The Shift from Defined Benefit to Defined Contribution Plans
As defined benefit plans continue to become a thing of the past and workers realize they will not have a pension (and possibly Social Security) to rely on during retirement, it is important to be educated on the investments and opportunities available in employer sponsored defined contribution plans. This newsletter will briefly discuss the difference between defined benefit plans and defined contribution plans, why the dramatic shift from one to the other, and why it is important to be educated on retirement and the investment options available.
Defined Benefit Plans
Defined benefit plans (commonly referred to as pension plans) are promises made by an organization to pay a specific amount, usually monthly, to an employee during retirement. These amounts are calculated based on a number of factors including an employees earnings history, service, and age. Since the organization is responsible for funding these plans during an employee’s retirement, investment returns are the concern of the organization, not the employee.
Defined Contribution Plans
Rather than an employer guaranteeing a benefit during retirement as is the case with defined benefit plans, the employee (and often times the employer) will make contributions to a defined contribution plan which accumulates over time and is drawn upon by the employee during retirement. One of the most common forms of defined contribution plans available to workers is the 401(k) plan. Since the guarantee of a monthly benefit during retirement is not there in a 401(k) plan, whatever is accumulated from employee/employer contributions and investment returns over the years is what will be available to the employee throughout retirement. In other words, this is the amount that must last throughout retirement.
Why the shift to 401(k)s and other defined contribution plans?
Defined benefit plans were set up to reward employees with consistent income during retirement since they are no longer earning. This is a great benefit to employees if available but these plans are becoming obsolete. As baby boomers continue to retire and live longer than previous generations, defined benefit plans are becoming too expensive to fund.
It is extremely difficult for companies (and municipalities) to turn a profit when they continue paying employees twenty years after their last day. Think of a defined benefit plan like you would a bad contract in baseball. Let me use one of the most scrutinized contracts in baseball history as an example. The Mets contract with Bobby Bonilla.
The last time Bonilla had an at bat for the Mets was in 1999, yet in 2015 he received a check for $1.19 million dollars. That amount is more than 17 of the current 25 players will make in 2015. Not the best business model when you are paying that kind of money to a player that hasn’t filled a seat (generated income for a company) in 15 years. The payment is guaranteed to Bonilla through 2035, which can be compared to a worker retiring at 55 and receiving a guaranteed payment for life.
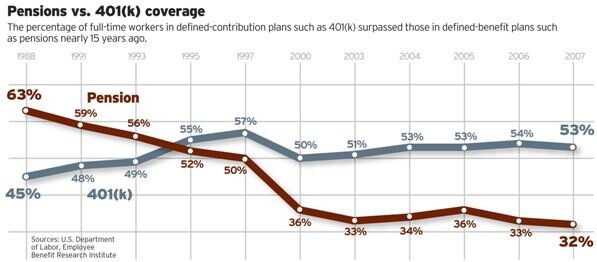
For the reasons that seem obvious now, the past 30 years has seen a dramatic shift from defined benefit plans to defined contribution plans.
This chart illustrates the shift noted above. The breakeven point is shown around 1990 with no signs of the trend reversing.
As of June 30, 2014, 401(k) plans held an estimated $4.4 trillion in assets which is compared to $2.2 trillion in 2004.
Savings and Investment Performance
So, with less retirees having a pension plan to rely on for consistent income throughout retirement, how well are people preparing for retirement? The USA Today released an article in March 2015 titled “For millions, 401(k) plans have fallen short”, which describes the lack of retirement savings and inability for the majority of retirees to maintain their current lifestyle during retirement. The article references a report issued by the Employee Benefit Research Institute that stated the median amount in 401(k) savings accounts is $18,433. The median is higher for older employees as Vanguard 401(k) accounts for savers age 55 to 64 was $76,381 in 2013.
The Social Security website calculates life expectancy and determined that a man reaching age 65 today is expected to live until 84.3 years old (86.6 years old for women). That being said, an employee expecting to retire at age 65 with less than $100,000 in retirement savings has to live off that and social security for 20 plus years. The shift in retirement has led to many retirees not enjoying the retirement they had once planned.
As mentioned earlier, the migration from defined benefit plans to defined contribution plans has led to employees being responsible for managing their retirement. It is apparent that the savings rate for the average employee has not been sufficient to fund retirement, so now let us look at how employees are performing compared to major asset classes.
Contributions are only one part of a 401(k) balance with the other being interest earned. The chart above shows how the average investor has performed compared to different asset classes over the past 20 years. The 2.5% earned by the average investor was only .1% higher than inflation. This essentially means that in real dollars the average investor did not have any earnings during this period.
We typically look at the S&P 500 when determining how the stock market is performing which was up 9.9% over the same period. The other highlighted bar in the graph shows a portfolio with 60% in stocks and 40% in bonds, which is more of a conservative allocation but still saw an increase of 8.7%. When participating in a 401(k) for 20, 30, or 40 years, the majority of the balance when approaching retirement is not the contributions made but the interest that has compounded over an extended period of time. Losing 6-8% annually has a dramatic impact on an account, especially over a 20 year period.
This chart shows the impact of lost earnings over 40 years. In the example, the investor makes an initial investment of $10,000 earning 0%, 2%, 5%, and 8% annually with no additional contributions. Two quick takeaways are the interest that compounds at 5% and 8% are much more than the initial investment and after 20 years the difference between 5% and 8% is almost double.
Taking Control Of Your 401(k)
As defined contribution plans continue to takeover as the main income vehicle for retirees, how can employees benefit and take advantage of the available resources from these plans?
Start contributing as soon as possible - As shown earlier, the interest that compounds in a retirement account makes up the majority of the balance when invested for an extended period of time. The sooner you can start contributing the longer the account has to grow and the need to play catch-up as you approach retirement may be avoided. Also, you will be less reliable on the dollars being contributed as you are not used to the income each pay period.
Take advantage of the employer match - If your employer is generous enough to offer a match, take advantage of it. For example, you make $50,000 a year and your employer matches up to 3% of your compensation. This means that you can contribute $1,500 of pre-tax money and automatically double your investment. That is a 100% return just for participating in the plan.
Use the available resources - If your plan has a financial advisor, sit down with him or her and discuss your retirement goals and how to invest your contributions. The reason the average investor performs so poorly compared to the indexes is because they try to time the market and when they pull out they are reluctant to get back in. Discuss your time horizon and risk tolerance with your advisor and let them allocate your investments in a way that makes sense.
It is important to be educated, and historically, investors do not benefit over longer periods if they try to beat the market. JP Morgan put out a study that showed an investor who missed the 10 best days in the stock market from 1994-2014 earned a little more than half of an investor who was fully invested during the same period. If you have a long time horizon, it is important to hold through the ups and downs as historically the stock market goes up over long periods. For most investors, 10-15 years from retirement is when participants should start reassessing their allocation and determine if it is still the appropriate position for them.
Final Thoughts
As money continues to pour into defined contribution plans, it is important that the public be educated on what this means for retirement. Now more than ever it is up to employees to take responsibility for their retirement and save enough to last as defined benefit plans become obsolete and Social Security needs an overhaul that no one will touch.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.