverage. And this doesn’t include supplemental or out-of-pocket costs for things Medicare doesn’t cover.
NOTE: Some public sector or state plans even provide Medicare Part B premium reimbursement once you reach 65—a feature that can be extremely valuable in retirement.
Medicare Advantage and Medicare Supplement Plans
While Medicare provides essential coverage, it doesn’t cover everything. Most retirees need to choose between two main options to fill in the gaps:
Medicare Advantage (Part C) plans, offered by private insurers, bundle Parts A, B, and often D into one plan. These plans usually have lower premiums but can come with higher out-of-pocket costs and limited provider networks.
Medicare Supplement (Medigap) plans, which work alongside traditional Medicare, help pay for deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
It’s important not to simply choose the lowest-cost plan. A retiree’s prescription needs, frequency of care, and preferred doctors should all factor into the decision. Choosing the cheapest plan could lead to much higher out-of-pocket expenses in the long run if the plan doesn’t align with your actual healthcare needs.
Prescription Drug Costs: A Hidden Retirement Expense
Prescription drug coverage is one of the biggest cost surprises for retirees. Even with Medicare Part D, out-of-pocket expenses can add up quickly depending on the medications you need.
Medicare Part D plans categorize drugs into tiers:
Tier 1: Generic drugs (lowest cost)
Tier 2: Preferred brand-name drugs (moderate cost)
Tier 3: Specialty drugs (highest cost, often with no generic alternatives)
If you’re prescribed specialty or non-generic medications, you could spend hundreds—or even thousands—per month despite having coverage.
To help, some states offer programs to reduce these costs. For example, New York’s EPIC program helps qualifying seniors pay for prescription drugs by supplementing their Medicare Part D coverage. It’s worth checking if your state offers a similar benefit.
Planning for Long-Term Care
One of the most misunderstood aspects of Medicare is long-term care coverage—or rather, the lack of it.
Medicare only covers a limited number of days in a skilled nursing facility following a hospital stay. Beyond that, the costs become the retiree’s responsibility. Considering that long-term care can easily exceed $120,000 per year, this can be a major financial burden.
Planning ahead is essential. Options include:
Purchasing a long-term care insurance policy to offset future costs.
Self-insuring, by setting aside savings or investments for potential care needs.
Planning to qualify for Medicaid through strategic trust planning
Whichever route you choose, addressing long-term care early is key to protecting both your assets and your peace of mind.
Final Thoughts
Healthcare is one of the largest—and most underestimated—expenses in retirement. While Medicare provides a foundation, retirees need to plan for premiums, prescription costs, supplemental coverage, and potential long-term care needs.
If you plan to retire before 65, early planning becomes even more critical to bridge the gap until Medicare begins. By taking the time to understand your options and budget accordingly, you can enter retirement with confidence—knowing that your healthcare needs and your financial future are both protected.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why isn’t Medicare enough to cover all healthcare costs in retirement?
While Medicare provides a solid foundation of coverage starting at age 65, it doesn’t pay for everything. Retirees are still responsible for premiums, deductibles, copays, prescription drugs, and long-term care—expenses that can add up significantly over time.
What should I do for healthcare coverage if I retire before age 65?
If you retire before Medicare eligibility, you’ll need to bridge the gap with options like COBRA, ACA marketplace plans, or employer-sponsored retiree coverage. These plans can be costly, so it’s important to factor early healthcare premiums and out-of-pocket expenses into your retirement budget.
What are the key differences between Medicare Advantage and Medicare Supplement plans?
Medicare Advantage (Part C) plans combine Parts A, B, and often D, offering convenience but limited provider networks. Medicare Supplement (Medigap) plans work alongside traditional Medicare to reduce out-of-pocket costs. The right choice depends on your budget, health needs, and preferred doctors.
How much should retirees expect to pay for Medicare premiums?
In 2025, the standard Medicare Part B premium is around $185 per month, while a basic Part D plan averages about $36 monthly. For a married couple, that’s roughly $440 per month for both—before adding supplemental coverage or out-of-pocket expenses. These costs should be built into your retirement spending plan.
Why are prescription drugs such a major expense in retirement?
Even with Medicare Part D, out-of-pocket drug costs can vary widely based on your prescriptions. Specialty and brand-name medications often carry high copays. Programs like New York’s EPIC can help eligible seniors manage these costs by supplementing Medicare coverage.
Does Medicare cover long-term care expenses?
Medicare only covers limited skilled nursing care following a hospital stay and does not pay for most long-term care needs. Since extended care can exceed $120,000 per year, retirees should explore options like long-term care insurance, Medicaid planning, or setting aside savings to self-insure.
How can a financial advisor help plan for healthcare costs in retirement?
A financial advisor can estimate future healthcare expenses, evaluate Medicare and supplemental plan options, and build these costs into your retirement income plan. At Greenbush Financial Group, we help retirees design strategies that balance healthcare needs with long-term financial goals.
Special Tax Considerations in Retirement
Retirement doesn’t always simplify your taxes. With multiple income sources—Social Security, pensions, IRAs, brokerage accounts—comes added complexity and opportunity. This guide from Greenbush Financial Group explains how to manage taxes strategically and preserve more of your retirement income.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
You might think that once you stop working, your tax situation becomes simpler — after all, no more paychecks! But for many retirees, taxes actually become more complex. That’s because retirement often comes with multiple income sources — Social Security, pensions, pre-tax retirement accounts, brokerage accounts, cash, and more.
At the same time, retirement can present unique tax-planning opportunities. Once the paychecks stop, retirees often have more control over which tax bracket they fall into by strategically deciding which accounts to pull income from.
In this article, we’ll cover:
How Social Security benefits are taxed
Pension income rules (and how they vary by state)
Taxation of pre-tax retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s
Developing an efficient distribution strategy
Special tax deductions and tax credits for retirees
Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) planning
Charitable giving strategies, including QCDs and donor-advised funds
How Social Security Is Taxed
Social Security benefits may be tax-free, partially taxed, or mostly taxed — depending on your provisional income. Provisional income is calculated as:
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) + Nontaxable Interest + ½ of Your Social Security Benefits.
Here’s a quick summary of how benefits are taxed at the federal level:
While Social Security is taxed at the federal level, most states do not tax these benefits. However, a handful of states — including Colorado, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, Rhode Island, Utah, and Vermont — do impose some form of state tax on Social Security income.
Pension Income
If you’re fortunate to receive a state pension, your state of residence plays a big role in determining how that income is taxed.
If you have a state pension and continue living in the same state where you earned the pension, many states exclude that income from state tax.
However, with state pensions, if you move to another state, and that state has income taxation at the stateve level, your pension may become taxable in your new state of domicile.
If you have a pension with a private sector employer, often times those pension payment are full taxable at both the federal and state level.
Some states also provide preferential treatment for private pensions or IRA income. For example, New York excludes up to $20,000 per person in pension or IRA distributions from state income tax each year — a significant benefit for retirees managing taxable income.
Taxation of Pre-Tax Retirement Accounts
Pre-tax retirement accounts — including Traditional IRAs, 401(k)s, 403(b)s, and inherited IRAs — are typically taxed as ordinary income when distributions are made.
However, the tax treatment at the state level varies:
Some states (like New York) exclude a set amount – for example New York excludes the first $20,000 per person per year — from state taxation.
Others tax all pre-tax distributions in full.
A few states offer income-based exemptions or reduced rates for lower-income retirees.
Because these rules differ so widely, it’s important to research your state’s tax laws.
Developing a Tax-Efficient Distribution Strategy
A well-designed distribution strategy can make a big difference in how much tax you pay throughout retirement.
Many retirees have income spread across:
Pre-tax accounts (401(k), IRA)
After-tax brokerage accounts
Roth IRAs
Social Security
Let’s say you need $70,000 per year to maintain your lifestyle. Some of that may come from Social Security, but you’ll need to decide where to withdraw the rest.
With smart planning, you can blend withdrawals from different accounts to minimize your overall tax liability and control your tax bracket year by year. The goal isn’t just to reduce taxes today — it’s to manage them over your lifetime.
Special Deductions and Credits in Retirement
Your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) or Modified AGI doesn’t just determine your tax bracket — it also affects which deductions and credits you can claim.
A few important highlights:
The Big Beautiful Tax Bill that just passed in 2025 introduces a new Age 65+ tax deduction of $6,000 per person over and above the existing standard deduction.
Certain deductions and credits, however, phase out once income exceeds specific thresholds.
Your income level also affects Medicare premiums for Parts B and D, which increase if your income surpasses the IRMAA thresholds (Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount).
Managing your taxable income through careful distribution planning can therefore help preserve deductions and keep Medicare premiums lower.
Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) Planning
Once you reach age 73 or 75 (depending on your birth year), you must begin taking Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) from your pre-tax retirement accounts — even if you don’t need the money.
These RMDs can significantly increase your taxable income, especially when stacked on top of Social Security and other income sources.
A proactive strategy is to take controlled distributions or perform Roth conversions before RMD age. Doing so can reduce the size of your future RMDs and potentially lower your lifetime tax bill by spreading taxable income across more favorable tax years.
Charitable Giving Strategies
Many retirees are charitably inclined, but since most take the standard deduction, they don’t receive an additional tax benefit for their donations.
There are two primary strategies to consider:
Donor-Advised Funds (DAFs) – You can “bunch” several years’ worth of charitable giving into one tax year to exceed the standard deduction, then direct the funds to charities over time.
Qualified Charitable Distributions (QCDs) – Once you reach age 70½, you can donate directly from your IRA to a qualified charity. These QCDs are excluded from taxable income and count toward your RMD once those begin.
Final Thoughts
Retirement opens up new opportunities — and new complexities — when it comes to managing taxes. Understanding how your various income sources interact and planning your distributions strategically can help you:
Reduce taxes over your lifetime
Preserve more of your retirement income
Maintain flexibility and control over your financial future
As always, it’s wise to coordinate with a financial advisor and tax professional to ensure your retirement tax strategy aligns with your goals, income sources, and state tax rules.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How are Social Security benefits taxed in retirement?
Depending on your provisional income, up to 85% of your Social Security benefits may be subject to federal income tax. Most states don’t tax these benefits, though a few—including Colorado, Minnesota, and Utah—do.
How is pension income taxed, and does it vary by state?
Pension income is typically taxable at the federal level, but state rules differ. Some states exclude public pensions from taxation or offer partial exemptions—like New York’s $20,000 per person exclusion for pension or IRA income. If you move to another state in retirement, your pension’s tax treatment could change.
What taxes apply to withdrawals from pre-tax retirement accounts?
Distributions from Traditional IRAs, 401(k)s, and similar pre-tax accounts are taxed as ordinary income. Some states offer exclusions or partial deductions, while others tax these withdrawals in full. Understanding your state’s rules is essential for accurate tax planning.
What is a tax-efficient withdrawal strategy in retirement?
A tax-efficient strategy blends withdrawals from different account types—pre-tax, Roth, and after-tax—to control your annual tax bracket. The goal is not just to lower taxes today but to reduce lifetime taxes by managing income across multiple years and minimizing required minimum distributions later.
What new tax deductions or credits are available for retirees?
The 2025 tax law introduced an additional $6,000 deduction per person age 65 and older, in addition to the standard deduction. Keeping taxable income lower through smart planning can also help retirees preserve deductions and avoid higher Medicare IRMAA surcharges.
How do Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) impact taxes?
Starting at age 73 or 75 (depending on birth year), retirees must withdraw minimum amounts from pre-tax retirement accounts, which increases taxable income. Performing partial Roth conversions or strategic withdrawals before RMD age can help reduce future tax exposure.
What are Qualified Charitable Distributions (QCDs) and how do they work?
QCDs allow individuals age 70½ or older to donate directly from an IRA to a qualified charity, satisfying all or part of their RMD while excluding the amount from taxable income. This strategy helps maximize charitable impact while reducing taxes in retirement.
Putting Your Child on Payroll: Tax Benefits and Planning Considerations for Business Owners
Hiring your child in your business can reduce family taxes and create powerful retirement savings opportunities. Greenbush Financial Group explains how payroll wages allow Roth IRA contributions, open the door to retirement plan participation, and provide long-term wealth benefits—while highlighting the rules and compliance concerns you need to know.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
For business owners, employing your child in the family business can be both financially and personally rewarding. Not only does it teach children about responsibility and work ethic, but it can also open up meaningful tax and retirement planning opportunities. However, this strategy comes with important rules and limitations that need to be carefully understood before implementation.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Why parents consider putting their children on payroll
The tax benefits of shifting income
How retirement plan contributions can supercharge long-term wealth for kids
Using W-2 wages to fund Roth IRAs
Key limitations and compliance concerns to keep in mind
Shifting Income: The Tax Advantage
One of the primary motivations for hiring your child is income shifting—moving taxable income from a higher-bracket parent to a lower-bracket child.
For example, instead of paying yourself additional compensation taxed at 37%, you could pay your child for legitimate work at their much lower (or even 0%) tax bracket. The wages are deductible for the business, and the child may owe little to no federal income tax, depending on their total earnings.
This strategy can effectively lower the family’s overall tax bill while compensating your child fairly for real work.
Retirement Plan Contributions for Your Child
If your child is legitimately on payroll, they may also become eligible for participation in the company’s retirement plan. With the right plan design, this could allow:
401(k) deferrals (including Roth contributions) up to $23,500 per year in 2025
Employer contributions in addition to employee deferrals, depending on plan rules.
Imagine the power of decades of tax-free Roth 401(k) growth starting in your child’s teenage years. Even modest contributions today could compound into significant wealth by retirement.
Funding a Roth IRA
Even if your child doesn’t earn enough to max out a 401(k) or work enough hour to become eligible for the company’s 401(k) plan, any earned income reported on a W-2 makes them eligible to contribute to a Roth IRA.
The 2025 contribution limit is $7,000 for individuals under age 50.
Contributions must not exceed the child’s earned income for the year.
This is one of the most effective long-term wealth accumulation strategies available for young workers, given the decades of tax-free growth that a Roth IRA can provide.
Practical Limitations and Compliance Concerns
While the benefits are clear, there are serious rules and restrictions that business owners must respect:
Reasonable work and pay: The job duties and pay must be appropriate for the child’s age and abilities. A 6-year-old making $30,000 a year for “marketing or consulting” is not likely to pass IRS scrutiny.
Labor laws: States impose restrictions on how much and what type of work minors can do. These vary by state, and compliance is essential.
Payroll compliance: Children on payroll must be treated like any other employee—filed on W-2s, subject to FICA taxes (unless an exception applies), and paid at reasonable market rates.
Retirement plan eligibility: Not all plans allow immediate participation. Some require minimum service or age thresholds. Plan design must be reviewed before assuming your child can make contributions.
Audit risk: Employing family members can attract IRS attention. Documentation of actual work performed (e.g., timesheets, job descriptions, projects completed) is important.
Other Considerations
While putting children on payroll can save taxes and accelerate wealth-building, it’s not a one-size-fits-all strategy. Business owners must weigh:
The cost of payroll taxes on the child’s wages
Retirement plan contribution obligations for other employees if the child becomes eligible
Administrative requirements and state-specific child labor rules
The optics of compensation relative to duties performed
Key Takeaways
Hiring your child can shift income into a lower tax bracket and reduce the family’s overall tax bill.
Payroll wages open the door to retirement savings strategies like Roth 401(k) contributions (if the plan allows) and Roth IRAs (up to $7,000 per year).
Plan design, labor laws, and IRS scrutiny mean you must be cautious, document carefully, and ensure the arrangement is reasonable.
This strategy can be powerful for both tax savings today and long-term wealth accumulation for your child—but it must be implemented correctly.
Before putting your child on payroll, consult with both your tax advisor and your retirement plan administrator. Done right, this can be a smart family wealth-building strategy. Done wrong, it can create compliance headaches.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Why would a business owner put their child on payroll?
Hiring your child allows you to shift income from a higher tax bracket to a lower one, reducing the family’s overall tax liability. It also helps children learn valuable work and financial skills while legitimately earning income.
How does hiring a child create tax benefits?
Wages paid to a child for real work are deductible business expenses, lowering the company’s taxable income. Meanwhile, the child may owe little to no federal income tax if their earnings stay below standard deduction thresholds.
Can my child contribute to a retirement plan if they work for my business?
Yes. If they meet eligibility requirements, children can make 401(k) contributions—including Roth deferrals—through your company’s retirement plan. Even small contributions in their early years can compound significantly over time.
Can my child open a Roth IRA with earned income?
Absolutely. As long as your child earns income reported on a W-2, they can contribute up to $7,000 per year (2025 limit) to a Roth IRA, not exceeding their total earned income. Roth IRAs are especially powerful for young workers due to decades of tax-free growth.
What are the key IRS and labor law rules when employing your child?
The work must be age-appropriate, pay must be reasonable for the duties performed, and proper payroll procedures must be followed. Employers must also comply with state child labor laws and maintain documentation of actual work performed.
Are there any risks or downsides to hiring your child?
Yes. Improper pay, lack of documentation, or failure to follow labor laws can trigger IRS scrutiny. Additionally, adding your child to the company’s payroll may create additional administrative costs or affect retirement plan participation rules.
What should business owners do before putting their child on payroll?
Consult with your tax advisor and retirement plan administrator to ensure the arrangement complies with IRS and labor regulations. Proper planning helps you maximize tax benefits while avoiding compliance issues.