Coronavirus Relief: $100K 401(k) Loans & Penalty Free Distributions
With the passing of the CARES Act, Congress made new distribution and loan options available within 401(k) plans, IRA’s, and other types of employer sponsored plans.
With the passing of the CARES Act, Congress made new distribution and loan options available within 401(k) plans, IRA’s, and other types of employer sponsored plans. These new distribution options will provide employees and business owners with access to their retirement accounts with the:
10% early withdrawal penalty waived
Option to spread the income tax liability over a 3-year period
Option to repay the distribution and avoid taxes altogether
401(k) loans up to $100,000 with loan payments deferred for 1 year
Many individuals and small businesses are in a cash crunch. Individuals are waiting for their IRS Stimulus Checks and many small business owners are in the process of applying for the new SBA Disaster Loans and SBA Paycheck Protection Loans. Since no one knows at this point how long it will take the IRS checks to arrive or how long it will take to process these new SBA loans, people are looking for access to cash now to help bridge the gap. The CARES Act opened up options within pre-tax retirement accounts to provide that bridge.
10% Early Withdrawal Penalty Waived
Under the CARES Act, “Coronavirus Related Distributions” up to $100,000 are not subject the 10% early withdrawal penalty for individuals under the age of 59½. The exception will apply to distributions from:
IRA’s
401(K)
403(b)
Simple IRA
SEP IRA
Other types of Employer Sponsored Plans
To qualify for the waiver of the 10% early withdrawal penalty, you must meet one of the following criteria:
You, your spouse, or a dependent was diagnosed with the COVID-19
You are unable to work due to lack of childcare resulting from COVID-19
You own a business that has closed or is operating under reduced hours due to COVID-19
You have experienced adverse financial consequences as a result of being quarantined, furloughed, laid off, or having work hours reduced because of COVID-19
They obviously made the definition very broad and it’s anticipated that a lot of taxpayers will qualify under one of the four criteria listed above. The IRS may also take a similar broad approach in the application of these new qualifying circumstances.
Tax Impact
While the 10% early withdrawal penalty can be waived, in most cases, when you take a distribution from a pre-tax retirement account, you still have to pay income tax on the distribution. That is still true of these Coronavirus Related Distributions but there are options to help either mitigate or completely eliminate the income tax liability associated with taking these distributions from your retirement accounts.
Tax Liability Spread Over 3 Years
Normally when you take a distribution from a pre-tax retirement account, you have to pay income tax on the full amount of the distribution in the year that the distribution takes place.
However, under these new rules, by default, if you take a Coronavirus-Related Distribution from your 401(k), IRA, or other type of employer sponsored plan, the income tax liability will be split evenly between 2020, 2021, and 2022 unless you make a different election. This will help individuals by potentially lowering the income tax liability on these distributions by spreading the income across three separate tax years. However, taxpayers do have the option to voluntarily elect to have the full distribution taxed in 2020. If your income has dropped significantly in 2020, this may be an attractive option instead of deferring that additional income into a tax year where your income has returned to it’s higher level.
1099R Issue
I admittedly have no idea how the tax reporting is going to work for these Coronavirus-Related Distributions. Normally when you take a distribution from a retirement account, the custodian issues you a 1099R Tax Form at the end of the year for the amount of the distribution which is how the IRS cross checks that you reported that income on your tax return. If the default option is to split the distribution evenly between three separate tax years, it would seem logical that the custodians would now have to issue three separate 1099R tax forms for 2020, 2021, and 2022. As of right now, we don’t have any guidance as to how this is going to work.
Repayment Option
There is also a repayment option associated with these Coronavirus Related Distributions, that will provide taxpayers with the option to repay these distributions back into their retirement accounts within a 3-year period and avoid having to pay income tax on these distributions. If individuals elect this option, not only did they avoid the 10% early withdrawal penalty, but they also avoided having to pay tax on the distribution. The distribution essentially becomes an “interest free loan” that you made to yourself using your retirement account.
The 3-year repayment period begins the day after the individual receives the Coronavirus Related Distribution. The repayment is technically treated as a “rollover” similar to the 60 day rollover rule but instead of having only 60 days to process the rollover, taxpayers will have 3 years.
The timing of the repayment is also flexible. You can either repay the distribution as a:
Single lump sum
Partial payments over the course of the 3 year period
Even if you do not repay the full amount of the distribution, any amount that you do repay will avoid income taxation. If you take a Coronavirus Related Distribution, whether you decide to have the distribution split into the three separate tax years or all in 2020, if you repay a portion or all of the distribution within that three year window, you can amend your tax return for the year that the taxes were paid on that distribution, and recoup the income taxes that you paid.
Example: I take a $100,000 distribution from my IRA in April 2020. Since my income is lower in 2020, I elect to have the full distribution taxed to me in 2020, and remit that taxes with my 2020 tax return. The business has a good year in 2021, so in January 2022 I return the full $100,000 to my IRA. I can now amend my 2020 tax return and recapture the income tax that I paid for that $100,000 distribution that qualified as a Coronavirus Related Distribution.
No 20% Withholding Requirement
Normally when you take cash distributions from employee sponsored retirement plans, they are subject to a mandatory 20% federal tax withholding; that requirement has been waived for these Coronavirus Related Distributions up to the $100,000 threshold, so plan participants have access to their full account balance.
Cash Bridge Strategy
Here are some examples as to how individuals and small business owners may be able to use these strategies.
For small business owners that intend to apply for the new SBA Disaster Loan (EIDL) and/or SBA Paycheck Protection Program (PPP), the underwriting process will most likely take a few weeks before the company actually receives the money for the loan. Some businesses need cash sooner than that just to keep the lights on while they are waiting for the SBA money to arrive. A business owner could take a $100,000 from the 401(K) plan, use that money to operate the business, and they have 3 years to return that money to 401(k) plan to avoid having to pay income tax on that distribution. The risk of course, is if the business goes under, then the business owner may not have the cash to repay the loan. In that case, if the owner was under the age of 59½, they avoided the 10% early withdrawal penalty, but would have to pay income tax on the distribution amount.
For individuals and families that are struggling to make ends meet due to the virus containment efforts, they could take a distribution from their retirement account to help subsidize their income while they are waiting for the IRS Stimulus checks to arrive. When they receive the IRS stimulus checks or return to work full time, they can repay the money back into their retirement account prior to the end of the year to avoid the tax liability associated with the distribution for 2020.
401(k) Plan Sponsors
I wanted to issue a special note the plan sponsors of these employer sponsored plans, these Coronavirus Related Distributions are an “optional” feature within the retirement plan. If you want to provide your employees with the opportunity to take these distributions from the plan, you will need to contact your third party administrator, and authorize them to make these distributions. This change will eventually require a plan amendment but companies have until 2022 to amend their plan to allow these Coronavirus Related Distributions to happen now, and the amendment will apply retroactively.
$100,000 Loan Option
The CARES Act also opened up the option to take a $100,000 loan against your 401(k) or 403(b) balance. Normally, the 401(k) maximum loan amount is the lesser of:
50% of your vested balance OR $50,000
The CARES Act includes a provision that will allow plan sponsors to amend their loan program to allow “Coronavirus Related Loans” which increases the maximum loan amount to the lesser of:
100% of your vested balance OR $100,000
To gain access to these higher loan amounts, plan participants have to self attest to the same criteria as the waiver of the 10% early withdrawal penalty. But remember, loans are an optional plan provision within these retirement plans so your plan may or may not allow loans. If the plan sponsors want to allow these high threshold loans, similar to the Coronavirus Related Distributions, they will need to contact their plan administrator authorizing them to do so and process the plan amendment by 2022.
No Loan Payments For 1 Year
Normally when you take a 401(K) loan, the company begins the payroll deductions for your loan payment immediately after you receive the loan. The CARES act will allow plan participants that qualify for these Coronavirus loans to defer loan payments for up to one year. The loan just has to be taken prior to December 31, 2020.
Caution
While the CARES ACT provides some new distribution and loan options for individuals impacted by the Coronavirus, there are always downsides to using money in your retirement account for purposes other than retirement. The short list is:
The money is no longer invested
If the distribution is not returned to the account within 3 years, you will have a tax liability
If you use your retirement account to fund the business and the business fails, you could have to work a lot longer than you anticipated
If you take a big 401(k) loan, even though you don’t have to make loan payments now, a year from the issuance of the loan, you will have big deductions from your paycheck as those loan payments are required to begin.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
$5,000 Penalty Free Distribution From An IRA or 401(k) After The Birth Of A Child or Adoption
New parents have even more to be excited about in 2020. On December 19, 2019, Congress passed the SECURE Act, which now allows parents to withdraw up to $5,000 out of their IRA’s or 401(k) plans following the birth of their child
New parents have even more to be excited about! On December 19, 2019, Congress passed the SECURE Act, which now allows parents to withdraw up to $5,000 out of their IRA’s or 401(k) plans following the birth of their child without having to pay the 10% early withdrawal penalty. To take advantage of this new distribution option, parents will need to know:
Effective date of the change
Taxes on the distribution
Deadline to make the withdrawal
Is it $5,000 for each parent or a total per couple?
Do all 401(k) plans allow these types of distributions?
Is it a per child or is it a one-time event?
Can you repay the money to your retirement account at a future date?
How does it apply to adoptions?
This article will provide you with answers to these questions and also provide families with advanced tax strategies to reduce the tax impact of these distributions.
SECURE Act
The SECURE Act was passed in December 2019 and Section 113 of the Act added a new exception to the 10% early withdrawal penalty for taking distributions from retirement accounts called the “Qualified Birth or Adoption Distribution.”
Prior to the SECURE Act, if you were under the age of 59½ and you distributed pre-tax money from an IRA or 401(k) plan, in addition to having to pay ordinary income tax on the amount distributed, you were also hit with a 10% early withdrawal penalty from the IRS. The IRS prior to the SECURE Act did have a list of exceptions to the 10% penalty but having a child or adopting a child was not on that list. Now it is.
How It Works
After the birth of a child, a parent is allowed to distribute up to $5,000 out of either an IRA or a 401(k) plan. Notice the word “after”. You are not allowed to withdraw the money prior to the child being born. New parents have up to 12 months following the date of birth to process the distribution from their retirement accounts and avoid the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
Example: Jim and Sarah have their first child on May 5, 2025. To help with some of the additional costs of a larger family, Jim decides to withdraw $5,000 out of his rollover IRA. Jim’s window to process that distribution is between May 5, 2025 – May 4, 2026.
The Tax Hit
Assuming Jim is 30 years old, he would avoid having to pay the 10% early withdrawal penalty on the $5,000 but that $5,000 still represents taxable income to him in the year that the distribution takes place. If Jim and Sarah live in New York and make a combined income of $100,000, in 2025, that $5,000 would be subject to federal income tax of 22% and state income tax of 6.85%, resulting in a tax liability of $1,440.
Luckily under the current tax laws, there is a $2,000 federal tax credit for dependent children under the age of 17, which would more than offset the total 22% in fed tax liability ($1,100) created by the $5,000 distribution from the IRA. Essentially reducing the tax bill to $340 which is just the state tax portion.
TAX NOTE: While the $2,000 fed tax credit can be used to offset the federal tax liability in this example, if the IRA distribution was not taken, that $2,000 would have reduced Jim & Sarah’s existing tax liability dollar for dollar.
For more info on the “The Child Tax Credit” see our article: More Taxpayers Will Qualify For The Child Tax Credit
$5,000 Per Parent
But it gets better. The $5,000 limit is available to EACH parent meaning if both parents have a pre-tax IRA or 401(k) plan, they can each distribute up to $5,000 from their retirement accounts within 12 months following the birth of their child and avoid the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
ADVANCED TAX STRATEGY: If both parents are planning to distribute the full $5,000 out of their retirement accounts and they are in a medium to high tax bracket, it may make sense to split the two distributions between separate tax years.
Example: Scott and Linda have a child on October 3, 2025 and they both plan to take the full $5,000 out of their IRA accounts. If they are in a 24% federal tax bracket and they process both distributions prior to December 31, 2025, the full $10,000 would be taxable to them in 2025. This would create a $2,400 federal tax liability. Since this amount is over the $2,000 child tax credit, they will have to be prepared to pay the additional $400 federal income tax when they file their taxes, since it was not fully offset by the $2,000 tax credit.
In addition, by taking the full $10,000 in the same tax year, Scott and Linda also run the risk of making that income subject to a higher tax rate. If instead, Linda processes her distribution in November 2025 and Scott waits until January 2026 to process his $5,000 IRA distribution, it could result in a lower tax liability and less out of pocket expense come tax time.
Remember, you have 12 months following the date of birth to process the distribution and qualify for the 10% early withdrawal exemption.
$5,000 For Each Child
This 10% early withdrawal exemption is available for each child that is born. It does not have a lifetime limit.
Example: Building on the Scott and Linda example above, they have their first child October 2025, and both of them process a $5,000 distribution from their IRA’s avoiding the 10% penalty. They then have their second child in November 2026. Both Scott and Linda would be eligible to withdraw another $5,000 each out of their IRA or 401(k) within 12 months after the birth of their second child and again avoid having to pay the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
IRS Audit
One question that we have received is “Do I need to keep track of what I spend the money on in case I’m ever audited by the IRS?” The short answer is “No”. The new law does not require you to keep track of what the money was spent on. The birth of your child is the “qualifying event” which makes you eligible to distribute the $5,000 penalty free.
Not All 401(k) Plans Will Allow These Distributions
This 10% early withdrawal exception will apply to all pre-tax IRA accounts but it does not automatically apply to all 401(k), 403(b), or other types of qualified employer sponsored retirement plans.
While the SECURE Act “allows” these penalty-free distributions to be made, companies can decide whether or not they want to provide this special distribution option to their employees. For employers that have existing 401(k) or 403(b) plans, if they want to allow these penalty-free distributions to employees after the birth of a child, they will need to contact their third-party administrator and request that the plan be amended.
For companies that intend to add this distribution option to their plan, they may need to be patient with the timeline for the change. 401(k) providers will most likely need to update their distribution forms, tax codes on their 1099R forms, and update their recordkeeping system to accommodate this new type of distribution.
Ability To Repay The Distribution
The new law also offers parents the option to repay the amounts to their retirement account that were distributed due to a qualified birth or adoption. The repayment of the amounts previously distributed from the IRA or 401(k) would be in addition to the annual contribution limits. There is not a lot of clarity at this point as to how these “repayments” will work so we will have to wait for future guidance from the IRS on this feature.
Adoptions
The 10% early withdrawal exception also applies to adoptions. An individual is allowed to take a distribution from their retirement account up to $5,000 for any children under the age of 18 that is adopted. Similar to the timing rules of the birth of a child, the distribution must take place AFTER the adoption is finalized, but within 12 months following that date. Any money distributed from retirement accounts prior to the adoption date will be subject to the 10% penalty for individuals under the age of 59½.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Percentage of Pay vs Flat Dollar Amount
Enrolling in a company retirement plan is usually the first step employees take to join the plan and it is important that the enrollment process be straight forward. There should also be a contact, i.e. an advisor (wink wink), who can guide the employees through the process if needed. Even with the most efficient enrollment process, there is a lot of
Retirement Contributions - Percentage of Pay vs Flat Dollar Amount
Enrolling in a company retirement plan is usually the first step employees take to join the plan and it is important that the enrollment process be straight forward. There should also be a contact, i.e. an advisor (wink wink), who can guide the employees through the process if needed. Even with the most efficient enrollment process, there is a lot of information employees must provide. Along with basic personal information, employees will typically select investments, determine how much they’d like to contribute, and document who their beneficiaries will be. This post will focus on one part of the contribution decision and hopefully make it easier when you are determining the appropriate way for you to save.
A common question you see on the investment commercials is “What’s Your Number”? Essentially asking how much do you need to save to meet your retirement goals. This post isn’t going to try and answer that. The purpose of this post is to help you decide whether contributing a flat dollar amount or a percentage of your compensation is the better way for you to save.
As we look at each method, it may seem like I favor the percentage of compensation because that is what I use for my personal retirement account but that doesn’t mean it is the answer for everyone. Using either method can get you to “Your Number” but there are some important considerations when making the choice for yourself.
Will You Increase Your Contribution As Your Salary Increases?
For most employees, as you start to earn more throughout your working career, you should probably save more as well. Not only will you have more money coming in to save but people typically start spending more as their income rises. It is difficult to change spending habits during retirement even if you do not have a paycheck anymore. Therefore, to have a similar quality of life during retirement as when you were working, the amount you are saving should increase.
By contributing a flat dollar, the only way to increase the amount you are saving is if you make the effort to change your deferral amount. If you do a percentage of compensation, the amount you save should automatically go up as you start to earn more without you having to do anything.
Below is an example of two people earning the same amount of money throughout their working career but one person keeps the same percentage of pay contribution and the other keeps the same flat dollar contribution. The percentage of pay person contributes 5% per year and starts at $1,500 at 25. The flat dollar person saves $2,000 per year starting at 25.
The percentage of pay person has almost $50,000 more in their account which may result in them being able to retire a full year or two earlier.
A lot of participants, especially those new to retirement plans, will choose the flat dollar amount because they know how much they are going to be contributing each pay period and how that will impact them financially. That may be useful in the beginning but may harm someone over the long term if changes aren’t made to the amount they are contributing. If you take the gross amount of your paycheck and multiply that amount by the percent you are thinking about contributing, that will give you close to, if not the exact, amount you will be contributing to the plan. You may also be able to request your payroll department to run a quick projection to show the net impact on your paycheck.
There are a lot of factors to take into consideration to determine how much you need to be saving to meet your retirement goals. Simply setting a percentage of pay and keeping it the same your entire working career may not get you all the way to your goal but it can at least help you save more.
Are You Maxing Out?
The IRS sets limits on how much you can contribute to retirement accounts each year and for most people who max out it is based on a dollar limit. For 2024, the most a person under the age of 50 can defer into a 401(k) plan is $23,000. If you plan to max out, the fixed dollar contribution may be easier to determine what you should contribute. If you are paid weekly, you would contribute approximately $442.31 per pay period throughout the year. If the IRS increases the limit in future years, you would increase the dollar amount each pay period accordingly.
Company Match
A company match as it relates to retirement plans is when the company will contribute an amount to your retirement account as long as you are eligible and are contributing. The formula on how the match is calculated can be very different from plan to plan but it is typically calculated based on a dollar amount or a percentage of pay. The first “hurdle” to get over with a company match involved is to put in at least enough money out of your paycheck to receive the full match from the company. Below is an example of a dollar match and a percent of pay match to show how it relates to calculating how much you should contribute.
Dollar for Dollar Match Example
The company will match 100% of the first $1,000 you contribute to your plan. This means you will want to contribute at least $1,000 in the year to receive the full match from the company. Whether you prefer contributing a flat dollar amount or percentage of compensation, below is how you calculate what you should contribute per pay period.
Flat Dollar – if you are paid weekly, you will want to contribute at least $19.23 ($1,000 / 52 weeks = $19.23). Double that amount to $38.46 if you are paid bi-weekly.
Percentage of Pay – if you make $30,000 a year, you will want to contribute at least 3.33% ($1,000 / $30,000).
Percentage of Compensation Match Example
The company will match 100% of every dollar up to 3% of your compensation.
Flat Dollar – if you make $30,000 a year and are paid weekly, you will want to contribute at least $17.31 ($30,000 x 3% = $900 / 52 weeks = $17.31). Double that amount to $34.62 if you are paid bi-weekly.
Percentage of Pay – no matter how much you make, you will want to contribute at least 3%.
If the match is based on a percentage of pay, not only is it easier to determine what you should contribute by doing a percent of pay yourself, you also do not have to make changes to your contribution amount if your salary increases. If the match is up to 3% and you are contributing at least 3% as a percentage of pay, you know you should receive the full match no matter what your salary is.
If you do a flat dollar amount to get the 3% the first year, when your salary increases you will no longer be contributing 3%. For example, if I set up my contributions to contribute $900 a year, at a salary of $30,000 I am contributing 3% of my compensation (900 / 30,000) but at a salary of $35,000 I am only contributing 2.6% (900 / 35,000) and therefore not receiving the full match.
Note: Even though in these examples you are receiving the full match, it doesn’t mean it is always enough to meet your retirement goals, it is just a start.
In summary, either the flat dollar or percentage of pay can be effective in getting you to your retirement goal but knowing what that goal is and what you should be saving to get there is key.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
What Happens To My Pension If The Company Goes Bankrupt?
Given the downward spiral that GE has been in over the past year, we have received the same question over and over again from a number of GE employees and retirees: “If GE goes bankrupt, what happens to my pension?” While it's anyone’s guess what the future holds for GE, this is an important question that any employee with a pension should
Over the past few years, we have seen a number of companies go bankrupt that sponsored pension plans for their employees which causes the employees to ask “If my company goes bankrupt, what happens to my pension?” While some employees are aware of the PBGC (Pension Benefit Guarantee Corporation), which is an organization that exists to step in and provide pension benefits to employees if the employer becomes insolvent, very few are aware that the PBGC itself may face insolvency within the next ten years. So, if the company can’t make the pension payments and the PBGC is out of money, are employees left out in the cold?
Pension shortfall
When a company sponsors a pension plan, they are supposed to make contributions to the plan each year to properly fund the plan to meet the future pension payments that are due to the employees. However, if the company is unable to make those contributions or the underlying investments that the pension plan is invested in underperform, it can lead to shortfalls in the funding.
We have seen instances where a company files for bankruptcy and the total dollar amount owed to the pension plan is larger than the total assets of the company. When this happens, the bankruptcy courts may allow the company to terminate the plan and the PBGC is then forced to step in and continue the pension payments to the employees. While this seems like a great system since up until now that system has worked as an effective safety net for these failed pension plans, the PBGC in its most recent annual report is waiving a red flag that it faces insolvency if Congress does not make changes to the laws that govern the premium payments to the PBGC.
What is the PBGC?
The PBGC is a federal agency that was established in 1974 to protect the pension benefits of employees in the private sector should their employer become insolvent. The PBGC does not cover state or government-sponsored pension plans. The number of employees who were plan participants in an insolvent pension plan that now receive their pension payments from the PBGC is daunting. According to the 2017 PBGC annual report, the PBGC “currently provides pension payments to 840,000 participants in 4,845 failed single-employer plans and an additional 63,000 participants across 72 multi-employer plans.”
Wait until you hear the dollar amounts associated with those numbers. The PBGC paid out $5.7 Billion dollars in pension payments to the 840,000 participants in the single-employer plans and $141 Million to the 63,000 participants in the multi-employer plans in 2017.
Where Does The PBGC Get The Money To Pay Benefits?
So where does the PBGC get all of the money needed to make billions of dollars in pension payments to these plan participants? You might have guessed “the taxpayers” but for once that’s incorrect. The PBGC’s operations are financed by premiums payments made by companies in the private sector that sponsor pension plans. The PBGC receive no taxpayer dollars. The corporations that sponsor these pension plans pay premiums to the PBGC each year and the premium amounts are set by Congress.
Single-Employer vs Multi-Employer Plans
The PBGC runs two separate insurance programs: “Single-Employer Program” and “Multi-Employer Program”. It’s important to understand the difference between the two. While both programs are designed to protect the pension benefits of the employees, they differ greatly in the level of benefits guaranteed. The assets of the two programs are also kept separate. If one programs starts to fail, the PBGC is not allowed to shift assets over from the other program to save it.
The single-employer program protects plans that are sponsored by single employers. The PBGC steps in when the employer goes bankrupt or can no longer afford to sponsor the plan. The Single-Employer Program is the larger of the two programs. About 75% of the annual pension payments from the PBGC come from this program. Some examples of single-employer companies that the PBGC has had to step into to make pension payments are United Airlines, Lehman Brothers, and Circuit City.
The Multi-Employer program covers pension plans created and funded through collective bargaining agreements between groups of employers, usually in related industries, and a union. These pension plans are most commonly found in construction, transportation, retail food, manufacturing, and services industries. When a plan runs out of money, the PBGC does not step in and takeover the plan like it does for single-employer plans. Instead, it provides “financial assistance” and the guaranteed amounts of that financial assistants are much lower than the guaranteed amounts offered under the single-employer program. For example, in 2017, the PBGC began providing financial assistance to the United Furniture Workers Pension Fund A (UFW Plan), which covers 10,000 participants.
Maximum Guaranteed Amounts
The million dollar question. What is the maximum monthly pension amount that the PBGC will guarantee if the company or organization goes bankrupt? There are maximum dollar amounts for both the single-employer and multi-employer program. The maximum amounts are indexed for inflation each year and are listed on the PBGC website. To illustrate the dramatic difference between the guarantees associated with the pension pensions in a single-employer plan versus a multi-employer plan; here is an example from the PBGC website based on the 2018 rates.
“PBGC’s guarantee for a 65-year-old in a failed single-employer plan can be up to $89,181 annually, while a participant with 30 years of service in a failed multi-employer plan caps out at $12,870 per year. The multi-employer program guarantee for a participant with only 10 years of service caps out at $4,290 per year.”
It’s a dramatic difference.
For the single-employer program the PBGC provides participants with a nice straight forward benefits table based on your age. Below is a sample of the 2025 chart. However, the full chart with all ages can be found on the PBGC website.
Unfortunately, the lower guaranteed amounts for the multi-employer plans are not provided by the PBGC in a nice easy to read table. Instead they provide participant with a formula that is a headache for even a financial planner to sort through. Here is a link to the formula for 2018 on the PBGC website.
PBGC Facing Insolvency In 2025
If the organization guaranteeing your pension plan runs out of money, how much is that guarantee really worth? Not much. If you read the a previous year’s annual report issued by the PBGC (which was painful), at least 20 times throughout the report you will read the phase:
“The Multi-employer Program faces very serious challenges and is likely to run out of money by the end of fiscal year 2025.”
They have placed a 50% probability that the multi-employer program runs out of money by 2025 and a 99% probability that it runs out of money by 2036. Not good. However, as of September of 2024, the Multi-Employer program reported a net positive position, of $2.1 billion.
There is also good news for the Single-Employer Program. As of 2025, even though the Single-Employer Program ran a cumulative deficit in the billions of dollars in previous years, the program now has a net surplus of $54.1 billion.
Difficult Decision For Employees
While participants in Single-Employer plans may be breathing a little easier after reading this article, if the next recession results in a number of large companies defaulting on their pension obligations, the financial health of the PBGC could change quickly without help from Congress. Employees are faced with a one-time difficult decision when they retire. Option one, take the pension payments and hope that the company and PBGC are still around long enough to honor the pension payments. Or option two, elect the lump sum, and rollover then present value of your pension benefit to your IRA while the company still has the money. The right answer will vary on a case by case basis but the projected insolvency of the PBGC’s Multi-employer Program makes that decision even more difficult for employees.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Volatility, Market Timing, and Long-Term Investing
For many savers, the objective of a retirement account is to accumulate assets while you are working and use those assets to pay for your expenses during retirement. While you are in the accumulation phase, assets are usually invested and hopefully earn a sufficient rate of return to meet your retirement goal. For the majority,
Volatility, Market Timing, and Long-Term Investing
For many savers, the objective of a retirement account is to accumulate assets while you are working and use those assets to pay for your expenses during retirement. While you are in the accumulation phase, assets are usually invested and hopefully earn a sufficient rate of return to meet your retirement goal. For the majority, these accounts are long-term investments and there are certain investing ideas that should be taken into consideration when managing portfolios. This article will discuss volatility, market timing and their role in long-term retirement accounts.
“Market timing is the act of moving in and out of the market or switching between asset classes based on using predictive methods such as technical indicators or economic data” (Investopedia). In other words, trying to sell investments when they are near their highest and buy investments when they are near their lowest. It is difficult, some argue impossible, to time the market successfully enough to generate higher returns. Especially over longer periods. That being said, by reallocating portfolios and not experiencing the full loss during market downturns, investors could see higher returns. When managing portfolios over longer periods, this should be done without the emotion of day to day volatility but by analyzing greater economic trends.
So far, the stock market in 2018 has been volatile; particularly when compared to 2017. Below are charts of the S&P 500 from 1/1/2018 – 10/21/2018 and the same period for 2017.
Source: Yahoo Finance. Information has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable and are subject to change without notification.
Based on the two charts above, one could conclude the majority of investors would prefer 2017 100% of the time. In reality, the market averages a correction of over 10% each year and there are years the market goes up and there are years the market goes down. Currently, the volatility in the market has a lot of investors on edge, but when comparing 2018 to the market historically, one could argue this year is more typical than a year like 2017 where the market had very little to no volatility.
Another note from the charts above are the red and green bars on the bottom of each year. The red represent down days in the market and the green represent up days. You can see that even though there is more volatility in 2018 compared to 2017 when the market just kept climbing, both years have a mixture of down days and up days.
A lot of investors become emotional when the market is volatile but even in the midst of volatility and downturns, there are days the market is up. The chart below shows what happens to long-term portfolio performance if investors miss the best days in the market during that period.
Source: JP Morgan. Information has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable and are subject to change without notification.
Two main takeaways from the illustration above are; 1) missing the best days over a period in the market could have a significant impact on a portfolios performance, and 2) some of the best days in the market over the period analyzed came shortly after the worst days. This means that if people reacted on the worst days and took their money from the market then they likely missed some of the best days.
Market timing is difficult over long periods of time and making drastic moves in asset allocation because of emotional reactions to volatility isn’t always the best strategy for long-term investing. Investors should align their portfolios taking both risk tolerance and time horizon into consideration and make sure the portfolio is updated as each of these change multiple times over longer periods.
When risk tolerance or time horizon do not change, most investors should focus on macro-economic trends rather than daily/weekly/monthly volatility of the market. Not experiencing the full weight of stock market declines could generate higher returns and if data shows the economy may be slowing, it could be a good time to take some “chips off the table”. That being said, looking at past down markets, some of the best days occur shortly after the worst days and staying invested enough to keep in line with your risk tolerance and time horizon could be the best strategy.
It is difficult to take the emotion out of investing when the money is meant to fund your future needs so speaking with your financial consultant to review your situation may be beneficial.
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Target Date Funds: A Public Service Announcement
Before getting into the main objective of this article, let me briefly explain a Target Date Fund. Investopedia defines a target date fund as “a fund offered by an investment company that seeks to grow assets over a specified period of time for a targeted goal”. The specified period of time is typically the period until the date you “target” for retirement
Target Date Funds: A Public Service Announcement
Before getting into the main objective of this article, let me briefly explain a Target Date Fund. Investopedia defines a target date fund as “a fund offered by an investment company that seeks to grow assets over a specified period of time for a targeted goal”. The specified period of time is typically the period until the date you “target” for retirement or to start withdrawing assets. For this article, I will refer to the target date as the “retirement date” because that is how Target Date Funds are typically used.
Target Date Funds are continuing to grow in popularity as Defined Contribution Plans (i.e. 401(k)’s) become the primary savings vehicle for retirement. Per the Investment Company Institute, as of March 31, 2018, there was $1.1 trillion invested in Target Date Mutual Funds. Defined Contribution Plans made up 67 percent of that total.
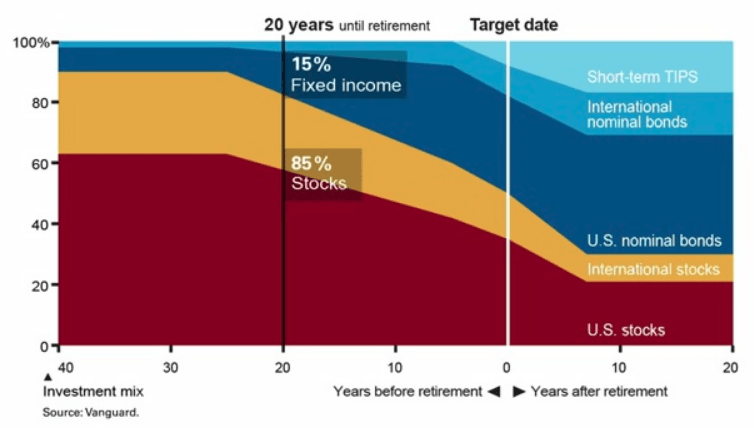
Target Date Funds are often coined as the “set it and forget it” of investments for participants in retirement plans. Target Date Funds that are farther from the retirement date will be invested more aggressively than target date funds closer to the retirement date. Below is a chart showing the “Glide Path” of the Vanguard Target Date Funds. The horizontal access shows how far someone is from retirement and the vertical access shows the percentage of stocks in the investment. In general, more stock means more aggressive. The “40” in the bottom left indicates someone that is 40 years from their retirement date. A common investment strategy in retirement accounts is to be more aggressive when you’re younger and become more conservative as you approach your retirement age. Following this strategy, someone with 40 years until retirement is more aggressive which is why at this point the Glide Path shows an allocation of approximately 90% stocks and 10% fixed income. When the fund is at “0”, this is the retirement date and the fund is more conservative with an allocation of approximately 50% stocks and 50% fixed income. Using a Target Date Fund, a person can become more conservative over time without manually making any changes.
Note: Not every fund family (i.e. Vanguard, American Funds, T. Rowe Price, etc.) has the same strategy on how they manage the investments inside the Target Date Funds, but each of them follows a Glide Path like the one shown below.
The Public Service Announcement
The public service announcement is to remind investors they should take both time horizon and risk tolerance into consideration when creating a portfolio for themselves. The Target Date Fund solution focuses on time horizon but how does it factor in risk tolerance?Target Date Funds combine time horizon and risk tolerance as if they are the same for each investor with the same amount of time before retirement. In other words, each person 30 years from retirement that is using the Target Date strategy as it was intended will have the same stock to bond allocation.This is one of the ways the Target Date Fund solution can fall short as it is likely not possible to truly know somebody’s risk tolerance without knowing them. In my experience, not every investor 30 years from retirement is comfortable with their biggest retirement asset being allocated to 90% stock. For various reasons, some people are more conservative, and the Target Date Fund solution may not be appropriate for their risk tolerance.The “set it and forget it” phrase is often used because Target Date Funds automatically become more conservative for investors as they approach their Target Date. This is a strategy that does work and is appropriate for a lot of investors which is why the strategy is continuing to increase in popularity. The takeaway from this article is to think about your risk tolerance and to be educated on the way Target Date Funds work as it is important to make sure both are in line with each other.For a more information on Target Date Funds please visit https://www.greenbushfinancial.com/target-date-funds-and-their-role-in-the-401k-space/
About Rob……...
Hi, I’m Rob Mangold. I’m the Chief Operating Officer at Greenbush Financial Group and a contributor to the Money Smart Board blog. We created the blog to provide strategies that will help our readers personally, professionally, and financially. Our blog is meant to be a resource. If there are questions that you need answered, please feel free to join in on the discussion or contact me directly.
Big Changes For 401(k) Hardship Distributions
While it probably seems odd that there is a connection between the government passing a budget and your 401(k) plan, this year there was. On February 9, 2018, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 was passed into law which ended the government shutdown by raising the debt ceiling for the next two years. However, also buried in the new law were
While it probably seems odd that there is a connection between the government passing a budget and your 401(k) plan, this year there was. On February 9, 2018, the Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 was passed into law which ended the government shutdown by raising the debt ceiling for the next two years. However, also buried in the new law were changes to rules that govern hardship distributions in 401(k) plans.
What Is A Hardship Distribution?
A hardship distribution is an optional distribution feature within a 401(k) plan. In other words, your 401(k) plan may or may not allow them. To answer that question, you will have to reference the plan’s Summary Plan Description (SPD) which should be readily available to plan participants.
If your plan allows hardship distributions, they are one of the few in-service distribution options available to employees that are still working for the company. There are traditional in-service distributions which allow employees to take all or a portion of their account balance after reaching the age 59½. By contrast, hardship distributions are for employees that have experienced a “financial hardship”, are still employed by the company, and they are typically under the age of 59½.
Meeting The "Hardship" Requirement
First, you have to determine if your financial need qualifies as a "hardship". They typically include:
Unreimbursed medical expenses for you, your spouse, or dependents
Purchase of an employee's principal residence
Payment of college tuition and relative education costs such as room and board for the next 12 months for you, your spouse, dependents, or children who are no longer dependents.
Payment necessary to prevent eviction of you from your home, or foreclosure on the mortgage of your primary residence
For funeral expenses
Certain expenses for the repair of damage to the employee's principal residence
Second, there are rules that govern how much you can take out of the plan in the form of a hardship distribution and restrictions that are put in place after the hardship distribution is taken. Below is a list of the rules under the current law:
The withdrawal must not exceed the amount needed by you
You must first obtain all other distribution and loan options available in the plan
You cannot contribute to the 401(k) plan for six months following the withdrawal
Growth and investment gains are not eligible for distribution from specific sources
Changes To The Rules Starting In 2019
Plan sponsors need to be aware that starting in 2019 some of the rules surrounding hardship distributions are going to change in conjunction with the passing of the Budget Act of 2018. The reasons for taking a hardship distribution did not change. However, there were changes made to the rules associated with taking a hardship distribution starting in 2019. More specifically, of the four rules listed above, only one will remain.
No More "6 Month Rule"
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2018 eliminated the rule that prevents employees from making 401(k) contributions until 6 months after the date the hardship distribution was issued. The purpose of the 6 month wait was to deter employees from taking a hardship distribution. In addition, for employees that had to take a hardship it was a silent way of implying that “if things are bad enough financially that you have to take a distribution from your retirement account, you probably should not be making contributions to your 401(k) plan for the next few months.”
However, for employees that are covered by a 401(k) plan that offers an employer matching contribution, not being able to defer in the plan for 6 months also meant no employer matching contribution during that 6 month probationary period. Starting in 2019, employees will no longer have to worry about that limitation.
Loan First Rule Eliminated
Under the current 401(k) rules, if loans are available in the 401(k) plan, the plan participant was required to take the maximum loan amount before qualifying for a hardship distribution. That is no longer a requirement under the new law.
We are actually happy to see this requirement go away. It never really made sense to us. If you have an employee, who’s primary residence is going into foreclosure, why would you make them take a loan which then requires loan payments to be made via deductions from their paycheck? Doesn’t that put them in a worse financial position? Most of the time when a plan participant qualifies for a hardship, they need the money as soon as possible and having to go through the loan process first can delay the receipt of the money needed to remedy their financial hardship.
Earnings Are Now On The Table
Under the current 401(k) rules, if an employee requests a hardship distribution, the portion of their elective deferral source attributed to investment earnings was not eligible for withdrawal. Effective 2019, that rule has also changed. Both contributions and earnings will be eligible for a hardship withdrawal.
Still A Last Resort
We often refer to hardship distributions as the “option of last resort”. This is due to the taxes and penalties that are incurred in conjunction with hardship distributions. Unlike a 401(k) loan which does not trigger immediate taxation, hardship distributions are a taxable event. To make matters worse, if you are under the age of 59½, you are also subject to the 10% early withdrawal penalty.
For example, if you are under the age of 59½ and you take a $20,000 hardship distribution to make the down payment on a house, you will incur taxes and the 10% penalty on the $20,000 withdrawal. Let’s assume you are in the 24% federal tax bracket and 7% state tax bracket. That $20,000 distribution just cost you $8,200 in taxes.
Gross Distribution: $20,000
Fed Tax (24%): ($4,800)
State Tax (7%): ($1,400)
10% Penalty: ($2,000)
Net Amount: $11,800
There is also an opportunity cost for taking that money out of your retirement account. For example, let’s assume you are 30 years old and plan to retire at age 65. If you assume an 8% annual rate of return on your 401(K) investment that $20,000 really cost you $295,707. That’s what the $20,000 would have been worth, 35 years from now, compounded at 8% per year.
Plan Amendment Required
These changes to the hardship distribution rule will not be automatic. The plan sponsor of the 401(k) will need to amend the plan document to adopt these new rules otherwise the old hardship distribution rules will still apply. We recommend that companies reach out to their 401(k) providers to determine whether or not amending the plan to adopt the new hardship distribution rules makes sense for the company and your employees.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
403(b) Lawsuits Continue To Spread To More Colleges
In the last 3 years, the number of lawsuits filed against colleges for excessive fees and compliance issues related to their 403(b) plans has increased exponentially. Here is a list of just some of the colleges that have had lawsuit brought against them by their 403(b) plan participants:
In the last 3 years, the number of lawsuits filed against colleges for excessive fees and compliance issues related to their 403(b) plans has increased exponentially. Here is a list of just some of the colleges that have had lawsuit brought against them by their 403(b) plan participants:
Yale
NYU
Duke
John Hopkins
MIT
Columbia
Emory
Cornell
Vanderbilt
Northeastern
USC
The fiduciary landscape has completely changed for organizations, like colleges, that sponsor ERISA 403(b) plans. In 2009, new regulations were passed that brought 403(b) plans up to the compliance standards historically found in the 401(k) market. Instead of slowly phasing in the new regulations, the 403(b) market basically went from zero to 60 mph in a blink of an eye. While some of the basic elements of the new rules were taken care of by the current service providers such as the required written plan documents, contract exchange provisions, and new participant disclosures, we have found that colleges, due to a lack of understanding of what is required to fulfill their fiduciary role to the plan, have fallen very short of putting the policies and procedures in place to protect the college from liabilities that can arise from the 403(b) plan.
Top Violations
Based on the lawsuits that have been filled against the various colleges, here is a list of the most common claims that have been included in these lawsuits:
Excessive fees
Fees associated with multiple recordkeepers
Too many investment options
Improper mutual fund share class
Variable annuity products
Excessive Fees
This is by far number one on the list. As you look at these lawsuits, most of them include a claim that the university breached their fiduciary duty under ERISA by allowing excessive fees to be charged to plan participants.
Here is the most common situation that we see when consulting with colleges that leads to this issue. A college had been with the same 403(b) provider for 60 years. Without naming names, they assume that their 403(b) plan has reasonable fees because all of the other colleges that they know of also use this same provider. So their fees must be reasonable right? Wrong!!
If you are member of the committee that oversees that 403(b) plan at your college, how do you answer this question? How do you know that the fees for your plan are reasonable? Can you show documented proof that you made a reasonable effort to determine whether or not the plan fees are reasonable versus other 403(b) providers?
The only way to answer this question is by going through an RFP process. For colleges that we consult with we typically recommend that they put an RFP out every 3 to 5 years. That is really the only way to be able to adequately answer the question: “Are the plan fees reasonable?” Now if you go through the RFP process and you find that another reputable provider is less expensive than your current provider, you are not required to change to that less expensive provider. However, from a fiduciary standpoint, you should acknowledge at the end of the RFP process that there were lower fee alternatives but the current provider was selected because of reasons X, Y, and Z. Document, document, document!!
Investment Fees / Underperformance / Investment Options
Liability is arising in these 403(b) plans due to
Revenue sharing fees buried in the mutual fund expense rations
Underperformance of the plan investments versus the benchmark / peer group
Too many investment options
Investment options concentrated all in one fund family
Restrictions associate with the plan investment
Investment Policy Statement violations or No IPS
Failure to document quarterly and annual investment reviews
Here is the issue. Typically members of these committees that oversee the 403(b) plan are not investment experts and you need to basically be an investment expert to understand mutual fund share classes, investment revenue sharing, peer group comparisons, asset classes represented within the fund menu, etc. To fill the void, colleges are beginning to hire investment firms to serve as third party consultants to the 403(b) committee. In most cases these firms charge a flat dollar fee to:
Prepare quarterly investment reports
Investment benchmarking
Draft a custom Investment Policy Statement
Coordinate the RFP process
Negotiation plan fees with the current provider
Conduct quarterly and annual reviews with the 403(b) committee
Compliance guidance
Multiple Recordkeepers
While multiple recordkeepers is becoming more common for college 403(b) plans, it requires additional due diligence on the part of the college to verify that it’s in the best interest of the plan participants. Multiple recordkeepers means that your 403(b) plan assets are split between two or more custodians. For example, a college may use both TIAA CREF and Principal for their 403(b) platform. Why two recordkeepers? Most of the older 403(b) accounts are setup as individual annuity contracts. As such, if the college decides to charge their 403(b) provider, unlike the 401(k) industry where all of the plan assets automatically move over to the new platform, each plan participant is required to voluntarily sign forms to move their account balance from the old 403(b) provider to the new 403(b) provider. It’s almost impossible to get all of the employee to make the switch so you end up with two separate recordkeepers.
Why does this create additional liability for the college? Even through the limitation set forth by these individual annuity contracts is out of the control of the college, by splitting the plan assets into two pieces you may be limiting the economies of scale of the total plan assets. In most cases the asset based fees for a 403(b) plan decreases as the plan assets become larger with that 403(b) provider. By splitting the assets between two 403(b) platforms, you are now creating two smaller plans which could result in larger all-in fees for the plan participants.
Now, it may very well be in the best interest of the plan participants to have two separate platforms but the college has to make sure that they have the appropriate documentation to verify that this due diligence is being conducts. This usually happens as a result of an RFP process. Here is an example. A college has been using the same 403(b) provider for the last 50 years but to satisfy their fiduciary obligation to the plan they going through the RFP process to verify that their plan fees are reasonable. Going into the RFP process they had no intention of change provides but as a result of the RFP process they realize that there are other 403(b) providers that offer better technology, more support for the plan sponsor, and lower fees than their current platform. While they are handcuffed by the individual contracts in the current 403(b) plan, they still have control over where the future contributions of the plan will be allocated so they decide that it’s in both the plan participants and the college’s best interest to direct the future contributions to the new 403(b) platform.
Too Many Investment Options
More is not always better in the retirement plan world. The 403(b) oversite committee, as a fiduciary, is responsible for selecting the investments that will be offered in accordance with the plan’s investment menu. Some colleges unfortunately take that approach that if we offer 80+ different mutual funds for the investment that should “cover all of their bases” since plan participants have access to every asset class, mutual fund family, and ten different small cap funds. The plaintiffs in these 403(b) lawsuits alleged that many of the plan’s investment options were duplicates, performed poorly, and featured high fees that are inappropriate for large 403(b) plans.
To make matters worse, if you have 80+ mutual funds on your 403(b) investment menu, you have to conduct regular and on-going due diligence on all 80+ mutual funds in your plan to make sure that they still meet the investment criteria set out in the plan’s IPS. If you have mutual funds in your plan that fall outside of the IPS criteria and those issues have not been addressed and/or documented, if a lawsuit is brought against the college it will be very difficult to defend that the college was fulfilling its fiduciary obligation to the investment menu.
Improper Mutual Fund Share Classes
To piggyback on this issue, what many plan sponsors don’t realize is that by selecting a more limited menu of mutual funds it can lower the overall plan fees. Mutual funds have different share classes and some share classes require a minimum initial investment to gain asset to that share class. For example you may have Mutual Fund A retail share class with a 0.80% internal expense ratio but there is also a Mutual Fund A institutional share class with a 0.30% internal expense ratio. However, the institutional share class requires an initial investment of $100,000 to gain access. If Mutual Fund A is a U.S. Large Cap Stock Fund and your plan offers 10 other U.S. Large Cap Stock Funds, your plan may not meet the institutional share requirement because the assets are spread between 10 different mutual funds within the same asset class. If instead, the committee decided that it was prudent to offer just Mutual Fund A to represent the U.S. Large Cap Stock holding on the investment menu, the plan may be able to meet that $100,000 minimum initial investment and gain access to the lower cost institutional share class.
Variable Annuity Products
While variable annuity products have historically been a common investment option for 403(b) plans, they typically charge fees that are higher than the fees that are charged by most standard mutual funds. In addition, variable annuities can place distribution restrictions on select investment investments which may not be in the plan participants best interest.
The most common issue we come across is with the TIAA Traditional investment. While TIAA touts the investment for its 3% guarantee, we have found that very few plan participants are aware that there is a 10 year distribution restriction associated with that investment. When you go to remove money from the TIAA Traditional fund, TIAA will inform you that you can only move 1/10th of your balance out of that investment each year over the course of the next ten years. You can see how this could be a problem for a plan participant that may have 100% of their balance in the TIAA Traditional investment as they approach retirement. Their intention may have been to retire at age 65 and rollover the balance to their own personal IRA. If they have money in the TIAA Traditional investment that is no longer an option. They would be limited to process a rollover equal to 1/10th of their balance in the TIAA Tradition investment between the age of 65 and 74. Only after age 74 would they completely free from this TIAA withdrawal restriction.
Consider Hiring A Consultant
While this may sound self-serving, colleges are really going to need help with the initial and on-going due diligence associate with keeping their 403(b) plan in compliance. For a reasonable cost, colleges should be able to engage an investment firm that specialized in this type of work to serve as a third party consultant for the 403(b) investment committee. Just make sure the fee is reasonable. The consulting fee should be expressed as a flat dollar amount fee, not an asset based fee, because they are fulfilling that role as a “consultant”, not the “investment advisor” to the 403(b) plan assets.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.