Stock Options 101: ISO, NQSO, and Restricted Stock
If you are reading this article, your company has probably granted you stock options. Stock options give you the potential share in the growth of your company’s value without any financial risk to you until you exercise the options and buy shares of your company’s stock.
If you are reading this article, your company has probably granted you stock options. Stock options give you the potential share in the growth of your company’s value without any financial risk to you until you exercise the options and buy shares of your company’s stock.
Stock options give you the right to purchase a specific number of shares of the company’s stock at a fixed price. There is typically a vesting schedule attached to option grants that specify when you have the right to exercise your stock options. Companies can offer employees:
Incentive Stock Options (“ISO”)
Nonqualified Stock Options (“NQSO”)
Restricted Stock
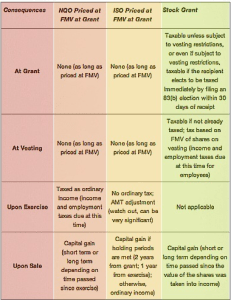
It is very important to understand how these different types of options and grants are taxed otherwise it could lead to unfortunate tax surprises down the road.
Non-Qualified Stock Options (NQSO)
A non-qualified stock option (NQSO) is a type of stock option that does not qualify for special favorable tax treatment under the US Internal Revenue Code. Thus the word nonqualified applies to the tax treatment (not to eligibility or any other consideration). NQSOs are the most common form of stock option and may be granted to employees, officers, directors, contractors, and consultants.
You pay taxes on these options at the time of exercise. For tax purposes, the exercise spread is compensation income and is therefore reported on your IRS Form W-2 for the calendar year of exercise.
Example: Your stock options have an exercise price of $30 per share. You exercise them when the price of your company stock is $100 per share. You have a $70 spread ($100 – 30) and thus $70 per share is included in your W2 as ordinary income.
Your company will withhold taxes—income tax, Social Security, and Medicare—when you exercise the options.
When you sell the shares, whether immediately or after a holding period, your proceeds are taxed under the rules for capital gains and losses. You report the stock sale on Form 8949 and Schedule D of your IRS Form 1040 tax return.
Incentive Stock Options (ISO)………..
Incentive stock options (ISOs) qualify for special tax treatment under the Internal Revenue Code and are not subject to Social Security, Medicare, or withholding taxes. However, to qualify they must meet rigid criteria under the tax code. ISOs can be granted only to employees, not to consultants or contractors. There is a $100,000 limit on the aggregate grant value of ISOs that may first become exercisable (i.e. vest) in any calendar year. Also, for an employee to retain the special ISO tax benefits after leaving the company, the ISOs must be exercised within three months after the date of termination.
After you exercise these options, if you hold the acquired shares for at least two years from the date of grant and one year from the date of exercise, you incur favorable long-term capital gains tax (rather than ordinary income tax) on all appreciation over the exercise price. However, the paper gains on shares acquired from ISOs and held beyond the calendar year of exercise can subject you to the alternative minimum tax (AMT). This can be problematic if you are hit with the AMT on theoretical gains but the company's stock price then plummets, leaving you with a big tax bill on income that has evaporated.
Very Important: If you have been granted ISOs, it’s important to understand how the alternative minimum tax can affect you prior to exercising your stock options.
Restricted Stock……………….
Your company may no longer be granting you stock options, or may be granting fewer than before. Instead, you may be receiving restricted stock. While these grants don't give you the same potentially life-altering, wealth-building upside as stock options, they do have additional benefits compared to ISO’s and NQSO’s.
The value of stock options, such as ISO’s and NQSO’s, depend on how much (or whether) your company's stock price rises above the price on the grant date. By contrast, restricted stock has value at vesting even if the stock price has not moved or even dropped since grant.
Depending on your attitude toward risk and your experience with swings in your company's stock price, the certainty of your restricted stock's value can be appealing. By contrast, stock options (ISO & NQSO) have great upside potential but can be "underwater" (i.e. having a market price lower than the exercise price). This is why restricted stock is often granted to a newly hired executive. It may be awarded as a hiring bonus or to make up for compensation and benefits, including in-the-money options and nonqualified retirement benefits, forfeited by leaving a prior employer.
Of course, the very essence of restricted stock is that you must remain employed until the shares vest to receive its value. While you may have between 30 and 90 days to exercise stock options after voluntary termination, unvested grants of restricted stock are often forfeited immediately. Thus, it is an extremely effective “golden handcuff” to keep you at your company.
Fewer Decisions
Unlike a stock option, which requires you to decide when to exercise and what exercise method to use, restricted stock involves fewer decisions. When you receive the shares at vesting—which can be based simply on the passage of time or the achievement of performance goals—you may have a choice of tax-withholding methods (e.g. cash, sell shares for taxes), or your company may automatically withhold enough vested shares to cover the tax withholding. Restricted stock is considered "supplemental" wages, following the same tax rules and W-2 reporting that apply to grants of nonqualified stock options.
Tax Decisions
The most meaningful decision with restricted stock grants is whether to make a Section 83(b) election to be taxed on the value of the shares at grant instead of at vesting. Whether to make this election, named after the section of the Internal Revenue Code that authorizes it, is up to you. (It is not available for Restricted Stock Units (RSUs), which are not "property" within the meaning of Internal Revenue Code Section 83)
If a valid 83(b) election is made within 30 days from the date of grant, you will recognize as of that date ordinary income based on the value of the stock at grant instead of recognizing income at vesting. As a result, any appreciation in the stock price above the grant date value is taxed at capital gains rates when you sell the stock after vesting.
While this can appear to provide an advantage, you face significant disadvantages should the stock never vest and you forfeit it because of job loss or other reasons. You cannot recover the taxes you paid on the forfeited stock. For this reason, and the earlier payment date of required taxes on the grant date value, you usually do better by not making the election. However, this election does provide one of the few opportunities for compensation to be taxed at capital gains rates. In addition, if you work for a startup pre-IPO company, it can be very attractive for stock received as compensation when the stock has a very small current value and is subject to a substantial risk of forfeiture. Here, the downside risk is relatively small.
Dividends
Unlike stock options, which rarely carry dividend equivalent rights, restricted stock typically entitles you to receive dividends when they are paid to shareholders.
However, unlike actual dividends, the dividends on restricted stock are reported on your W-2 as wages (unless you made a Section 83(b) election at grant) and are not eligible for the lower tax rate on qualified dividends until after vesting.
Comparison Chart
Disclosure: The information listed above is for educational purposes only. Greenbush Financial Group, LLC does not provide tax advice. For tax advice, please consult your accountant.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Types of Retirement Plans
The comparing retirement plans chart gives business owners the ability to compare different types of plans available to their company.
Types of Retirement Plans
The comparing retirement plans chart gives business owners the ability to compare different types of plans available to their company.
Click on the PDF link in the green box below.
Rollover Chart
Provides individuals with clarification on the rollover rules for retirement accounts and IRA’s.
Rollover Chart
Provides individuals with clarification on the rollover rules for retirement accounts and IRA’s.
Click on the PDF link in the green box below.
Expense Planner
The expense planner is used to determine your annual after tax expenses both now and in retirement.
Financial Planning Questionnaire
The financial planning questionnaire is used to gather information in the initial phase of the financial planning process with Greenbush Financial Group.
Year End Tax Strategies
The end of the year is always a hectic time but taking the time to sit with a tax professional and determine what tax strategies will work best for you may save thousands on your tax bill due April 15th. As the deadline for your taxes starts to get closer, you may be in such a rush to file them on time that you make some mistakes in the process, but
The end of the year is always a hectic time but taking the time to sit with a tax professional and determine what tax strategies will work best for you may save thousands on your tax bill due April 15th. As the deadline for your taxes starts to get closer, you may be in such a rush to file them on time that you make some mistakes in the process, but don't worry, you won't be the only one. If you don't have the relevant tax strategy in place, you are more prone to mistakes. So, the purpose of this article is to discuss some of the most common tax strategies that may apply to you. It may be worth contacting a company that specializes in tax services if you're unsure of how to go about these strategies though. Some of the deadlines for these strategies aren't until tax filing but the majority include an action item that must be done by December 31st to qualify and therefore taking the time before year end is crucial.
Taxable Investment Accounts
Offset some of the realized gains incurred during the year by selling investments in loss positions. Often times dividends received and sales made in a taxable investment account are reinvested. Although the owner of the account never received cash in the transaction, the gain is still realized and therefore taxable. This may cause an issue when the cash is not available to pay the tax bill. By selling investments in a loss position prior to 12/31, you will offset some, if not all, of the gain realized during the year. If possible, sell enough investments in a loss position to take advantage of the maximum $3,000 loss that can be claimed on your tax return.
Note: The IRS recognized this strategy was being abused and implemented the "wash sale" rule. If you sell an investment in a loss position to diminish gains and then repurchase the same investment within 30 days, the IRS does not allow you to claim the loss therefore negating the strategy.
Convert a Traditional IRA to a Roth IRA
If you are in a low income year and will be taxed at a lower tax bracket than projected in the future, it may make sense to convert part of a traditional IRA to a Roth IRA. The current maximum contribution to a Roth IRA in a single year is $5,500 if under 50 and $6,500 if 50 plus. You will pay taxes on the distributions from the traditional but the benefit of a Roth is that all the contributions and earnings accumulated is tax free when distributed as long as the account has been opened for at least 5 years. Roth accounts are typically the last touched during retirement because you want the tax free accumulation as long as possible. Also, Roth accounts can be passed to a beneficiary who can continue accumulating tax free. Roth money is after tax money and therefore the IRS allows you to withdraw contributions tax and penalty free and let the earnings continue to accumulate tax free. If you don't have the cash come tax time to cover the conversion, you can convert the Roth money back to a traditional IRA by tax filing plus extension and the account will be treated as the Roth conversion never took place.
Donate to Charity if you Itemize
If you itemize deductions on your tax return, go through your closet and donate any clothing or household goods that you no longer use. There are helpful tools online that will allow you to value the items donated but be sure you keep record of what was donated and have the charity give you a receipt.
Max Out Your Employer Sponsored Retirement Plan
If you know you will be hit with a big tax bill and want to defer some of the taxes, max out your retirement plan if you haven't already. Employer sponsored plans, such as 401(k)'s, must be funded through payroll by 12/31 and therefore it is important to make this determination early and request your payroll department start upping your contribution for the remaining payroll periods in the year. The maximum for 401(k)'s in 2015 and 2016 is $18,000 if under 50 and $24,000 if 50 plus.
Business Owners – Cut Checks by 12/31
If your company had a great year and the cash is available, use it to pay for expenses you would normally hold off on. This could mean paying state taxes early, paying invoices you usually wait until the end of the payment term, paying monthly expenses like health or general insurance, or buying new office equipment. This might also mean investing in new office furniture such as chairs and desks, or more storage space for all of your paperwork and electronics. Above all, by getting the checks cut by 12/31, you realize the expense in the current year and will decrease your tax bill.
Business Owners – Set Up a Retirement Plan
For owners with no full time employees, a Single(k) plan being put in place by 12/31 will allow you to fund a retirement account up to the 401(k) limits mentioned early. As long as the plan is established by 12/31, the owner will be able to fund the plan any time before tax filing plus extension. If the plan is not established by 12/31, other options like the SEP IRA are available to take money off the table come tax time.With tax laws continuously changing, it is important to consult with your tax professional as there may be strategies available to you that could save you money. Don't procrastinate as some planning before the end of the year may be necessary to take full advantage.
About Rob.........
Hi, I'm Rob Mangold. I'm the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally , professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, pleas feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Should I Establish an Employer Sponsored Retirement Plan?
Employer sponsored retirement plans are typically the single most valuable tool for business owners when attempting to:
Reduce their current tax liability
Attract and retain employees
Accumulate wealth for retirement
Employer-sponsored retirement plans are typically the single most valuable tool for business owners when attempting to:
Reduce their current tax liability
Attract and retain employees
Accumulate wealth for retirement
But with all of the different types of plans to choose from, which one is the right one for your business? Most business owners are familiar with how 401(k) plans work, but that might not be the right fit given variables such as:
# of Employees
Cash flows of the business
Goals of the business owner
There are four main stream employer-sponsored retirement plans that business owners have to choose from:
SEP IRA
Single(k) Plan
Simple IRA
401(k) Plan
Since there are a lot of differences between these four types of plans, we have included a comparison chart at the conclusion of this newsletter, but we will touch on the highlights of each type of plan.
SEP IRA PLAN
This is the only employer-sponsored retirement plan that can be set up after 12/31 for the previous tax year. So, when you are sitting with your accountant in the spring and they deliver the bad news that you are going to have a big tax liability for the previous tax year, you can establish a SEP IRA up until your tax filing deadline plus extension, fund it, and take a deduction for that year.
However, if the company has employees who meet the plan's eligibility requirement, these plans become very expensive very quickly if the owner(s) want to make contributions to their own accounts. The reason is that these plans are 100% employer-funded, which means there are no employee contributions allowed, and the employer contribution is uniform for all plan participants. For example, if the owner contributes 15% of their income to the SEP IRA, they have to make an employer contribution equal to 15% of compensation for each employee who has met the plan's eligibility requirement. If the 5305-SEP Form, which serves as the plan document, is set up correctly, a company can keep new employees out of the plan for up to 3 years, but often it is either not set up correctly or the employer cannot find the document.
Single(k) Plan or "Solo(k)"
These plans are for owner-only entities. As soon as you have an employee who works more than 1000 hours in a 12-month period, you cannot sponsor a Single(k) plan.
The plans are often the most advantageous for self-employed individuals who have no employees and want to have access to higher pre-tax contribution levels. For all intents and purposes, it is a 401(k) plan, with the same contribution limits, ERISA protected, they allow loans and Roth contributions, etc. However, they can be sponsored at a much lower cost than traditional 401(k) plans because there are no non-owner employees. So there is no year-end testing, it's typically a boilerplate plan document, and the administration costs to establish and maintain these plans are typically under $400 per year compared to traditional 401(k) plans, which may cost $1,500+ per year to administer.
The beauty of these plans is the "employee contribution" of the plan, which gives it an advantage over SEP IRA plans. With SEP IRA plans, you are limited to contributions up to 25% of your income. So if you make $24,000 in self-employment income, you are limited to a $6,000 pre-tax contribution.
With a Single(k) plan, for 2025, I can contribute $23,500 per year (another $7,500 if I'm age 50-59 or 64 or over or $11,250 if I’m age 60-63) up to 100% of my self-employment income and in addition to that amount I can make an employer contribution up to 25% of my income. In the previous example, if you make $24,000 in self-employment income, you would be able to make a salary deferral contribution of $23,500 and an employer contribution of $500, effectively wiping out all of your taxable income for that tax year.
Simple IRA
Simple IRA's are the JV version of 401(k) plans. Smaller companies that have 1 – 50 employees that are looking to start are retirement plan will often times start with implementing a Simple IRA plan and eventually graduate to a 401(k) plan as the company grows. The primary advantage of Simple IRA Plans over 401(k) Plans is the cost. Simple IRA's do not require a TPA firm since they are self-administered by the employer and they do not require annual 5500 filings so the cost to setup and maintain the plan is usually much less than a 401(k) plan.
What causes companies to choose a 401(k) plan over a Simple IRA plan?
Owners want access to higher pre-tax contribution limits
They want to limit to the plan to just full time employees
The company wants flexibility with regard to the employer contribution
The company wants a vesting schedule tied to the employer contributions
The company wants to expand investment menu beyond just a single fund family
401(k) Plans
These are probably the most well-recognized employer-sponsored plans since, at one time or another, each of us has worked for a company that has sponsored this type of plan. So we will not spend a lot of time going over the ins and outs of these types of plan. These plans offer a lot of flexibility with regard to the plan features and the plan design.
We will issue a special note about the 401(k) market. For small business with 1 -50 employees, you have a lot of options regarding which type of plan you should sponsor but it's our personal experience that most investment advisors only have a strong understanding of 401(k) plans so they push 401(k) plans as the answer for everyone because it's what they know and it's what they are comfortable talking about. When establishing a retirement plan for your company, make sure you consult with an advisor who has a working knowledge of all these different types of retirement plans and can clearly articulate the pros and cons of each type of plan. This will assist you in establishing the right type of plan for your company.
About Michael.........
Hi, I'm Michael Ruger. I'm the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
How is my Social Security Benefit Calculated?
The top two questions that we receive from individuals approaching retirement are:
What amount will I received from social security?
When should I turn on my social security benefits?
The top two questions that we receive from individuals approaching retirement are:
What amount will I received from social security?
When should I turn on my social security benefits?
Are you eligible to receive benefits?
As you work and pay taxes, you earn Social Security “credits.” In 2015, you earn one credit for each $1,220 in earnings—up to a maximum of four credits a year. The amount of money needed to earn one credit usually goes up every year. Most people need 40 credits (10 years of work) to qualify for benefits.
When will I begin receiving my social security benefit?
You are entitled to your full social security benefit at your “Normal Retirement Age” (NRA). Your NRA varies based on your date of birth. Below is the chart that social security uses to determine your “normal retirement age” or “full retirement age”:
For example, if you were born in 1965, your NRA would be 67. At 67, you would be eligible for your full retirement benefit.
Delayed Retirement or Early Retirement
You can claim benefits as early as age 62, but your monthly check will be cut by 25% for the rest of your life. The way the math works out, for each year you take your social security benefit prior to your normal retirement age, you benefit is permanently reduce by 6% for each year you take it prior to your NRA.
On the opposite end of that scenario, if you delay claiming past your NRA, you will get a delayed credit of approximately 8% per year plus cost of living adjustments.
There are a number of variables that factor into this decision as to when to turn on your benefit. Some of the main factors are:
Your health
Do you plan to keep working?
What is your current tax bracket?
The amount of retirement savings that you have
Income difference between spouses
What amount will I receive from social security?
Social security uses a fairly complex formula for calculating social security retirement benefits but the short version is the formula uses your highest 35 years of income. If you have less than 35 years are income, zeros are entered into the average for the number of years you are short of 35 years of income. They also apply an inflation adjustment to your annual earnings in the calculation.
You can obtain your Social Security statement by creating an account at www.ssa.gov. Your statement contains lots of valuable information, such as:
Your estimated benefit amount at full retirement age
Eligibility for benefits
A detailed history of how much you've earned each year
Keep in mind that the figures in your statement are just estimates, and your eventual benefit amount could be quite different, especially if you're relatively young now.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.