Special Rules for S-Corps with Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans
Missing a Required Minimum Distribution can feel overwhelming, but the rules have changed under SECURE Act 2.0. In this article, we explain how to correct a missed RMD, reduce IRS penalties, and file the right tax forms to stay compliant.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
S-Corporations can be an excellent structure for small business owners, especially from a tax perspective. But when it comes to retirement plans—such as 401(k)s and profit-sharing plans—S-Corps play by a slightly different set of rules compared to other business entities. Understanding these differences is critical for maximizing retirement savings and avoiding unpleasant surprises.
In this article, we’ll cover:
How compensation is defined for S-Corp owners in a retirement plan
Why relying too heavily on distributions can limit retirement savings
The impact of employer contributions for S-Corp owners with staff
Timing considerations for employee deferrals in S-Corps versus pass-through entities
A practical example that shows how these rules work in real life
W-2 Wages Drive Retirement Contributions for S-Corp Owners
Here’s the key difference:
Partnerships and sole proprietorships – Contributions are based on total pass-through earnings from the business.
S-Corporations – Contributions are based only on W-2 wages paid to the owner.
This matters because many S-Corp owners try to minimize their W-2 salary and take more of their income in shareholder distributions. Distributions avoid payroll taxes, which can be a big tax advantage. But retirement plans only look at W-2 wages when calculating contribution limits.
Example: High Income, Low W-2
Suppose an S-Corp owner earns $500,000 total income, but only pays themselves $100,000 in W-2 wages.
Maximum employer contribution = 25% of W-2 wages = $25,000
Add employee salary deferral = up to $23,500 (2025 limit, or $31,000 if age 50+)
Total = roughly $48,500 (or $56,000 with catch-up)
That’s far below the 2025 annual addition limit of $70,000 ($77,500 with catch-up). By keeping W-2 wages artificially low, the owner unintentionally caps their retirement contributions.
The Ripple Effect on Employees
If the owner sets their employer contribution at 25% of W-2 compensation, that percentage generally applies to eligible employees as well.
In our example, if the owner receives a 25% contribution on $100,000 ($25,000), employees may also need to receive a large employer contribution for the plan to pass testing.
For a company with multiple employees, this can become a very expensive retirement plan design.
Timing of Deferrals: Another S-Corp Quirk
Another important difference involves the timing of employee salary deferrals:
S-Corp owners are on payroll, so any employee deferrals must be processed through payroll no later than the final paycheck in December. If you wait until after year-end, it’s too late to make employee deferrals for that tax year.
Partnership or sole proprietor owners may have more flexibility, since contributions can often be made up to the tax filing deadline (with extensions) and still count toward the prior year.
Translation: If you’re an S-Corp owner, don’t wait until tax season to think about retirement contributions. Deferrals need to be in place before December 31st.
Key Takeaways for S-Corp Owners
Only W-2 wages count toward retirement contributions, not shareholder distributions.
Keeping W-2 wages too low may limit your ability to maximize contributions.
Large employer contributions for the owner can trigger equally large contributions for employees.
Employee salary deferrals must run through payroll and be completed by the last December paycheck.
Careful planning throughout the year—not just at tax time—is essential.
If you’re an S-Corp owner considering a retirement plan, make sure your payroll and compensation strategy aligns with your retirement savings goals. The right plan design can help you strike a balance between tax efficiency today and meaningful retirement wealth in the future.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do retirement plan contributions work for S-Corporation owners?
For S-Corp owners, retirement contributions are based only on W-2 wages—not total business income or shareholder distributions. This makes salary decisions especially important for maximizing 401(k) or profit-sharing plan contributions.
Why can keeping W-2 wages low hurt retirement savings for S-Corp owners?
While taking more income as shareholder distributions can reduce payroll taxes, it also limits how much you can contribute to a retirement plan. Employer contributions are capped at 25% of W-2 wages, so a lower salary means smaller allowable contributions.
How do employer contributions for owners affect employees in an S-Corp retirement plan?
If an owner contributes a high percentage of their W-2 income (such as 25%), nondiscrimination testing may require giving the same percentage to eligible employees. This can significantly increase plan costs for businesses with multiple staff members.
When must S-Corp owners make 401(k) salary deferrals?
Employee deferrals must be processed through payroll no later than the final paycheck of the year. Unlike partnerships or sole proprietors, S-Corp owners cannot make deferrals after December 31 for the prior tax year.
Can S-Corp owners include distributions when calculating 401(k) contributions?
No. Only W-2 wages qualify for retirement plan contribution calculations. Distributions from the S-Corp are not considered “earned income” for 401(k) or profit-sharing purposes.
What steps should S-Corp owners take to maximize retirement contributions?
Plan ahead by setting a reasonable W-2 salary that supports both tax efficiency and contribution goals. Coordinate payroll timing, plan design, and employee testing requirements with your tax advisor and retirement plan administrator early in the year.
How to Correct Missed Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
Missing a Required Minimum Distribution can feel overwhelming, but the rules have changed under SECURE Act 2.0. In this article, we explain how to correct a missed RMD, reduce IRS penalties, and file the right tax forms to stay compliant.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
Missing a Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) can cause a lot of stress, especially when you hear the words IRS excise tax. Fortunately, the rules around missed RMDs were updated under the SECURE Act 2.0, which provides some relief compared to the old law. In this article, we’ll break down:
What happens if you miss an RMD and how to correct it
The updated excise tax penalties under SECURE Act 2.0
The “first year” April 1st rule and why you may need to take two RMDs in one year
The new IRS guidance for beneficiaries who inherit retirement accounts
What tax forms need to be filed if you miss an RMD
A quick before-and-after look at the old rules versus SECURE Act 2.0
What Happens if You Miss an RMD?
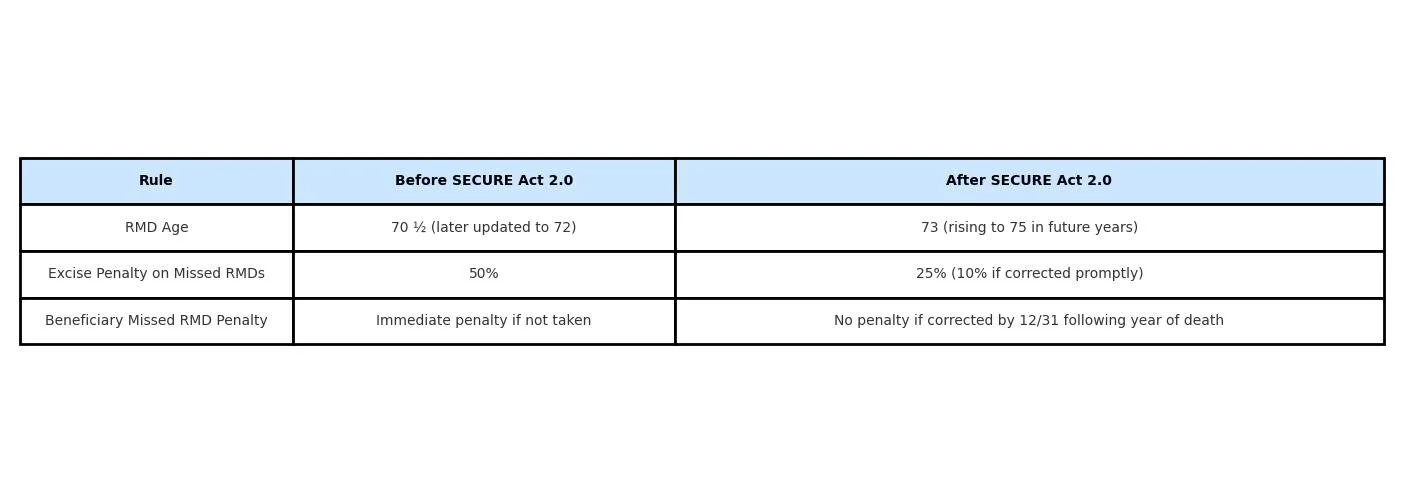
If you forget to take an RMD, the IRS assesses an excise tax penalty on the amount you should have withdrawn. Under the old law, that penalty was steep—50% of the missed RMD.
Under SECURE Act 2.0, the penalty was reduced to a much more manageable amount:
25% penalty on the missed distribution.
If corrected quickly (by taking the missed RMD and filing the proper paperwork), the penalty may be further reduced to 10%.
Example: If you missed a $10,000 RMD:
Old rule: You owed $5,000 in penalties.
New rule: You may owe only $1,000 (if corrected promptly).
The First-Year April 1st Rule
When you reach RMD age (currently age 73 under SECURE Act 2.0), your very first required distribution doesn’t have to be taken in that calendar year. Instead, you can delay it until April 1st of the following year.
But here’s the catch: if you delay your first RMD, you’ll still need to take two RMDs in that next year—the delayed one (by April 1st) plus the regular one (by December 31st).
Example:
Jane turns 73 in 2025.
She can delay her first RMD until April 1, 2026.
If she does, she must also take her 2026 RMD by December 31, 2026—meaning two taxable distributions in one year.
IRS Relief for Inherited Accounts (New Guidance)
For beneficiaries of inherited IRAs or retirement accounts, the IRS just issued new guidance under SECURE Act 2.0.
If a decedent had an RMD due in the year of their death and it wasn’t taken, the beneficiary must still withdraw it. However, the IRS has clarified that as long as the missed RMD is taken by December 31st of the year following the decedent’s death, no excise penalty will be assessed.
This is a significant update and provides more flexibility for beneficiaries who may be navigating a difficult time.
Before SECURE Act 2.0 vs. After
Filing Tax Forms for Missed RMDs
If you missed an RMD, you need to do two things:
Take the missed distribution as soon as possible.
File Form 5329 with your federal tax return to report the missed RMD and calculate the excise penalty.
If you qualify for the reduced 10% penalty, you’ll indicate this on Form 5329.
The actual RMD amount you withdraw will be reported on your Form 1099-R and included in your taxable income for the year you take it.
In some cases, the IRS has historically waived penalties if you can show “reasonable cause” for missing the RMD and that you’ve corrected the mistake. While SECURE Act 2.0 made the penalties less severe, requesting a waiver may still be an option worth considering with your tax professional.
Key Takeaways
SECURE Act 2.0 lowered the penalty for missed RMDs from 50% down to 25% (or 10% if fixed promptly).
The first-year April 1st rule gives you some flexibility but may cause two RMDs in one year.
Beneficiaries now have until December 31st of the year following the decedent’s death to take missed RMDs without penalty.
File Form 5329 to report missed RMDs and claim reduced penalties.
Missing an RMD isn’t ideal, but it’s not the end of the world—especially under the updated SECURE Act 2.0 rules. The most important step is to correct it quickly and make sure you file the proper paperwork with your tax return.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What happens if you miss a Required Minimum Distribution (RMD)?
If you miss an RMD, the IRS may assess an excise tax penalty on the amount that should have been withdrawn. Under SECURE Act 2.0, the penalty is now 25% of the missed amount, reduced to 10% if you correct the mistake promptly by taking the distribution and filing the appropriate tax form.
How did SECURE Act 2.0 change the penalties for missed RMDs?
Previously, missing an RMD triggered a 50% penalty on the shortfall. SECURE Act 2.0 lowered this to 25%, with a further reduction to 10% if the missed distribution is corrected in a timely manner. This change provides much-needed relief for retirees who make honest errors.
What is the April 1st rule for first-year RMDs?
When you first reach RMD age (currently 73), you can delay your initial withdrawal until April 1st of the following year. However, doing so means you must take two RMDs that year—the delayed one and the new year’s required amount—potentially increasing your taxable income.
What are the new IRS rules for inherited IRAs and missed RMDs?
If a deceased account owner had an RMD due in the year of death, the beneficiary must still take that distribution. Under new guidance, if the missed RMD is taken by December 31st of the year following the death, no excise penalty will apply.
What should you do if you missed an RMD?
Take the missed distribution as soon as possible and file IRS Form 5329 with your tax return to report the oversight and calculate any applicable penalty. Your financial or tax advisor can help determine if you qualify for the reduced 10% penalty or a possible waiver.
Can the IRS waive the RMD penalty entirely?
Yes. The IRS may waive the penalty if you can demonstrate reasonable cause for missing the RMD and show that you corrected the issue promptly. While SECURE Act 2.0 reduced the penalties, requesting a waiver may still be worthwhile in some cases.
What Happens When You Inherit an Already Inherited IRA?
When you are the successor beneficiary of an Inherited IRA the rules are very complex.
When someone passes away and they have a retirement account, if there are non-spouse beneficiaries listed on the account, they will typically rollover the balance in the inherited retirement account to either an Inherited Traditional IRA or Inherited Roth IRA. But what happens when the original beneficiary passes away and there is still a balance remaining in that inherited IRA account? The answer is that a successor beneficiary inherits the account, and then the distribution rules become complex very quickly.
Beneficiary of an Inherited IRA (Successor Beneficiaries)
As a beneficiary of an inherited IRA, it's important to understand that the options available to you for taking distributions for the account will be determined by the distribution options that were available to the original beneficiary of the retirement account that you inherited it from, which vary from beneficiary to beneficiary.
Non-spouse Inherited IRA Rule
The IRS changed the rules for non-spouse beneficiaries back in 2019 with the passing of the Secure Act, which put original non-spouse beneficiaries in two camps: beneficiaries that inherited a retirement account from someone that passed away prior to January 1, 2020, and beneficiaries that inherited retirement accounts some someone that passed January 1, 2020 or later.
We have a whole article dedicated to these new non-spouse beneficiary rules that can be found on our website but for now I will move forward with the cliff notes version.
Stretch Rule vs 10-Year Rule Beneficiaries
As the beneficiary of an inherited IRA, you must be able to answer two questions:
Was the original beneficiary subject to the “RMD stretch rule” or “10-year rule”?
If that beneficiary was required to take an RMD in the year they passed, did they already distribute the full amount?
Original Beneficiary was the Spouse
A common situation is that a child has two parents - the first parent passes away, and the balance in those retirement accounts are then inherited by the surviving spouse and moved into the surviving spouse’s own retirement accounts. A spouse of an original owner of a retirement account has special rules available to them which allow them to roll their deceased spouse’s retirement accounts into their own retirement accounts and treat them as their own. When their children inherited the remaining balance in the retirement accounts from the second to parent, they are considered non spouse beneficiaries and are most likely subject to the new 10-year distribution rule unless they qualify for an exception.
Non-spouse Beneficiary 10-Year Rule
If the original beneficiary of the Inherited IRA received that account from someone that passed away after December 31, 2019 and they are a non-spouse beneficiary, they are most likely subject to the new 10-Year Rule which requires the original beneficiary to fully deplete that retirement within 10 year of the year following the original decedent’s death.
Example: Sue, the original owner of a Traditional IRA passes away in 2022, and her daughter Katie is the sole beneficiary of her IRA. Since Katie is a non-spouse beneficiary, she would be required to fully deplete the IRA by 2032, 10 years following the year after that Sue passed away.
But what happens if Katie, the original beneficiary of that inherited IRA passes away in 2026, and she is only 4 years into the 10-year depletion cycle? In this example, when Katie set up her inherited IRA, she named her two children Scott & Mara as 50/50 beneficiary on her inherited IRA account. Scott and Mara would move their respective 50% balance into their own inherited IRA account but as beneficiaries of an already inherited IRA, the 10-year rule does not reset. Scott & Mara would be bound to the same 10-year depletion date that Katie was subject to so Scott & Mara would have to deplete the Inherited IRA (2 times inherited) by 2032 which was Katie’s original 10-year depletion date.
10-Year Rule: The basic rule is if the original beneficiary of the inherited IRA was subject to the 10-year rule, as the new beneficiary of that existing inherited IRA, you get whatever time is remaining in that original 10-year period to fully deplete that Inherited IRA. It does not matter whether the inherited IRA that you inherited was a Traditional IRA or a Roth IRA, the same rules apply.
Original Beneficiary was a “Stretch Rule” beneficiary or the Spouse
For original non-spouse beneficiaries that inherited the retirement account from an account owner that passed away before January 1st, 2020, they have access to what is called the Stretch Rule. Those non-spouse beneficiaries are allowed to move the original owners balance of the retirement account to their own inherited IRA and they are not required to deplete the account in 10 years.
Instead, those non-spouse beneficiaries are only required to take an annual RMD (required minimum distribution) each year, which are small distributions from the Inherited IRA each year, but they could effectively stretch the existence of that inherited account over their lifetime. But it’s also important to note, that some non-spouse beneficiaries that inherited a retirement account from someone who passes on or after January 1, 2020, may have qualified for a stretch rule exception which are as follows:
Surviving spouse
Person less than 10 years younger than the decedent
Minor children
Disabled person
Chronically ill person
Some See-Through Trusts benefitting someone on this exception list
If the original beneficiary of the inherited IRA was eligible for the stretch rule, and you inherited that inherited IRA from that individual, you would NOT be eligible for the Stretch Rule, you would be subject to the 10-year rule, but you would have a full 10-years after the owner of that inherited IRA passes away to fully deplete the balance in that inherited IRA that you inherited.
When we are talking about beneficiaries of an already inherited IRA, it does not matter whether you were their spouse or non-spouse because the spouse exceptions only apply to the spouse of the original decedent.
Example: John inherited a Traditional IRA from his father who passed away in 2018. John was a non-spouse beneficiary, but since his father passed before 2020, he was eligible for the stretch provision which allowed John to roll over the Traditional IRA to an inherited IRA in his name and he was only required to take annual RMD’s each year but was not required to deplete the account in 10 years. John passes in 2025, his daughter Sarah is the beneficiary of the Inherited IRA, since Sarah inherited the inherited IRA from John who passes after December 31, 2019, Sarah would be required to deplete the balance in John’s inherited IRA by 2035, 10-year following the year after John passes.
RMD of Beneficiaries of Inherited IRAs
Now we have to move on to the second question that beneficiaries of Inherited IRAs need to ask, which is “does the successor beneficiary of an inherited IRA need to take annual RMD’s from the account each year?” The answer is “it depends”.
It’s common for beneficiaries of Inherited IRAs to be subject to both the 10-year rule and be required to take annual required minimum distributions from the account. Whether or not the beneficiary needs to take an RMD will depend on the whether or not the original beneficiary of the account was required to take RMDs. The basic rule is if the current owner of the Inherited IRA was required to take annual RMD’s from the account, you as the beneficiary of the Inherited will be required to continue to take RMD’s from the account. The IRS has a rule that once an owner of an IRA or Inherited IRA has started taking RMDs, they cannot be stopped.
If the answer is “Yes:”, the person that you inherited the Inherited IRA from was already taking RMD’s from the Inherited IRA account, then you as the beneficiary of that inherited IRA would be subject to whatever time is left in the 10-year rule, and you would also be required to take RMDs from the account each year.
Don’t Forget To Take The Decedent’s RMD
RMD’s are usually required to begin the year after an individual passes away which is true of Inherited IRAs but as the beneficiary of an retirement account, where the decedent was required to take an RMD for that year, you have to ask the question: did they satisfy their RMD requirement before they passed away.
If the answer is “yes”, no action is required in the year that they passed away unless they were in year 10 year of the depletion cycle.
If the answer is “no”, then you as the beneficiary of that existing Inherited IRA are required to take the undistributed RMD amount from that inherited IRA in the year that the decedent passed away.
Example: Kelly inherits an Inherited IRA from her mother Linda. Linda originally inherited the IRA from her father when he passed in 2022. At the time that her father passed, he was 80, which made him subject to RMDs. When Linda inherited the account from her father, since he was subject to RMDs, Linda was subject to the 10-year rule and annual RMDs. Linda passed in 2024, her daughter Kelly inherits her Inherited IRA, and Kelly would be required to fully deplete the inherited IRA by 2032 (Linda original 10 year rule date), she would be required to take annual RMD’s from the account because Linda was receiving RMDs, and if Linda did not receive her full RMD in 2024 when she passed, Kelly would have to distribute any amount that Linda would have been required to take in the year that she passes.
A lot of rules, but all very important to avoid the IRS penalties that await the taxpayers that fail to take the proper RMD amount or fail to adhere to the new 10-year rule.
Summary of 3 Successor IRA Questions
When you are the beneficiary of an inherited IRA, you must be able to answer the following questions:
Was the person that you inherited the inherited IRA from subject to the 10-year rule?
Was the person that you inherited the Inherited IRA from required to take annual RMDs?
Did the decedent take their RMD before they passed?
What was the age of the decedent when that passed?
The last question is important because there are potential situations where someone is the original beneficiary of an Inherited IRA subject to the 10-year rule, based on the age of the original owner when they passed and the age when the original beneficiary when they inherited the IRA may not make them subject to the annual RMD requirement. However, if the original beneficiary passes away after their “Required Beginning Date” for RMDs, the beneficiary of that inherited IRA may be subject to an annual RMD requirements even though the original beneficiary was not.
The IRS has unfortunately made the rules very complex for beneficiaries of an Inherited IRA account, so I would strongly recommend consulting with a professional to make sure you fully understand the rules.
General Rules Successor IRA Rules
If you are a successor beneficiary:
If the owner on the inherited IRA was subject to the stretch rule, you as the successor beneficiary are now subject to the 10-year rule
If the owner of the Inherited IRA was subject to the 10-year rule, you have whatever time is remaining within that original 10 year window to deplete the account balance.
Whether or not you have to take an RMD in the year they pass and in future years, is more complex, seek help from a professional.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What happens when a beneficiary of an inherited IRA passes away?
When the original beneficiary of an inherited IRA dies, the account passes to a successor beneficiary. The successor inherits both the account and the distribution rules that applied to the original beneficiary, meaning the timing and requirements for withdrawals depend on how the first beneficiary inherited the IRA.
Do successor beneficiaries get a new 10-year window to deplete the inherited IRA?
No. If the original beneficiary was subject to the 10-year rule, the successor beneficiary only has the remaining time left in that original 10-year period to fully deplete the account. The clock does not reset when the account passes to a new beneficiary.
What if the original beneficiary was following the stretch rule?
If the first beneficiary inherited the IRA before 2020 and was allowed to “stretch” distributions over their lifetime, the successor beneficiary must follow the 10-year rule instead. They have a full 10 years from the year after the first beneficiary’s death to empty the account.
How do required minimum distributions (RMDs) work for successor beneficiaries?
If the person you inherited the IRA from was already taking RMDs, you must continue taking them each year and still meet the 10-year depletion rule. Once RMDs have begun on an IRA or inherited IRA, they cannot be stopped.
Do successor beneficiaries need to take the decedent’s final RMD?
Yes. If the previous account holder had not yet taken their full RMD for the year in which they passed away, the successor beneficiary is responsible for distributing that remaining amount before year-end to avoid IRS penalties.
Does it matter if the IRA was Traditional or Roth?
The same successor rules apply to both Traditional and Roth IRAs. The difference is that distributions from inherited Roth IRAs are tax-free if the account has met the five-year rule, while withdrawals from inherited Traditional IRAs are taxed as ordinary income.
What key questions should successor beneficiaries ask?
Successor beneficiaries should confirm:
Was the prior owner under the 10-year rule or stretch rule?
Were they already taking RMDs?
Did they complete their RMD for the year of death?
What was their age at death?
The Final Rules For Non-spouse Beneficiary Inherited IRAs Has Been Released: The 10-Year Rule, Annual RMD Requirement, Tax Strategies, New 401(k) Roth Rules, and More…….
In July 2024, the IRS released its long-awaited final regulations clarifying the annual RMD (required minimum distribution) rules for non-spouse beneficiaries of retirement accounts that are subject to the new 10-year rule. But like most IRS regulations, it’s anything but simple and straightforward.
In July 2024, the IRS released its long-awaited final regulations clarifying the annual RMD (required minimum distribution) rules for non-spouse beneficiaries of retirement accounts that are subject to the new 10-year rule. But like most IRS regulations, it’s anything but simple and straightforward. The short answer is for non-spouse beneficiaries that are subject to the 10-year rule; some beneficiaries will be required to begin taking annual RMDs starting in 2025 while others will not. In this article, we will review:
The RMD requirement for non-spouse beneficiaries
RMD start date
IRS penalty relief for missed RMDs
Are one-time distributions required for missed RMDs 2020 - 2024?
Different RMD rules for Traditional IRAs versus Roth IRAs
Different RMD rules for Roth 401(k) versus Roth IRAs
Common RMD mistake for stretch rule beneficiaries
In addition to covering the topics above related to the new RMD rules, we want this article to be a “one-stop shop” for non-spouse beneficiaries to understand how these non-spouse inherited IRAs work from start to finish, so we will start this article by covering:
How Inherited IRA work for non-spouse beneficiaries
Rules for a decedent that pass either before or after 2019
The new 10-year Rule
Beneficiaries that are granted an exception to the new 10-year rule
Required minimum distributions (RMDs)
Taxation of distributions from inherited IRAs
Tax strategies and Pitfalls associated with Inherited IRA accounts
Special rules for minor children with Inherited IRAs
(If you are reading this just for the new RMD rules, you can skip to the second half of the article)
Non-spouse Beneficiaries of Retirement Accounts
When you inherit a retirement account, there are different options available to you depending on whether you are a “spouse beneficiary” or a “non-spouse beneficiary”. In this article, we are going to be focusing on the options available to a non-spouse beneficiary.
Non-spouse Beneficiary Rules Prior to 2020
In 2019, the SECURE Act 1.0 was passed, which greatly limited the inherited IRA options that were available to non-spouse beneficiaries of IRAs, 401(k)’s, and other types of employer-sponsored retirement plans. Under the old rules, if someone passed away prior to January 1, 2020, you as a non-spouse beneficiary, were allowed to move the balance of that IRA into an inherited IRA in your name, avoid any immediate tax implications, and you only had to take small distributions each year called RMDs (required minimum distributions) based on IRS life expectancy table. This was called the “stretch rule” which allowed a non-spouse beneficiary to stretch the distributions over their lifetime.
If you wanted to take more out of the account, you could, since it’s an inherited IRA, even if you were under the age of 59 ½, you avoided the 10% early withdrawal penalty and either had to pay income tax on a pre-tax retirement account or avoided tax altogether on Roth inherited IRA accounts. These beneficiaries had a lot of flexibility with this option with minimal emergency tax planning needed.
For individuals in this camp who inherited a retirement account from someone who passed away prior to January 1, 2020, the good news is you are grandfathered in under the old rules, and none of the changes that we are going to cover in this article apply to you. You still have access to the stretch provision.
Non-spouse Beneficiary of Decedent That Passed After December 31, 2019
SECURE Act 1.0, which passed in 2019, took away the “stretch option” for most non-spouse beneficiaries and replaced it with a much more restrictive “10-Year Rule,” which requires a non-spouse beneficiary to fully deplete the account balance of that inherited retirement account within 10 years start the year after the decedent passed away. If you inherited a retirement account from someone who passed away AFTER December 31, 2019, and you are non-spouse beneficiaries, you are subject to the new 10-Year Rule UNLESS you meet one of the exceptions. Non-spouse beneficiaries that qualify for an exception to the 10-year rule are referred to as “Eligible Designated Beneficiaries” in the new tax regulations if you choose to read the 260 pages that were just released by the IRS.
Here is the list of beneficiaries that are exempt from the new 10-year rule and still have the stretch option available to them:
Surviving spouse
Person less than 10 years younger than the decedent
Minor children
Disabled person
Chronically ill person
Some See-Through Trusts benefitting someone on this exception list
Non-Spouse Beneficiary Not More Than 10 Years Younger Than The Decedent
I wanted to highlight this exception because it’s the most common exception to the 10-rule for non-spouse beneficiaries that we see amongst our clients. If you are a non-spouse beneficiary of a retirement account from someone that was not more than 10 years younger than you like a sibling or a cousin, the new 10-year distribution rule does not apply to you. You are allowed to roll over the balance to your own inherited IRA and stretch annual RMDs over your lifetime.
Example: Tim passes away at the age of 55 and his sister Susan age 58 is the 100% primary beneficiary of his Traditional IRA account, since Susan is a non-spouse beneficiary, she normally would be subject to the 10-year rule requiring her to fully distribute and pay tax on Tim’s IRA balance within a 10 year period. However, since Tim was less than 10 years younger than Susan, she qualifies for the exception to the 10-year rule. She can rollover Tim’s IRA balance into an Inherited IRA in her name, and she would only be required to take small required minimum distributions each year starting the year after Tim passed away.
Minor Children As Beneficiary of Retirement Accounts
The minor child exception is a little tricker. If a minor child is the beneficiary of a retirement account, and they inherited the retirement account from their parents, they are only required to take those small annual RMDs until they reach age 21, but then as soon as they turn 21, they switch over to the 10-Year Rule. If they inherited the retirement account from someone other than their parent, then the 10-year period begins the year after the decedent passes away like the rest of the non-spouse beneficiaries.
Example: Josh is age 12 and his mother unexpectedly passes away and Josh is listed as the primary beneficiary on his mother’s 401(K) account at work. Josh, as a non-spouse beneficiary, would not immediately be subject to the 10-year rule, but instead, he would be temporarily allowed to use the stretch provision; he would be required to take annual RMDs each year from the retirement account until he reaches age 21. Once Josh reaches age 21, he will then be subject to the 10-year rule, and he will be required to fully distribute the retirement account 10 years following when he turns age 21.
Age of Majority: Normally the “age of majority” is defined by the state that the minor lives in. For some states, it’s age 18, and in other states, it’s age 21. The new IRS regulations addressed this issue and stated that regardless of the age of majority for the state that the minor lives in and regardless of whether or not the child is a student past the age of 18, the age of majority for purposes of triggering the 10-year rule for non-spouse beneficiaries will be age 21.
Non-Spouse Beneficiary Subject To The 10-Year Rule
If you are a non-spouse beneficiary who inherited a retirement account from someone who passed away AFTER December 31, 2019, and you DO NOT qualify for one of the exceptions previously listed, then you are subject to the new “10-Year Rule”. The 10-Year Rule requires a non-spouse beneficiary to fully deplete the inherited retirement account balance no later than 10 years following the year after the decedent passes away.
The 10-Year Rule Applies to Both Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Accounts
Regardless of whether you inherited a pre-tax retirement account like a Traditional IRA, SEP IRA, or 401(k) account or a Roth retirement account like a Roth IRA or Roth 401(k), the 10-year rule applies.
Example: Sarah’s father just passed away in February 2024, and she was the 100% primary beneficiary of his Traditional IRA account with a balance of $300,000. Sarah is age 60. Sarah, as a non-spouse beneficiary, would be subject to the 10-year rule and would be required to fully distribute and pay tax on the full $300,000 before December 31, 2034, which is 10 years following the year after her father passed away.
The RMD Mystery
When the 10-Year Rule first came into being in 2020, it was assumed that this 10-year rule was an extension of the previous “5-year rule”, which only required the beneficiary to deplete the account balance within 5 years but there was no annual RMDs requirement during that 5-year period. The IRS just simply eliminated the “stretch option” and extended the 5-year rule to a 10-year rule.
But then, two after the IRS passed SECURE Act 1.0 with this new 10-year rule, the IRS came out with new proposed regulations that basically said, “Whoops, I know we wrote it that way, but that’s not what we meant.”
In the proposed regulations that the IRS released in February 2022, the IRS clarified that what they meant to say was that certain non-spouse beneficiaries that are subject to the new 10-year rule would ALSO be required to take annual RMDs during that 10-year period. This was not welcome news for many non-spouse beneficiaries, and it created a lot of confusion since a few years had already gone by since the new 10-year rule was signed into law.
The New RMD Rules for Inherited IRA for Non-spouse Beneficiaries
The finalized IRS regulations that were just released in July 2024 made their stance official. Whether or not a non-spouse beneficiary will be subject to BOTH the 10-Year Rule and annual RMDs will be dependent on two factors:
The age of the decedent when they passed away
The type of retirement account that the beneficiary inherited (Pre-tax or Roth)
RMD Requirement Based on Age of Decedent
If you are the original owner of a retirement account (Traditional IRA, 401(k), etc.), once you reach a specific age, the IRS requires you to start taking small distributions from that pre-tax account each year, which are called required minimum distributions (RMDs).
The age at which you are required to begin taking RMDs is called your Required Beginning Date (“RBD”), not to be confused with the “RMD”. There are too many acronyms in the finance world “The IRS wants you to take your RMD by your RBD ASAP so they can collect their TAX.”
The date at which RMDs are required to begin varies based on your date of birth:
Born 1950 or earlier: Age 72
Born 1951 – 1959: Age 73
Born 1960 or later: Age 75
Someone that is born in 1956 would be required to start taking RMDs from their pre-tax retirement accounts at age 73. Why is this relevant to non-spouse beneficiaries? Because whether or not the decedent died before or after their Required Beginning Date for RMDs will determine whether or not you, as the non-spouse beneficiary, are required to take annual RMDs during the 10-Year Rule period.
The Decedent Passes Away Prior to Their RMD Required Beginning Date
If the decedent passed away prior to their Required Beginning Date, then you, as the non-spouse beneficiary, are subject to the 10-Year Rule, but you ARE NOT REQUIRED to take annual RMDs during the 10-year period. You simply have to deplete the account balance prior to the end of the 10 years.
Example: Brad’s father passes away at age 68 and Brad is the 100% beneficiary of his Traditional IRA. Brad’s father was born in 1956, making his RMD start at age 73. Since Brad’s father passed away prior to reaching age 73 (RBD), Brad would be subject to the 10-year rule but would not be required to take annual RMDs during that 10-year period.
The Decedent Passes Away After Their RMD Required Beginning Date
If the decedent passes away AFTER their Required Beginning Date for RMDs, then the non-spouse beneficiary is subject to BOTH the 10-year rule AND is required to take annual RMDs during that 10-year period.
Example: Dave’s father passed away at age 80, and he had been taking RMDs for many years since he was beyond his Required Beginning Date. When Dave inherits his father’s Traditional IRA, he will not only be subject to the 10-year rule as a non-spouse beneficiary, but he will also be required to distribute annual RMDs every year from the Inherited IRA account since his father had already begun receiving RMDs for his account.
RMDs Not Required Until 2025
Since the IRS just released the final regulation in July 2024, for non-spouse beneficiaries that are subject to both the 10-Year Rule and annual RMDs, RMDs are not required to begin until 2025.
Good news: For non-spouse beneficiaries subject to the 10-year rule, the IRS has waived all penalties for the “missed RMDs” between 2020 and 2024, and they are not requiring these non-spouse beneficiaries to “make up” for missed RMDs for years leading up to 2025. The RMDs will be calculated in 2025 like everything has been working smoothly since Day 1.
No Reset of the 10-Year Depletion Timeline
It’s important to note that even though the IRS took 4 years to clarify the RMD rules associated with the new 10-year rule, it does not reset the 10-year clock for the depletion of the inherited retirement account.
Example: Jessica’s uncle passed away in 2020 at the age of 82. Jessica, as a non-spouse beneficiary, would be subject to the 10-year rule requiring her to fully deplete the Traditional IRA by December 31, 2030. Since her uncle was past his Required Beginning Date for RMDs, Jessica would be required to take annual RMD in the years 2025 – 2030. (Note that the 2021 – 2024 RMDs were waived due to the IRS delay). Even though her first RMD will not be until 2025, she is still required to deplete the Traditional IRA account by December 31, 2030.
Annual RMD Rules
Many of these examples incorporate the delay in annual RMDs due to the delay in the IRS regulations being released. However, if someone passes away in 2024 and has a non-spouse beneficiary listed on their pre-tax retirement account, the 10-year timeline and the first annual RMD calendar would begin in 2025, which is the year following the decedent’s date of death.
The first RMD is required to be taken by a non-spouse beneficiary by December 31st of the year following the decedent's death.
Inherited Roth IRAs – No RMD Requirement
You will notice in most of my examples that I specifically use a “Traditional IRA” or “Pre-tax Retirement Account.” That is because only pre-tax retirement accounts have the RMD requirement. If you are the original owner of a Roth IRA, Roth IRAs do not require you to take an RMD regardless of your age. So, under the new rules, if you inherit a Roth IRA, since the decedent would not have been required to take an RMD from a Roth IRA at any age, they never had a “Required Beginning Date”. This makes the non-spouse beneficiary subject to the 10-year rule, but no annual RMDs would be required from an inherited Roth IRA.
Note: If you inherit a Roth IRA and you are eligible for the stretch options, annual RMDs are then required from you Inherited Roth IRA account.
Roth 401(k)s Are Different
While typically, Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s have the same rules, the IRS included a weird rule for Roth 401(k)s in the final regulations regarding the RMD requirement. If you inherit a 401(k) plan, it’s possible that there are both Pre-tax and Roth monies within that same account since most 401(k) plans allow plan participants to make either pre-tax deferrals or Roth deferrals to the plan.
Normally I would have thought if a 401(k) account contains both Pre-tax and Roth dollars, as a non-spouse beneficiary, you would have the 10-year rule for the full account balance, but you could ignore the RMD requirement for the Roth dollars, but the annual RMDs on the pre-tax portion of the account would depend on whether or not the decedent passed away before or after their Required Beginning Date for RMDs. Assuming this, I would have been correct for the pre-tax portion of the 401(k) account but potentially wrong about no annual RMDs for the Roth portion of the 401(k) account.
The final regulations state that if the 401(k) account contains ONLY Roth dollars, no pre-tax dollars within the account, then a non-spouse beneficiary is subject to the 10-year rule but DOES NOT have to take annual RMDs during that 10-year period.
However, if the 401(k) account contains both Roth and any other type of pre-tax source, like employee pre-tax deferrals, employer match, and employer profit sharing, which is much more common for 401(k) plans, then the ENTIRE BALANCE in the 401(k) plan, INCLUDING THE ROTH SOURCE, is subject to the annual RMD requirement during the 10-year period. Yuck!!!
This new rule will encourage individuals who have a Roth source within their employer-sponsored retirement plans to roll over their Roth monies within the plan to a Roth IRA before they pass away. By removing that Roth source from the employer-sponsored retirement plans and moving it into a Roth IRA, now when the non-spouse beneficiary inherits the Roth IRA, they are allowed to accumulate those Roth dollars longer within the 10-year period since they are not required to take annual RMDs from a Roth IRA account.
Note: The pre-tax sources within a 401(k) works the same way as inheriting a Traditional IRA. A non-spouse beneficiary would be subject to the 10-year rule and may or may not have to take RMDs during the 10-year period depending on whether or not the decedent dies before or after their Required Beginning Date for RMDs.
Non-Spouse Beneficiaries Eligible For The Stretch Rule Only Had An RMD Waiver for 2020
In 2020, part of the COVID relief packages was the ability to waive taking an RMD during that calendar year. I have run into a few cases where non-spouse beneficiaries that were grandfathered in under the “stretch rules” requiring them to take an annual RMD each year, are getting confused with the delay in the RMD requirement for non-spouse beneficiaries that are subject to the new 10-year rule after December 2019. The delay in the annual RMDs until 2025 for non-spouse beneficiaries ONLY applies to individuals subject to the 10-year rule. If you inherited a retirement account from someone who passed away prior to 2020 or you qualify for one of the exceptions to the 10-Year Rule as a non-spouse beneficiary, you are grandfathered in under the old “Stretch Rule,” which requires the owner of that Inherited IRA to take annual RMD’s from that account each year starting in the calendar year following the decedent’s date of death.
In summary, if you are a stretch rule non-spouse beneficiary, the only year you were allowed to skip your RMD was 2020 per the COVID relief; you should have restarted your annual RMDs in 2021 and taken an RMD for 2021, 2022, and 2023, and subsequent years. If you missed this, the good news is the Secure Act 2.0 also lowered the IRS penalty amount for missed RMDs, from 50% to 25% and even lower to 10% if timely corrected.
Non-Spouse Inherited IRA Tax Strategies
We will be writing a separate article that contains all of the advanced tax strategies that we implement for clients who are non-spouse beneficiaries subject to the 10-year rule since there are a number of them, but here is some of the standard guidance that we provide to our clients.
If you inherit a Roth IRA, that is an ideal situation because even though you are subject to the 10-year rule as a non-spouse beneficiary, all of the accumulation in an Inherited Roth IRA can be withdrawn tax-free.
Example: John inherits a $200,000 Roth IRA from his mother in 2024. John, as a non-spouse beneficiary, will be subject to the 10-year rule, so the account has to be depleted by 2034, but he is not required to take annual RMDs because it’s a Roth IRA account. If John invests the $200,000 wisely and receives an 8% annual rate of return, at the end of 10-year the $200,000 has grown to $431,785 within that Inherited Roth IRA, and the full balance will be distributed to him ALL TAX-FREE.
For this reason, we have a lot more clients processing Roth Conversions in retirement to push more of their net worth from the pre-tax bucket over to the Roth bucket, which is much more favorable for non-spouse beneficiaries when they inherit the account.
For clients that inherit larger pre-tax retirement accounts that are subject to the 10-year rule, we have to develop a detailed tax plan for the next 10 years since we know all of that money will need to be distributed and taxed within the next 10 years, which could cause the money to be taxed at a higher tax rate, increased Medicare premiums, lower financial aid awards for parents with kids in college, have their social security taxed at a higher rate, lose tax deductions, or other negative consequences for showing too much income in a single year.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What did the IRS clarify about non-spouse beneficiary RMDs in 2024?
In July 2024, the IRS issued final regulations confirming that some non-spouse beneficiaries subject to the 10-year rule must begin taking annual required minimum distributions (RMDs) starting in 2025. Whether annual RMDs are required depends on the decedent’s age at death and the type of retirement account inherited.
Who must take annual RMDs under the 10-year rule?
If the decedent passed away after reaching their Required Beginning Date (the age at which RMDs must begin), the non-spouse beneficiary must take annual RMDs during the 10-year depletion period. If the decedent passed before reaching that age, the beneficiary is only required to deplete the account by the end of the 10 years—no annual RMDs are needed.
What are the new RMD start dates for non-spouse beneficiaries?
The IRS delayed required RMDs for non-spouse beneficiaries until 2025. Any missed RMDs for the years 2020–2024 are waived, and beneficiaries are not required to make catch-up distributions for those years.
Does the 10-year rule clock reset under the new regulations?
No. Even though the IRS delayed annual RMDs until 2025, the 10-year period to deplete the inherited account still begins the year after the decedent’s death. Beneficiaries must empty the account by the original deadline.
Do Roth IRAs have RMD requirements for non-spouse beneficiaries?
No. Inherited Roth IRAs are subject to the 10-year rule, but they do not require annual RMDs since Roth owners are never required to take RMDs during their lifetimes. Beneficiaries can let the Roth IRA grow tax-free for the full 10 years before withdrawing the balance.
Are Roth 401(k)s treated differently?
Yes. If a Roth 401(k) contains only Roth dollars, no annual RMDs are required during the 10-year period. However, if the account also contains any pre-tax sources—such as employer matches—the entire balance, including the Roth portion, becomes subject to annual RMDs. Rolling Roth 401(k) funds into a Roth IRA before death can avoid this issue.
What happens to non-spouse beneficiaries who still qualify for the stretch rule?
Those grandfathered under the old stretch rule must continue taking annual RMDs each year. Only 2020 distributions were waived under COVID relief. Any missed RMDs after 2020 may trigger penalties unless corrected under the new reduced penalty rules.
What are key tax considerations for non-spouse beneficiaries?
Inherited Roth IRAs are generally ideal since withdrawals are tax-free. Beneficiaries of large pre-tax accounts should work with a tax professional to spread distributions over several years, minimizing the impact on income taxes, Medicare premiums, and financial aid eligibility.
Secure Act 2.0: RMD Start Age Pushed Back to 73 Starting in 2023
On December 23, 2022, Congress passed the Secure Act 2.0, which moved the required minimum distribution (RMD) age from the current age of 72 out to age 73 starting in 2023. They also went one step further and included in the new law bill an automatic increase in the RMD beginning in 2033, extending the RMD start age to 75.
On December 23, 2022, Congress passed the Secure Act 2.0, which moved the required minimum distribution (RMD) age from the current age of 72 out to age 73 starting in 2023. They also went one step further and included in the new law bill an automatic increase in the RMD beginning in 2033, extending the RMD start age to 75.
This is the second time within the past 3 years that Congress has changed the start date for required minimum distributions from IRAs and employer-sponsored retirement plans. Here is the history and the future timeline of the RMD start dates:
1986 – 2019: Age 70½
2020 – 2022: Age 72
2023 – 2032: Age 73
2033+: Age 75
You can also determine your RMD start age based on your birth year:
1950 or Earlier: RMD starts at age 72
1951 – 1959: RMD starts at age 73
1960 or later: RMD starts at age 75
What Is An RMD?
An RMD is a required minimum distribution. Once you hit a certain age, the IRS requires you to start taking a distribution each year from your various retirement accounts (IRA, 401(K), 403(b), Simple IRA, etc.) because they want you to begin paying tax on a portion of your tax-deferred assets whether you need them or not.
What If You Turned Age 72 In 2022?
If you turned age 72 anytime in 2022, the new Secure Act 2.0 does not change the fact that you would have been required to take an RMD for 2022. This is true even if you decided to delay your first RMD until April 1, 2023, for the 2022 tax year.
If you are turning 72 in 2023, under the old rules, you would have been required to take an RMD for 2023; under the new rules, you will not have to take your first RMD until 2024, when you turn age 73.
Planning Opportunities
By pushing the RMD start date from age 72 out to 73, and eventually to 75 in 2033, it creates more tax planning opportunities for individuals that do need to take distributions out of their IRAs to supplement this income. Since these distributions from your retirement account represent taxable income, by delaying that mandatory income could allow individuals the opportunity to process larger Roth conversions during the retirement years, which can be an excellent tax and wealth-building strategy.
Delaying your RMD can also provide you with the following benefits:
Reduce the amount of your Medicare premiums
Reduce the percentage of your social security benefit that is taxed
Make you eligible for tax credits or deductions that you would have phased out of
Potentially allow you to realize a 0% tax rate on long-term capital gains
Continue to keep your pre-tax retirement dollars invested and growing
Additional Secure Act 2.0 Articles
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is the new RMD age under the Secure Act 2.0?
Starting in 2023, the required minimum distribution (RMD) age increased from 72 to 73. Beginning in 2033, the RMD age will rise again to 75.
How does the new RMD timeline compare to previous rules?
Before 2020, RMDs began at age 70½. The Secure Act of 2019 moved it to age 72, and Secure Act 2.0 now increases it to age 73 in 2023 and age 75 starting in 2033.
How do you determine your RMD start age based on birth year?
If you were born in 1950 or earlier, your RMD started at 72. Those born between 1951 and 1959 begin at 73, and anyone born in 1960 or later will start at 75.
What if I turned 72 in 2022?
If you reached age 72 in 2022, you are still required to take your first RMD for that tax year, even if you delayed it until April 1, 2023. The new rule applies only to individuals turning 72 in 2023 or later.
What are the benefits of delaying RMDs?
Delaying RMDs can create valuable tax planning opportunities, including the ability to complete larger Roth conversions, reduce taxable income, lower Medicare premiums, and minimize taxes on Social Security benefits.
Can delaying RMDs impact long-term investment growth?
Yes. By postponing mandatory withdrawals, your tax-deferred savings can remain invested and continue to grow, potentially increasing your retirement assets over time.
IRA RMD Start Date Changed From Age 70 ½ to Age 72 Starting In 2020
The SECURE Act was passed into law on December 19, 2019 and with it came some big changes to the required minimum distribution (“RMD”) requirements from IRA’s and retirement plans. Prior to December 31, 2019, individuals
The SECURE Act was passed into law on December 19, 2019 and with it came some big changes to the required minimum distribution (“RMD”) requirements from IRA’s and retirement plans. Prior to December 31, 2019, individuals were required to begin taking mandatory distributions from their IRA’s, 401(k), 403(b), and other pre-tax retirement accounts starting in the year that they turned age 70 ½. The SECURE Act delayed the start date of the RMD’s to age 72. But like most new laws, it’s not just a simple and straightforward change. In this article we will review:
Old Rules vs New Rules surrounding RMD’s
New rules surrounding Qualified Charitable Distributions from IRA’s
Who is still subject to the 70 ½ RMD requirement?
The April 1st delay rule
Required Minimum Distributions
A quick background on required minimum distributions, also referred to as RMD’s. Prior to the SECURE Act, when you turned age 70 ½ the IRS required you to take small distributions from your pre-tax IRA’s and retirement accounts each year. For individuals that did not need the money, they did not have a choice. They were forced to withdraw the money out of their retirement accounts and pay tax on the distributions. Under the current life expectancy tables, in the year that you turned age 70 ½ you were required to take a distribution equaling 3.6% of the account balance as of the previous year end.
With the passing of the SECURE Act, the start age from these RMD’s is now delayed until the calendar year that an individual turns age 72.
OLD RULE: Age 70 ½ RMD Begin Date
NEW RULE: Age 72 RMD Begin Date
Still Subject To The Old 70 ½ Rule
If you turned age 70 ½ prior to December 31, 2019, you will still be required to take RMD’s from your retirement accounts under the old 70 ½ RMD rule. You are not able to delay the RMD’s until age 72.
Example: Sarah was born May 15, 1949. She turned 70 on May 15, 2019 making her age 70 ½ on November 15, 2019. Even though she technically could have delayed her first RMD to April 1, 2020, she will not be able to avoid taking the RMD’s for 2019 and 2020 even though she will be under that age of 72 during those tax years.
Here is a quick date of birth reference to determine if you will be subject to the old 70 ½ start date or the new age 72 start date:
Date of Birth Prior to July 1, 1949: Subject to Age 70 ½ start date for RMD
Date of Birth On or After July 1, 1949: Subject to Age 72 start date for RMD
April 1 Exception Retained
OLD RULE: In the the year that an individual turned age 70 ½, they had the option to delay their first RMD until April 1st of the following year. This is a tax strategy that individuals engaged in to push that additional taxable income associated with the RMD into the next tax year. However, in year 2, the individual was then required to take two RMD’s in that calendar year: One prior to April 1st for the previous tax year and the second prior to December 31st for the current tax year.
NEW RULE: Unchanged. The April 1st exception for the first RMD year was retained by the SECURE Act as well as the requirement that if the RMD was voluntarily delayed until the following year that two RMD’s would need be taken in the second year.
Qualified Charitable Distributions (QCD)
OLD RULES: Individuals that had reached the RMD age of 70 ½ had the option to distribute all or a portion of their RMD directly to a charitable organization to avoid having to pay tax on the distribution. This option was reserved only for individuals that had reached age 70 ½. In conjunction with tax reform that took place a few years ago, this has become a very popular option for individuals that make charitable contributions because most individual taxpayers are no longer able to deduct their charitable contributions under the new tax laws.
NEW RULES: With the delay of the RMD start date to age 72, do individuals now have to wait until age 72 to be eligible to make qualified charitable distributions? The answer is thankfully no. Even though the RMD start date is delayed until age 72, individuals will still be able to make tax free charitable distributions from their IRA’s in the calendar year that they turn age 70 ½. The limit on QCDs is still $100,000 for each calendar year.
NOTE: If you plan to process a qualified charitable distributions from your IRA after age 70 ½, you have to be well aware of the procedures for completing those special distributions otherwise it could cause those distributions to be taxable to the owner of the IRA. See the article below for more on this topic:
ANOTHER NEW RULE: There is a second new rule associated with the SECURE Act that will impact this Qualified Charitable Distribution strategy. Under the old tax law, individuals were unable to contribute to Traditional IRA’s past the age of 70 ½. The SECURE Act eliminated that rule so individuals that have earned income past age 70 ½ will be eligible to make contributions to Traditional IRAs and take a tax deduction for those contributions.
As an anti-abuse provision, any contributions made to a Traditional IRA past the age of 70 ½ will, in aggregate, dollar for dollar, reduce the amount of your qualified charitable distribution that is tax free.
Example: A 75 year old retiree was working part-time making $20,000 per year for the past 3 years. To reduce her tax bill, she contributed $7,000 per year to a traditional IRA which is allowed under the new tax laws. This year she is required to take a $30,000 required minimum distribution (RMD) from her retirement accounts and she wants to direct that all to charity to avoid having to pay tax on the $30,000. Because she contributed $21,000 to a traditional IRA past the age of 70 ½, $21,000 of the qualified charitable distribution would be taxable income to her, while the remaining $9,000 would be a tax free distribution to the charity.
$30,000 QCD – $21,000 IRA Contribution After Age 70 ½ = $9,000 tax free QCD
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
New Rules For Non Spouse Beneficiaries Of Retirement Accounts Starting In 2020
The SECURE Act was signed into law on December 19, 2019 and with it comes some very important changes to the options that are available to non-spouse beneficiaries of IRA’s, 401(k), 403(b), and other types of retirement accounts
The SECURE Act was signed into law on December 19, 2019 and with it comes some very important changes to the options that are available to non-spouse beneficiaries of IRA’s, 401(k), 403(b), and other types of retirement accounts starting in 2020. Unfortunately, with the passing of this law, Congress took away one of the most valuable distribution options available to non-spouse beneficiaries called the “stretch” provision. Non-spouse beneficiaries would utilize this distribution option to avoid the tax hit associated with having to take big distributions from pre-tax retirement accounts in a single tax year. This article will cover:
The old inherited IRA rules vs. the new inherited IRA rules
The new “10 Year Rule”
Who is grandfathered in under the old inherited IRA rules?
Impact of the new rules on minor children beneficiaries
Tax traps awaiting non spouse beneficiaries of retirement accounts
The “Stretch” Option Is Gone
The SECURE Act’s elimination of the stretch provision will have a big impact on non-spouse beneficiaries. Prior to January 1, 2020, non-spouse beneficiaries who inherited retirement accounts had the option to either:
Take a full distribution of the retirement account within 5 years
Rollover the balance to an inherited IRA and stretch the distributions from the retirement account over their lifetime. Also known as the “stretch option”.
Since any money distributed from a pre-tax retirement account is taxable income to the beneficiary, many non-spouse beneficiaries would choose the stretch option to avoid the big tax hit associated with taking larger distributions from a retirement account in a single year. Under the old rules, if you did not move the money to an inherited IRA by December 31st of the year following the decedent’s death, you were forced to take out the full account balance within a 5 year period.
On the flip side, the stretch option allowed these beneficiaries to move the retirement account balance from the decedent’s retirement account into their own inherited IRA tax and penalty free. The non-spouse beneficiary was then only required to take small distributions each year from the account called a RMD (“required minimum distribution”) but was allowed to keep the retirement account intact and continuing to accumulate tax deferred over their lifetime. A huge benefit!
The New 10 Year Rule
For non-spouse beneficiaries, the stretch option was replaced with the “10 Year Rule” which states that the balance in the inherited retirement account needs to be fully distributed by the end of the 10th year following the decedent’s date of death. The loss of the stretch option will be problematic for non-spouse beneficiaries that inherit sizable retirement accounts because they will be forced to take larger distributions exposing those pre-tax distributions to higher tax rates.
RMD Requirement Depends on the Age of the Decedent
Whether or not the beneficiary of the inherited retirement account will need to take an RMD during the 10 year period, depends on the decedent age when that passed away. If the decedent was taking RMDs at the time they passed away, the beneficiary must continue to take annual RMD during the 10 year period. If the decedent died prior to the RMD start age, the beneficiary not required to take RMDs during the 10 year period.
Tax Traps For Non-Spouse Beneficiaries
These new inherited IRA distribution rules are going to require proactive tax and financial planning for the beneficiaries of these retirement accounts. I’m lumping financial planning into that mix because taking distributions from pre-tax retirement accounts increases your taxable income which could cause the following things to happen:
Reduce the amount of college financial aid that your child is receiving
Increase the amount of your social security that is considered taxable income
Loss of property tax credits such as the Enhanced STAR Program
Increase your Medicare Part B and Part D premiums the following year
You may phase out of certain tax credits or deductions that you were previously receiving
Eliminate your ability to contribute to a Roth IRA
Loss of Medicaid or Special Needs benefits
Ordinary income and capital gains taxed at a higher rate
You really have to plan out the next 10 years and determine from a tax and financial planning standpoint what is the most advantageous way to distribute the full balance of the inherited IRA to minimize the tax hit and avoid triggering an unexpected financial consequence associated with having additional income during that 10 year period.
Who Is Grandfathered In?
If you are the non-spouse beneficiary of a retirement account and the decedent passed away prior to January 1, 2020, you are grandfathered in under the old inherited IRA rules. Meaning you are still able to utilize the stretch provision. Here are a few examples:
Example 1: If you had a parent pass away in 2018 and in 2019 you rolled over their IRA into your own inherited IRA, you are not subject to the new 10 year rule. You are allowed to stretch the IRA distributions over your lifetime in the form of those RMD’s.
Example 2: On December 15, 2019, your father passed away and you are listed as the beneficiary on his 401(k) account. Since he passed away prior to January 1, 2020, you would still have the option of setting up an Inherited IRA prior to December 31, 2020 and then stretching the distributions over your lifetime.
Example 3: On February 3, 2020, your uncle passes away and you are listed as a beneficiary on his Rollover IRA. Since he passed away after January 1, 2020, you would be required to distribute the full IRA balance prior to December 31, 2030.
You are also grandfathered in under the old rules if:
The beneficiary is the spouse
Disabled beneficiaries
Chronically Ill beneficiaries
Individuals who are NOT more than 10 years younger than the decedent
Certain minor children (see below)
Even beyond 2020, the beneficiaries listed above will still have the option to rollover the balance into their own inherited IRA and then stretch the required minimum distributions over their lifetime.
Minor Children As Beneficiaries
The rules are slightly different if the beneficiary is the child of the decedent AND they are still a minor. I purposely capitalized the word “and”. Within the new law is a “Special Rule for Minor Children” section that states if the beneficiary is a child of the decedent but has not reached the age of majority, then the child will be able to take age-based RMD’s from the inherited IRA but only until they reach the age of majority. Once they are no longer a minor, they are required to distribute the remainder of the retirement account balance within 10 years.
Example: A mother and father pass away in a car accident and the beneficiaries listed on their retirement accounts are their two children, Jacob age 10, and Sarah age 8. Jacob and Sarah would be able to move the balances from their parent’s retirements accounts into an inherited IRA and then just take small required minimum distributions from the account based on their life expectancy until they reach age 18. In their state of New York, age 18 is the age of majority. The entire inherited IRA would then need to be fully distributed to them before the end of the calendar year of their 28th birthday.
This exception only applies if they are a child of the decedent. If a minor child inherits a retirement account from a non-parent, such as a grandparent, then they are immediately subject to the 10 year rule.
Note: the age of majority varies by state.
Advanced Planning
Under the old inherited IRA rules there was less urgency for immediate tax planning because the non-spouse beneficiaries just had to move the money into an inherited IRA the year after the decedent passed away and in most cases the RMD's were relatively small resulting in a minimal tax impact. For non-spouse beneficiaries that inherit a retirement account after January 1, 2020, it will be so important to have a tax plan and financial plan in place as soon as possible otherwise you could lose a lot of your inheritance to higher taxes or other negative consequences associated with having more income during those distribution years.
Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions on the new inherited IRA rules. We would also be more than happy to share with you some of the advanced tax strategies that we will be using with our clients to help them to minimize the tax impact of the new 10 year rule.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Spouse Inherited IRA Options
If your spouse passes away and they had either an IRA, 401(k), 403(b), or some other type of employer sponsored retirement account, you will have to determine which distribution option is the right one for you. There are deadlines that you will need to be aware of, different tax implications based on the option that you choose, forms that need to be
If your spouse passes away and they had either an IRA, 401(k), 403(b), or some other type of employer sponsored retirement account, you will have to determine which distribution option is the right one for you. There are deadlines that you will need to be aware of, different tax implications based on the option that you choose, forms that need to be completed, and accounts that may need to be established.
Spouse Distribution Options
As the spouse, if you are listed as primary beneficiary on a retirement account or IRA, you have more options available to you than a non-spouse beneficiary. Non-spouse beneficiaries that inherited retirement accounts after December 31, 2019 are required to fully distribution the account 10 years following the year that the decedent passed away. But as the spouse of the decedent, you have the following options:
Fulling distribute the retirement account with 10 years
Rollover the balance to an inherited IRA
Rollover the balance to your own IRA
To determine which option is the right choice, you will need to take the following factors into consideration:
Your age
The age of your spouse
Will you need to take money from the IRA to supplement your income?
Taxes
Cash Distributions
We will start with the most basic option which is to take a cash distribution directly from your spouse’s retirement account. Be very careful with this option. When you take a cash distribution from a pre-tax retirement account, you will have to pay income tax on the amount that is distributed to you. For example, if your spouse had $50,000 in a 401(k), and you decide to take the full amount out in the form of a lump sum distribution, the full $50,000 will be counted as taxable income to you in the year that the distribution takes place. It’s like receiving a paycheck from your employer for $50,000 with no taxes taken out. When you go to file your taxes the following year, a big tax bill will probably be waiting for you.
In most cases, if you need some or all of the cash from a 401(k) account or an IRA, it usually makes more sense to first rollover the entire balance into an inherited IRA, and then take the cash that you need from there. This strategy gives you more control over the timing of the distributions which may help you to save some money in taxes. If as the spouse, you need the $50,000, but you really need $30,000 now and $20,000 in 6 months, you can rollover the full $50,000 balance to the inherited IRA, take $30,000 from the IRA this year, and take the additional $20,000 on January 2nd the following year so it spreads the tax liability between two tax years.
10% Early Withdrawal Penalty
Typically, if you are under the age of 59½, and you take a distribution from a retirement account, you incur not only taxes but also a 10% early withdrawal penalty on the amount this is distributed from the account. This is not the case when you take a cash distribution, as a beneficiary, directly from the decedents retirement account. You have to report the distribution as taxable income but you do not incur the 10% early withdrawal penalty, regardless of your age.
IRA Options
Let's move onto the two IRA options that are available to spouse beneficiaries. The spouse has the decide whether to:
Rollover the balance into their own IRA
Rollover the balance into an inherited IRA
By processing a direct rollover to an IRA in either case, the beneficiary is able to avoid immediate taxation on the balance in the account. However, it’s very important to understand the difference between these two options because all too often this is where the surviving spouse makes the wrong decision. In most cases, once this decision is made, it cannot be reversed.
Spouse IRA vs Inherited IRA
There are some big differences comparing the spouse IRA and inherited IRA option.
There is common misunderstanding of the RMD rules when it comes to inherited IRA’s. The spouse often assumes that if they select the inherited IRA option, they will be forced to take a required minimum distribution from the account just like non-spouse beneficiaries had to under the old inherited IRA rules prior to the passing of the SECURE Act in 2019. That is not necessarily true. When the spouses establishes an inherited IRA, a RMD is only required when the deceases spouse would have reached age 70½. This determination is based on the age that your spouse would have been if they were still alive. If they are under that “would be” age, the surviving spouse is not required to take an RMD from the inherited IRA for that tax year.
For example, if you are 39 and your spouse passed away last year at the age of 41, if you establish an inherited IRA, you would not be required to take an RMD from your inherited IRA for 29 years which is when your spouse would have turned age 70½. In the next section, I will explain why this matters.
Surviving Spouse Under The Age of 59½
As the surviving spouse, if you are under that age of 59½, the decision between either establishing an inherited IRA or rolling over the balance into your own IRA is extremely important. Here’s why .
If you rollover the balance to your own IRA and you need to take a distribution from that account prior to reaching age 59½, you will incur both taxes and the 10% early withdrawal penalty on the amount of the distribution.
But wait…….I thought you said the 10% early withdrawal penalty does not apply?
The 10% early withdrawal penalty does not apply for distributions from an “inherited IRA” or for distributions to a beneficiary directly from the decedents retirement account. However, since you moved the balance into your own IRA, you have essentially forfeited the ability to avoid the 10% early withdrawal penalty for distributions taken before age 59½.
The Switch Strategy
There is also a little know “switch strategy” for the surviving spouse. Even if you initially elect to rollover the balance to an inherited IRA to maintain the ability to take penalty free withdrawals prior to age 59½, at any time, you can elect to rollover that inherited IRA balance into your own IRA.
Why would you do this? If there is a big age gap between you and your spouse, you may decide to transition your inherited IRA to your own IRA prior to age 59½. Example, let’s assume the age gap between you and your spouse was 15 years. In the year that you turn age 55, your spouse would have turned age 70½. If the balance remains in the inherited IRA, as the spouse, you would have to take an RMD for that tax year. If you do not need the additional income, you can choose to rollover the balance from your inherited IRA to your own IRA and you will avoid the RMD requirement. However, in doing so, you also lose the ability to take withdrawals from the IRA without the 10% early withdrawal penalty between ages 55 to 59½. Based on your financial situation, you will have to determine whether or not the “switch strategy” makes sense for you.
The Spousal IRA
So when does it make sense to rollover your spouse’s IRA or retirement account into your own IRA? There are two scenarios where this may be the right solution:
The surviving spouse is already age 59½ or older
The surviving spouse is under the age of 59½ but they know with 100% certainty that they will not have to access the IRA assets prior to reaching age 59½
If the surviving spouse is already 59½ or older, they do not have to worry about the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
For the second scenarios, even though this may be a valid reason, it begs the question: “If you are under the age of 59½ and you have the option of changing the inherited IRA to your own IRA at any time, why take the risk?”
As the spouse you can switch from inherited IRA to your own IRA but you are not allowed to switch from your own IRA to an inherited IRA down the road.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.