What Happened The Last Time The Dow Dropped By More Than 4% In A Day?
Yesterday was an “ouch”. The Dow Jones Industrial average dropped by more than 1000 points resulting in a 4.60% drop in the value of the index. While yesterday marked the largest “point” decline in the history of the Dow Jones Index, it was not anywhere near the largest percentage decline which is the metric that we care about.
Yesterday was an “ouch”. The Dow Jones Industrial average dropped by more than 1000 points resulting in a 4.60% drop in the value of the index. While yesterday marked the largest “point” decline in the history of the Dow Jones Index, it was not anywhere near the largest percentage decline which is the metric that we care about.
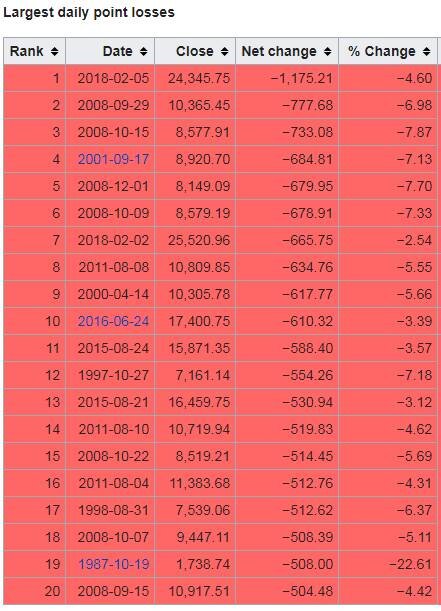
Below is a chart that shows the largest daily “point” losses in the history of the Dow Jones Industrial Index:
You will find yesterday at the top of the chart. Now look at the column all the way to the right labelled “% change”. You will notice that while yesterday topped the chart from a point decline, it does not come anywhere near the largest percentage decline that we have seen. In fact, it does not even make it in the top 20 worse days for the Dow. See the chart below that shows the largest daily percentage declines in the Dow’s history:
What Happened Last Time?
Whenever there is a big drop in the stock market, I immediately start looking back in history to find market events that are similar to the current one. So when was the last time the market dropped by more than 4% in a single day?
The answer: August 8, 2011
If you remember, 2011 was the start of the European Sovereign Debt Crisis. That was when Greece, Portugal, Spain, and Ireland announced that they were unable to repay their government debt and needed a bailout package from the European Union to survive. There were two single day declines in the month of August that rivaled what we saw yesterday.
How Long Did It Take The Market To Come Back?
If we are looking to history as a guide, how long did it take for the market to recoup the losses after these large single day declines? On July 31, 2011 the Dow Jones Industrial closed at 11,444, the Europe debt crisis hit, and the market experienced those two 4%+ decline days on August 4th and August 8th. By September 11, 2011, the Dow Jones closed at 11,509, recouping all of its losses from the beginning of August. Thus making the answer to the question: 38 days. The market took 38 days to recoup all of the losses from not one but two 4%+ decline days in 2011.
We Don’t Have A Crisis
The main difference between 2011 and now is we don’t have a global economic crisis. In my opinion, the market correction in 2011 was warranted. There was a real problem in Europe. We were not sure how and if those struggling Eurozone countries could be saved so the market dropped.
The only trigger that I hear analysts pointing to in an effort to explain the selloff yesterday is the 2.9% wage growth number that we got on Friday. This in turn has sparked inflation fears and in reaction, the Fed may decide to hike rates four times this year instead of three. Hardly a “crisis”. Outside of that nothing else meaningful has happened to trigger the volatility that we are seeing in the stock market. OK……so what should you do in reaction to this? Sometimes the right answer is “nothing”. It’s difficult to hear that because emotionally you want to pull money out of the market and run to cash or bonds but absent a sound economic reason for making that move, at this point, the best investment decision may be to just stay the course.
We Have Forgotten What Volatility Feels Like
When you are in a market environment like 2017, you very quickly forget what normal market volatility feels like. In 2017, the stock market just gradually climbed throughout the year without any hiccups. That’s not normal. Below is a chart that shows the magnitude of market corrections each year going back to 1990. As you will see, on average, when the economy is not in a recession, the market averages an 11.56% correction at some point during the year. In 2017, we only experienced a 3% correction.
Now the next chart shows you the big picture. Not only does it illustrate the amount of the largest market correction during the year but it also shows the return of the S&P 500 for the year.
Look at 2016. In 2016, at some point in the year the S&P 500 Index dropped by 11%. If you just held through it, the S&P 500 returned 10% for the year.
In 2011, the S&P 500 dropped by 19% during the year!! If you didn’t sell and just held through the volatility, you would have had a breakeven year.
Easier Said Than Done
Every big market correction feels like a new world ending crisis. It’s not. We have been fortunate enough to have a nice easy ride for the past 12 months but it seems like we are returning to more historical levels of volatility. Days like February 5, 2018 will test your patience and make you feel compelled to react. It’s easy to look back and confess that “yes, I should have just held through it” but it’s easier said than done.
It’s important to understand the catalysts that are driving the volatility in the markets. Sometimes the markets are dropping for a good reason and other times it’s just plain old fashion volatility. Based on what we have seen over the past few days and absent the emergence of a new economic, political, or global crisis, we expect it to be the later of the two.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
When Do Higher Interest Rates Become Harmful To The Stock Market?
On Friday, the jobs report came out and it was a strong report. The consensus was expecting 180,000 new jobs in January and the actual number released on Friday ended up being 200,000. So why did the markets drop? The answer: wage growth. The jobs report not only contains how many new employees were hired but it also includes the amount
On Friday, the jobs report came out and it was a strong report. The consensus was expecting 180,000 new jobs in January and the actual number released on Friday ended up being 200,000. So why did the markets drop? The answer: wage growth. The jobs report not only contains how many new employees were hired but it also includes the amount that wages for the current workforce either increased or decreased on a year over year basis. The report on Friday indicated that wages went up by 2.9% year over year. That is the strongest wage growth number since 2009.
Double Edged Sword
Wage growth is a double edged sword. On the positive side, when wages are going up, people have more money in their paychecks which allows them to spend more and consumer spending makes up 70% of our GDP in the United States. I'm actually surprised the market did not see this coming. The whole premise behind tax reform was "if we give U.S. corporations a tax break, they will use that money to hire more employees and increase wages." The big question people had with the tax reform was "would the trickle down of the dollars saved by the corporations eventually make it to the employees pockets?" Many corporations in January, as a result of tax reform, announced employee bonuses and increases to the minimum wage paid within their organizations. The wage growth number on Friday would seem to imply that this is happening. So again, I'm actually surprised that the market was not ready for this and while the market reacted negatively I see this more as a positive long term trend, instead of a negative one. If instead the U.S. corporations decided not to give the bonuses or increase wages for employees and just use the money from the tax reform savings to increase dividends or share buybacks, then you probably would have seen only a moderate increase in the wage growth number. But that also would imply that there would be no "trickle down" effect to the middle class.
The Downside
This all sounds really positive but what is the downside to wage growth? While wage growth is good for employees, it's bad for corporate earnings. If I was paying Employee A $50,000 in 2017 but now I'm paying them $55,000 per year in 2018, assuming the output of that employee did not change, the expenses to the company just went up by $5,000 per year. Now multiply that over thousands of employees. It's a simple fact that higher expenses without higher output equals lower profits.
Wage Growth = Inflation
There is another downside to wage growth. Wage growth is the single largest contributor to inflation. Inflation is what we use to measure the increase in the price of goods and services in the U.S.. Why are these two measurements so closely related? If your salary just increased by $300 per month, when you go to the grocery store to buy milk, you may not notice that the price of milk went up by $0.15 over last week because you are making more in your paycheck. That is inflation. The price of everything starts going up because, in general, consumers have more take home pay and it gives the sellers of goods and services more pricing power. Visa versa, when the economy is in a recession, people are losing their jobs, and wages are decreasing. If you sell cars and you decided to raise the price of the cars that you sell, that may cause the consumer to not buy from you and look for a lower priced alternative. Companies have less pricing power when the economy is contracting and you typically have "deflation" not inflation.
When Does Inflation Become Harmful?
Some inflation is good. It means the economy is doing well. A rapid increase in inflation is bad because it forces the Fed to use monetary policy to slow down the economy so it does not over heat. The Fed uses the Federal Funds Rate as their primary tool to keep inflation in check. When inflation starts heating up, the Fed will often raise the Fed Funds Rate to increase the cost of lending which in turn reduces the demand for lending. It’s like tapping the brakes in your car to make sure you do not accelerate too quickly and then go flying off the road.
If some inflation is good but too much inflation is bad, the question is at what point do higher interest rates really jeopardize economic growth? The chart below provides us with guidance as to what has happened in the past when interest rates were on the rise.
The chart compares every 2 year period in the stock market versus the level of the 10-Year Treasury yield between 1963 – 2017. For example, one dot would represent the time period 1963 – 1964. Another dot would represent 1964 – 1965 and so on. If the dot is above the “0.0” line, that means that there was a “positive correlation” between stock prices going up and the interest rate on the 10-Year Treasury yield going up during that same time period. Worded another way, when the dot is above the line that means the stock market was going up while interest rates were also increasing. In general, the dots above the line are good, when they are below the line, that’s bad.
Right now the 10-Year Treasury Bond is at 2.85% which is the red line on the chart. What we can conclude from this is going all the way back to 1963, at this data point, there has never been a two year period where interest rates were rising and stock prices were falling. Could it be different this time? It could, but it’s a low probability if we use historical data as our guide. History would suggest that we do not run into trouble until the yield on the 10-Year Treasury Bond gets above 4%. Once the yield on our 10-Year Treasury Bond reaches that level and interest rates are rising, historically the correlation between rising interest rates and stock prices turns negative. Meaning interest rates are going up but stock prices are going down.
It makes sense. Even though interest rates are moving up right now, they are still at historically low levels. So lending is still “cheap” by historical standards which will continue to fuel growth in the economy.
A Gradual Rise In Interest Rates
Most fixed income managers that we speak with are expecting a gradual rise in interest rates throughout 2018. While we expect interest rates to move higher throughout the year due to an increase in wage growth as a result of a tighter labor market, in our opinion, it’s a stretch to make the case that the yield on the 10-year Treasury will be at 4% by the end of the year.
If the U.S. was the only country in the world, I would feel differently. Our economy is continuing to grow, wages are increasing, the labor markets are tight which requires companies to pay more for good employees, and all of these factors would warrant a dramatic increase in the rate of inflation. But we are not the only country in the world and the interest rate environment in the U.S. is impacted by global rates.
The chart below illustrates the yield on a 10 year government bonds for the U.S., Japan, Germany, UK, Italy, Spain, and total “Global Ex-U.S.”.
On December 31, 2017 the yield on a 10-Year Government Bond in the U.S. was 2.71%. The yield on a 10-Year government bond in Germany was only 0.46%. So, if you bought a 10-Year Government Bond from Germany, they are going to hand you back a measly 0.46% in interest each year for the next 10 years.
Why is this important? The argument can be made that while the changes in the Fed Funds Rate may have a meaningful impact on short-term rates, it may have less of an impact on intermediate to longer term interest rates. When the U.S. government needs more money to spend they conduct “treasury auctions”. The government announces that on a specified date that they are going to be selling “30 million worth of 10-year treasury bonds at a 2.8% rate”. As long as there is enough demand to sell all of the bonds at the 2.8% rate, the auction is a success. If there is not enough demand, then they may have to increase the interest rate from 2.8% to 3% to sell all $30 million worth of the bonds. While the U.S. 10-Year Treasury Bond only had a yield of 2.71%, it’s a lot higher than the other trusted government lenders around the world. As you can see in the chart above, the average 10-year government bond yield excluding the U.S. is 1.03%. This keeps the demand for U.S. debt high without the need to dramatically increase the interest rate on new government debt issuance to attract buyers of the debt.
As for the trend in global interest rates, you will see in the chart that from September 30, 2017 to December 31, 2017, global 10-year government bond yields ex-U.S. decreased from 1.05% to 1.03%. While we are in the monetary tightening cycle in the U.S., there is still monetary easing happening around the world as a whole which should prevent our 10-year treasury yields from spiking over the next 12 months.
Impact on Investment Portfolios
The media will continue to pounce on this story about “the risk of rising interest rates and inflation” throughout 2018 but it’s important to keep it in context. If tax reform works the way that it’s supposed to, wage growth should continue but we may not see the positive impact of increased consumer spending due to the wage growth until corporate earnings are released for the first and second quarter of 2018. We just have to wait to see how the strength of consumer spending nets out against the pressure on corporate earnings from higher wages.
However, investors should be looking at the fixed income portion of their portfolio to make sure there is the right mix of bonds if inflation is expected to rise throughout the year. Bond duration and credit quality will play an important role in your fixed income portfolio in 2018.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Dow Dropped 362 Points Yesterday. Now What?
When you hear that the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped by over 300 points it gets your attention. It triggers that automatic emotional response which leads you to ask, "Is the market rally ending?" I'm going to start this article by saying "I'm not a cheerleader for the stock market". As a cheerleader, it's your job to cheer whether your team is
When you hear that the Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped by over 300 points it gets your attention. It triggers that automatic emotional response which leads you to ask, "Is the market rally ending?" I'm going to start this article by saying "I'm not a cheerleader for the stock market". As a cheerleader, it's your job to cheer whether your team is winning or losing. Sometimes the general public views investment advisors that way. "Of course my advisor has a rosy outlook. He wants me to stay invested".
My view is when the cycle is ending it's ending. When the data tells us that we are headed toward the next recession, you just have to accept a lower expected rate of return and make the necessary allocation changes to preserve principal during the market downturn. The answer is not always "just hold through it" which is unfortunately the answer that some investors receive from their advisor regardless of what's happening in the markets and the economy.
What Has Changed?
Whenever you have a big down day in the market the first question you should ask yourself is "What changed?" I know the value of the stock market changed but the question I'm really asking is what fundamental change happened in the U.S. economy to trigger the selloff?
Did GDP growth rate pull back unexpectedly?
Did the monthly jobs report come up short? Did inflation increase by a large number that wasn't expected?
Are corporate earnings deteriorating?
Has the leading indicators index turned negative?
These are the real questions that you should be asking. Remember, the economy leads the stock market. The stock market does not lead the economy. Watching the fluctuations in the stock market and using that as a tool to make investment decisions is a recipe for disaster. You are much more likely to find success in your investments if you use a trading app uk that is able to help you track prices and automate your trading.
A growing economy typically means higher corporate earnings
Higher corporate earnings often results in higher stock prices
With that said, sometimes the market is down because it's reacting to poor economic data. In those cases, the market downturn may be warranted. However, that is not what I think happened yesterday. We did not get a bad jobs number or shortfall in GDP growth. In short, as of yesterday, nothing has changed from an economic standpoint. Days like yesterday are just a reminder of what volatility in the markets feels like.
Higher Volatility Ahead
If you asked me if I expect more or less days like yesterday in 2018, my guess would be more. We are all suffering from "recency bias". 2017 was this nice smooth ride higher with very few interruptions. When you get used to sailing in smooth waters, a small wave can seem like a tsunami. Below is a chart of the CBEO Vix Index from January 2002 – January 2018 which is used to gauge the level of volatility in the U.S. stock market:
As you can see, we are coming off of historically low levels of volatility and we have to remember that volatility is normal. Every down tick in the stock market is not necessarily a signal that a recession is coming.
The Math Is Different
What if I told you that the market was only down 177 points yesterday? It probably does not trigger the same fear reaction as being down over 350 points. The reason why I ask this question is you have to remember that the price level of the Dow has doubled over the last 6 years. So a 300 point drop in the Dow Jones Industrial Average today does not mean the same thing as a 300 point drop in 2012. On February 17, 2012, the Dow Jones Industrial Average closed at 12,949. Today it sits just above 26,000. In percentage terms, a 300 drop in 2012 equaled a 2.3% drop in the stock market. If you translate that to where the stock market is today, you would need a 598 point drop in a single day to get that same 2.3% drop. It's just math but we have to remember this when the headlines in the media read:
"The Dow Dropped By 300 Points Today. Traders Are Worried That This Could Be The End Of The Rally?"
Never Hesitate
While I write these articles to help our clients and readers to become better investors and to put important market events into perspective, I have a special note that I want to leave off on for our clients. When you have that feeling of uncertainty, never hesitate to contact me. That quick phone call just to ask, "Mike, should I be worried?" That's what I'm here for. Have a great week everyone!!
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
The Government Is Shut Down. Should You Be Worried?
The senate was not able to pass a temporary spending bill in the late hours of the night so as of Saturday, January 20th the government is officially shut down. But what does that mean? How will it impact you? What will be the impact on the stock market?
The senate was not able to pass a temporary spending bill in the late hours of the night so as of Saturday, January 20th the government is officially shut down. But what does that mean? How will it impact you? What will be the impact on the stock market?
Don’t Let The Media Scare You
The media loves big disruptive events. Why? The news is a "for profit" business. The more viewers they have, the more profits they make. What makes you watch more news? Fear. If the weather forecasts is 80 degrees and sunny, you just go on with your day. Instead, if the weather is predicting “The Largest Winter Blizzard Of The Century”, my guess is you will be glued to the weather channel most of the day trying to figure out when the storm will hit, how many feet of snow is expected to fall, and are schools closing, etc.
You will undoubtedly wake up this morning to headlines about “The Government Shutdown” and all of the horrible things that could happen as a result. In the short term a government shutdown or a “funding gap” is not incredibly disruptive. Many government agencies have residual funding to keep operations going for a period of time. Only portions of the government really “shut down”. The “essential” government services continue to function such as national security and law enforcement. The risk lies in the duration of the government shutdown. If Congress does not pass either a temporary extension or reach a final agreement within a reasonable period of time, some of these government agencies will run out of residual funding and will be forced to halt operations.
The news will target the “what if’s” of the current government shutdown. What if the government stays shut down and social security checks stop? What if the U.S. cannot fund defense spending and we are left defenseless? All of these scenarios would require a very prolonged government shutdown which is unlikely to happen.
How Often Does This Happen?
When I woke up this morning, my first questions was “how often do government shutdowns happen?” Is this an anomaly that I should be worried about or is it a frequent occurrence? The last government shutdown took place on September 30, 2013 and the government stayed shut down for 16 days. Prior to the 2013 shutdown, you have to go back to December 15, 1995. The duration of the 1995 shutdown was 21 days. Making the current government shutdown only the third shutdown between December 15, 1995 – January 20, 2018. Not an anomaly but also not a frequent event.
But let’s look further back. How many times did the U.S. government experience a shutdown between 1976 – 2018? In the past 42 years, the U.S. government has experienced a shutdown 18 times. On average the government shutdowns lasted for about 7 days. This makes me less worried about the current government shutdown given the number of shutdowns that we have overcome in the past.
This Shutdown Could Be Longer
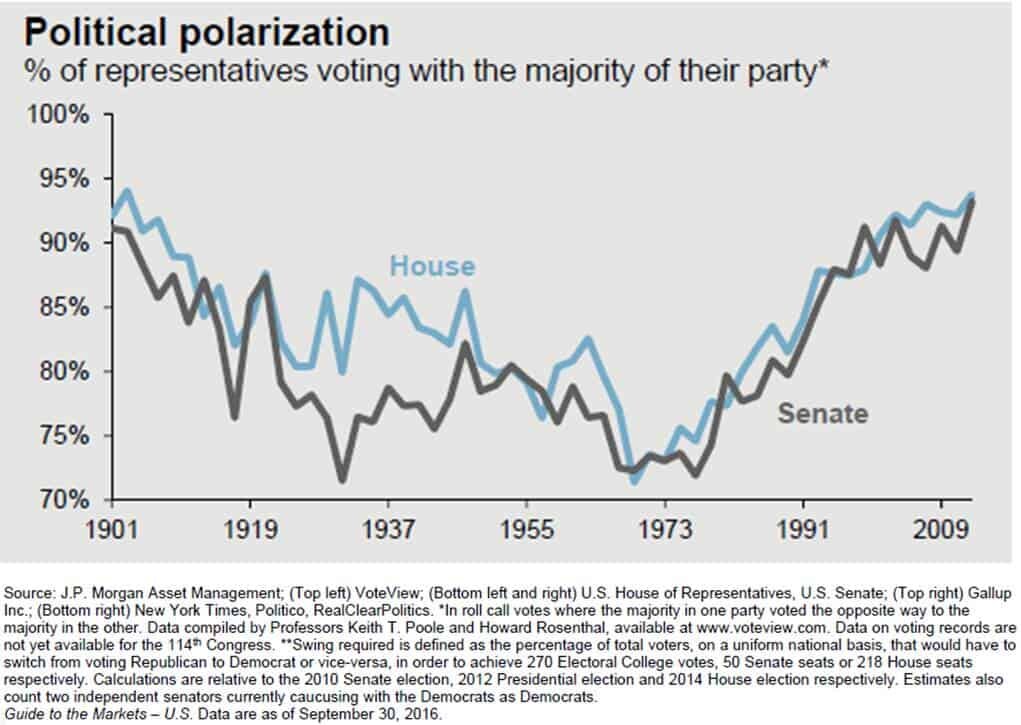
The only thing that worries me a little is the potential duration of the current government shutdown. I would not consider two data points to be a new “trend” but it is hard to ignore that the last two government shutdowns that occurred in 1995 and 2013 were much longer than the 7 day historical average. However, this could be the start of a new trend given how polarized Congress has become. It’s a clear trend that over the past 40 years fewer members of the Senate and House are willing to cross party lines during a vote. See the chart below: Back in 1973, only 73% of the members of Congress voted with the majority of their political party. It would seem rational to assume that during that time period members of Congress were more willing to step across the aisle for the greater good of the American people. Now, approximately 95% of the members of both the House and Senate vote with their own camp. This creates deadlock situations that take longer to resolve as the “blame game” takes center stage.
Impact On The Stock Market
In most cases, injecting uncertainty in our economy is never good for the stock market. However, given the fact that U.S. corporations are still riding the high of tax reform, if the government shutdown is resolved within the next two weeks it may have little or no impact on the markets.
If it were not for the recent passage of tax reform, my guess is this government shutdown may have been completely avoided. Not choosing a side here but just acknowledging the Democratic Party was delivered a blow with passage of tax reform in December. Since the spending bill requires 60 votes to pass in the Senate, it will require support from the Democrats. This situation provides the Democratic party with a golden opportunity to negotiate terms to help make up for some the lost ground from the passage of the Republican led tax bill. This challenging political environment could lengthen the duration of the government shutdown. However, it’s also important to remember that neither party benefits from a government shutdown, especially in a midterm election year.
Over the next two weeks, I would recommend that investors take all the media hype with a grain of salt. However, if a permanent or temporary spending bill is not passed within the next two weeks, it could result in increased volatility and downward pressure on the stock market as government agencies run out of cash reserves and begin to put workers on furlough. At this point, we are really in a “wait and see” environment.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
What Does Tax Reform Mean For The Markets In 2018?
2017 ended up being a huge year for the U.S. stock market. The rally in the stock market was unmistakably driven by the anticipated passing of tax reform and Congress delivered. However, the sheer magnitude of the stock market rally has presented investors with a moment of pause and a lot of unanswered questions as we enter into the first quarter
2017 ended up being a huge year for the U.S. stock market. The rally in the stock market was unmistakably driven by the anticipated passing of tax reform and Congress delivered. However, the sheer magnitude of the stock market rally has presented investors with a moment of pause and a lot of unanswered questions as we enter into the first quarter of 2018. The two main questions being:
What does tax reform mean for the markets in 2018?
We are now in the second longest economic expansion of ALL TIME!!! I know what goes up, eventually comes down. Are we overdue for a major correction in the stock market?
Without a crystal ball, no one knows for sure. However, the purpose of this article is to identify indicators in the economy and the financial markets that may help us gauge the direction of the U.S. economy and equity markets as we progress through 2018.
Tax Reform: Uncharted Waters
While tax reform is a welcome friend for corporate America, we have to acknowledge that this also puts us in uncharted waters. Looking back, there has never been a time in history where the U.S. has injected fiscal stimulus (tax reform) into an economy that is already healthy. The last major tax reform was in the early 1980’s when the U.S. economy was trying to dig itself out of the long 1970’s recession.
When the economy is in a recession, the U.S. can either inject fiscal stimulus or monetary stimulus to get the economy growing again. The U.S. used monetary stimulus to dig us out of the Great Recession of 2008 – 2009. They lowered interest rates to basically 0%, pumped cash into the economy in the form of bond buying, and provided a financial back stop for the U.S. banking system.
These economic stimulus tools are similar to the concept of giving a patient in a hospital a shot of adrenaline. If a patient is flat lining, it provides that patient with a huge surge of energy. The patient’s body goes from 0% to 60%+ in under a minute. So what happens when you give someone who is completely healthy a shot of adrenaline? Do they go from 100% to 110%? My point is a healthy patient does not go from 100% to 160%. Both patients get a boost but the boost to the healthy patient is much lower as a percentage of where they started.
While we have never given the U.S. economy an adrenaline shot after a long economic expansion, I think it’s reasonable to apply the same general concept as our two hospital patients. Tax reform may very well lead to another year of positive returns for the stock market in 2018 but I think it’s very important for investors to set a reasonable expectation of return for the U.S. equity markets given the fact that we are injecting growth into an economy that is already at “full employment”.
Not Enough Workers
One of the greatest challenges that the U.S. economy may face in 2018 is a shortage of qualified workers. Prior to tax reform being passed, companies both large and small, have had plenty of job openings but have not been able to find the employees with the skills necessary to fill those positions.
For example, if Apple had 1000 job openings in November 2017 just to meet the current demand for their goods and services but in 2018, due to tax reform, consumers have more money to spend, and the demand for Apple products increases further, Apple may need to find another 2000 employee to meet the increase in demand. They are having trouble now finding the 1000 employees to meet their current demand, how are they going to find another 2000 quick enough in 2018 to meet the increase in demand? If they can’t make the phones, they can’t sell the phones. Fewer sales equals less revenue, which equals less net profit, which may lead to a lower appreciation rate of the stock price. For disclosure purposes, I’m not picking on Apple. I’m just highlighting an issue that may be common among the companies that make up the S&P 500 Index if tax reform leads to a spike in demand in 2018. If Wall Street is expecting accelerated earnings, how are the companies expected to deliver those enhanced earnings without the employees that they need to increase supply?
The unemployment rate in the U.S. is currently 4.1%. You have to go all the way back to the late 1960’s to find an employment rate below 4%. So we are essentially at “full employment”.
Rising Wages
The blue line in the chart above is also very important. The blue line represents wage growth. This answers the question: "Are people making more for doing the same amount of work?" If you look back historically on the chart, when the unemployment rate was falling, typically wage growth was increasing. It makes sense. When the economy is good and the job market is healthy, companies have to pay their employees more to keep them. Otherwise they will go work for a competitor, who has 10 job openings, and they get paid more. Wage growth is good for employees but it's bad for companies. For companies, employee wages are usually their largest expense. If you increase wages, you are increasing expenses, which decreases profits. Lower profits typically results in lower stock prices. Companies in 2017 had the luxury of strong demand but limited wage growth. My guess is you will begin to see meaningful wage growth in 2018 as companies see an increase in demand as a result of tax reform and end up having to raise wages to retain and attract employees. This is just another reason why 2018 may be a good year for the stock market but not a great one.
What Fuels GDP Growth?
Gross Domestic Product ("GDP") is the economic indicator that is used to measure how much the U.S. economy produces in a year. It's how we gauge whether our economy is growing or contracting. Since March 2009, the GDP growth rate has averaged about 2.2% per year. This is subpar by historic standards. In most economic expansions, GDP is growing at an annual rate of 4%+.
Before we get into what pieces of tax reform may help to increase the GDP growth rate, let us first look at what GDP is made of. Our GDP is comprised of 5 categories (for my fellow econ nerds that assign 4 categories to GDP, we split capital spending into two separate categories):
Consumption or "Consumer Spending" 69.1%
Government Spending (includes defense) 17.3%
Investment (ex-housing) – "Business Spending 12.7%
Housing 3.8%
Net Exports -2.9%
Consumer Spending (+)
Consumer spending which makes up 69.1% of our GDP should increase as a result of tax reform in 2018. In general, if people have more discretionary income, they will spend all or a portion of it. Tax reform will lower the tax bill, for not all, but many U.S. households, increasing their disposable income. Also, if we see an increase in wage growth in 2018, people will be taking home more in their paychecks, allowing them to spend more.
Dr James Kelly, the chief economist of JP Morgan, made a very interesting observation about the evolution of the tax bill. When the tax bills were in their proposed state, one for the Senate and a separate bill for the House, each bill to stay under the $1.5 Trillion 10 year debt cap reduced taxes by about $150 Billion dollars per year. 50% of the annual tax reduction was going to businesses with the other 50% going to individual tax payers.
In order to get the bill passed before the end of the year, Congress was forced to shift a larger proportion of the $150 billion in tax brakes per year to individual taxpayers. In the tax bill’s final form, Dr Kelly estimated that approximately 75% of the tax reductions were now being retained by individual taxpayers with only 25% going to businesses. With a larger proportion of the tax breaks going to individual taxpayers that could increase the amount of discretionary income available to the U.S. consumer.
Government Spending (Push)
The anticipated increase in government spending really stems from the Trump agenda that has been communicated. One of the items that he campaigned on was increasing government spending on infrastructure. At this point we do not have many details as to when the infrastructure spending will begin or how much will be spent. Whatever ends up happening, we are not forecasting a dramatic increase or decrease in government spending in 2018.
Investment - Business Spending (+)
Even though business spending only represents 12.7% of our GDP, we could see a sizable increase in spending by businesses in 2018 for the following reasons:
Corporate tax rate is reduced from 35% to 21%
The repatriation tax will allow companies to bring cash back from overseas at a low tax rate
Prior to tax reform, companies already had historically high levels of cash on their balance sheet. What are they going to do with more cash? (See the chart below)
If having more cash was not a large enough incentive by itself for companies to spend money, the new tax rules allowing immediate expensing of the full cost of most assets purchased for the next five years should be. Under the current tax rules, when a business purchases a new piece of equipment, a fleet of trucks, office furniture, whatever it is, the IRS does not allow them to deduct 100% of purchase price in the year that they buy it. They have to follow a "depreciation schedule" and they can only realize a piece of that expense each year. The current tax rules put companies at a tax disadvantage because companies are always trying to shelter as much income as possible from taxation. If Company XYZ buys a piece of equipment that cost $1,000,000, the IRS may require Company XYZ to depreciate that expense over a 10 year period. Meaning they can only realize $100,000 in expenses each year over that 10 year period, even though they already paid the full $1,000,000 for that new piece of equipment.Under the new tax reform, if Company XYZ buys that same new piece of equipment for $1,000,000, they can deduct the full $1,000,000 expense against their income in 2018. Whoa!!! That's huge!! Yes it is and it's a big incentive for companies to spend money over the next five years.
Housing & Net Exports (Push)
We do not expect any significant change from either of these two categories and they represent the smallest portion of our total GDP.
Watch GDP In 2018
The GDP growth rate in 2018 may give us the first indication as to how many "extra innings" we have left in this already long bull market rally. If we do not see a meaningful acceleration in the annual growth rate of GDP above its 2.2% average rate, the rally could be very short lived. On the flip side, if due to tax reform consumer spending and business spending leaps forward in 2018 and 2019, we may be witnessing the longest economic expansion of all time. Time will tell.
Share Buybacks
You will undoubtedly hear a lot about “Share Buybacks” in 2018. Remember, U.S. corporations will most likely have piles of cash on their balance sheets. Instead of spending that money on hiring new employees, buying new equipment, or building a new plant, what else might they do with the cash? The answer, share buybacks.
If a public company like Nike has extra cash, they can go into the market, purchase their own stock, and then get rid of those outstanding shares. Basically it increases the earnings per share for the remaining shareholders.
Example: Let’s assume there are only 4 shares of Nike owned by 4 different people and Nike is worth $100,000. That means that each shareholder is entitled to 25% of that $100,000 or $25,000 each. Now because of tax reform, Nike has $50,000 of extra cash just sitting in its coffers that it otherwise would have paid to the government in taxes. Nike can go into the market with $50,000, purchase 2 shares back from 2 of the shareholders (assuming they would be willing to sell), and then “retire” those two outstanding shares. After that is done, there are 2 outstanding shares remaining but the value of Nike did not change. So the two remaining shareholders, without paying anything extra, now own 50% of Nike, and their shares are worth $50,000 each.
Share buyback may push stock prices higher from a simple math standpoint. If the formula is the value of the company divided by the number of shares outstanding, the fewer shares there are, assuming the value of the company stays the same, the price per share will go up. The incentive for these share buybacks will most likely be there in 2018. Not only will companies have the cash but share buybacks are a way that public companies can reward their current shareholders..
Is The Stock Market Too Expensive?
The P/E ratio of the S&P 500 Index is another barometer that investors will need to keep a close eye on in 2018. P/E ratios help us to answer the questions: “Is the stock market cheap, fairly valued, or expensive at this point?” The “Forward P/E Ratio” divides the price of a stock by the estimated future 12 months of earnings. The average Forward P/E ratio for the S&P 500 Index between December 1989 – September 30, 2017 was 16.0. As of December 22, 2017, the Forward P/E ratio of the S&P 500 Index is 19.99. In other words, it’s running at 25% above its 25 year historic average. See the chart below:
Conclusion, the U.S. stock market is not “cheap” and it’s a stretch to even classify it as “fairly valued”. I think we are well into what I would consider “expensive territory”. What does that mean for investors? You have to stay on your toes!!
Now, we have an anomaly in the mix with tax reform and history does not speak to how this could play out. If tax reform leads to an acceleration in corporate earnings, that in turn could slow the steady climb in the P/E ratio of the S&P 500 because earnings are the denominator in the formula. If stock prices and earnings are accelerating at the same pace, the stock market can go up without a further acceleration of the P/E ratio. Thus, keeping the stock market from becoming more overpriced and further increasing the risk of owning stocks in the S&P 500.
Summary
In 2018, investors should keep a close eye on the U.S. GDP growth rate, the level of spending by corporations and consumers, the volume of share buybacks by U.S. companies, and the P/E ratio of the S&P 500 Index.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Attention Middle Class: The End Is Near
I'm not a fan of conspiracy theories and I'm not a fan of "doom and gloom" articles. However, I feel compelled to write this article because I want people to be aware of a trend that is unfolding right now in our economy. This trend will strengthen over time, we will cheer for it as it's happening, but like many great things in history, it may have an
I'm not a fan of conspiracy theories and I'm not a fan of "doom and gloom" articles. However, I feel compelled to write this article because I want people to be aware of a trend that is unfolding right now in our economy. This trend will strengthen over time, we will cheer for it as it's happening, but like many great things in history, it may have an unintended consequence. I fear that the unintended consequence of this new trend will be the elimination of the U.S. middle class.
More Profits
I’m an investment advisor so I naturally love a strong bull market that results in large investment gains for our clients. The stock market generally goes up when companies are more profitable than the consensus expects. Higher profits equal higher stock prices which equal more wealth for investors. Corporations have become laser-focused on findings new ways to increase profits. This is important because businesses that struggle to make profits and have constant losses are not so successful and will probably end up shutting down in the near future, according to websites like https://www.laraedo.com/signs-that-my-business-is-ripe-for-a-shutdown/. The equation for net profit is easy:
Revenue – Expenses = Net Profit
Let me ask you this question: What is typically a company’s largest expense?
Answer: Payroll. Said another way, the employees. Salaries, benefits, the building to house the employees, training, workers comp, payroll taxes, and the list goes on and on. If you are the owner of a company that makes cell phones and I told you that I have a way that you can make TWICE as many cell phones with HALF the number of employees, what do you think is going to happen to profits? Up!!! In a big way.
The scenario that I just described is not something that might happen in the future, it’s something that is happening right now. Here is the data to support it.
The chart below compares the 10 largest companies in the S&P 500 Index in 1990 to the 10 largest companies in the S&P 500 in 2016. First, you may notice that none of the companies that were the largest in 1990 remained on the list in 2016. But here is the trend that I want to point out. When you look at the 10 largest companies in 1990, they produced $368 Billion dollars of revenue and employed 1.4 Million workers. Fast forward to 2016, the top 10 largest companies produced $1.2 Trillion dollars in revenue and employed about 1.6 Million workers. Now let’s do some quick math, between 1990 and 2016 the gross revenue of the largest 10 companies in the S&P 500 increased by 239% but the number of workers employed by those companies only increased by 14%. Companies are already doing more with less people.
Just when you thought things were going good for the company, I now come to you, the owner of the company, and tell you I have a way to make profits double within the next 3 years. Are you interested? Of course you are. All we have to do is buy these three machines that will replace another 50% of the employees. These machines work 24 hours a day, don’t need health insurance, don’t get sick, and we can move to a smaller building which will reduce rent by 60%. How is that possible? Welcome to the party…..artificial intelligence.
Not A Terminator Movie
What do we think of when we hear the words “artificial intelligence”? Terminators!! Fortunately for us that’s not the artificial intelligence that I’m referring too. But a machine that thinks and learns from its mistakes? The human mind is not as unique as we would like to think it is. Just take a Myers Briggs personality test. You answer 100 questions and then it tells you how you react to things, what annoys you, what your strengths are, how you communicate, and what you have difficulties with. It’s kind of scary as you read the results and realize “Yup. That’s me”
Think about it. Google may know more about you than your spouse. What do you want for Christmas? Your spouse may not know but Google knows all of the items that you looked at over the past 3 months, what items you spent the most time looking at, did you click on the description to read more, and what other items did you look at after you click on the initial item. It tells Google how you search for information. Also Google acknowledges that we all search for things differently and what we are searching for tells Google more about us. Essentially Google learns at little bit more about you every time you search for something via their website.
What about a machine that can respond to questions and it sounds just like a person when it speaks? Oh and it speaks perfect English. No more overseas call centers with people you can’t understand. With most call centers, there are probably 20 questions that represent 80% of all the questions asked. If the machine is unable to answer the question, it automatically routes that call to a living, breathing person. The programmers of the machines are notified when a question triggers a transfer to a live person, they listen to the call, and then update the software to be able to answer the question the next time it is asked. The easy math, this could reduce the number of customer service representatives that the company needs to employ by 80%. Oh and the number of employees will continue to decrease as the machines learn to answer more questions and the software gets more sophisticated.
While a company may go this direction to reduce expenses, we as the consumer will also champion this change. Think about how painful it is to call the cable company. What if I told you that when you call you won’t have to wait on hold, the “person” that you are speaking to will know how to resolve your problem, and you will be off the phone in less than 2 minutes. Time is a valuable commodity to us. Fix my problem and fix it quickly. If a machine can do that better than a real person, be my guest. If companies want it and we as the consumer want it, how fast do you think it’s going to happen?
I Can't Be Replaced By A Machine.....Wrong
While we will cheer how the new A.I. technology saves us time and makes life easier, many of us will have the hubris that “a machine can’t do what I do?”. While a machine may not be able to replace 100% of what you do, could it replace 50%? It’s going to be presented like this, “you know all of those daily tasks that you don’t like to do: paperwork, scanning forms, payroll, and preparing financial reports for the weekly managers meeting. Well you don’t have to do those anymore.” Yes!!!! Oh and more good news you don’t have to train a new employee to complete those tasks and wonder if they are going to leave a year from now and have to train someone else.
Programming a machine to complete a task is not too different from training a new employee. When you hire a new employee many of them may know very little about your industry, they have no idea how your company operates, how to answer tough questions from prospects, etc. You have to train them or “program” them. Then they learn on the job from there. The value of having 20 years of experience is you have seen many difficult situations throughout your career and you learned from your past experiences. The next time the same or similar problem surfaces you know how to react. Normally what you do is you teach those lessons to each new manager and employee over and over again. That takes time. What if you only had to teach that lesson one more time and every new employee already knew how to react in the same tough situation? That’s artificial intelligence.
My point, this trend will not be limited to just manufacturing or customer services. This new technology will eventually impact each of our careers in some way, shape, or form.
3 Stages
I expect this to happen in three stages.
Stage 1: Companies do MORE with only a FEW MORE employees
Stage 2: Companies do MORE with the SAME number of employees
Stage 3: Companies do MORE with LESS employees
We are already through Stage 1 and we are entering Stage 2. How long will it be before we reach stage 3? That’s anyone’s guess. But with most evolution, Stage 1 takes the longest and the following stages evolve more rapidly. If Stage 1 took 16 years, my guess would be that stage 3 will be here a lot sooner than we think.
So What Happens To All Of The Employees?
The million dollar question and I don't know the answer. If I had to guess, the current middle class is going to be divided into two. Half of the middle class is going move up into the "upper class" and the other half will be "unemployed". The level of education will be the dividing line. Companies will continue to do more with less people. The only way to stop it is to tell companies that need to stop trying to be more profitable. Good luck. Our entire economy is built on the premise that you should accumulate as much as you can as fast as you can.
War and Conflict
When I look back in history, major conflicts arise when there is a large deviation between the “Have’s” and the “Have Not’s”. The fancy name that is used today is “income inequality”. When you have a robust middle class, everyone has something to lose if a conflict arises because that conflict generally disrupts the current system, uncertainty prevails, the economy goes into a recession, people lose their job, and they in turn cannot make their mortgage payment.
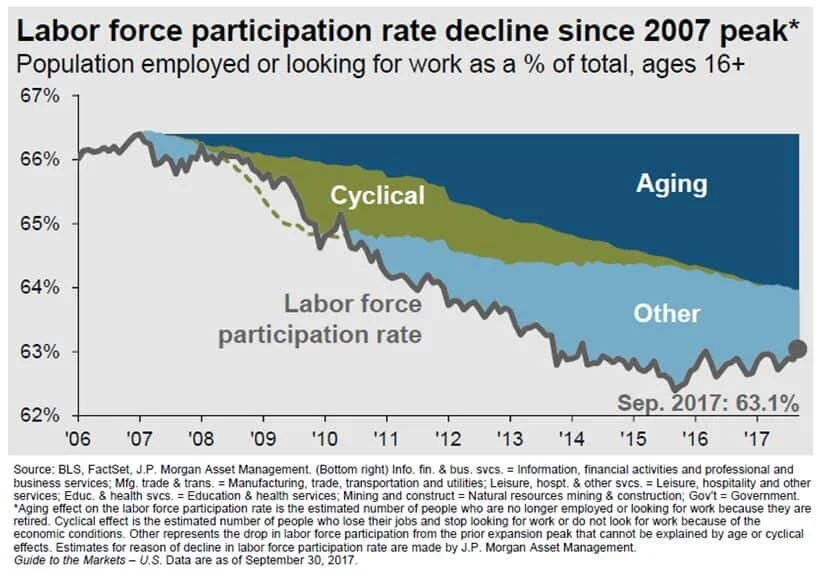
If instead, a majority of the population is unemployed and they can’t find a job because the jobs don’t exist anymore, that group of individuals has nothing to lose by burning the current system to the ground and rebuilding a new one from the ashes. I know that sounds dark but there is no arguing the gap between the Have’s and the Have Not’s is getting larger. Just look at the labor participation rate:
The Labor Participation Rate answers the question, how many people in the U.S. that could be working either are working or are looking for work? If there are individuals who could work, don’t have a job, and stop looking for work, they drop out of the labor force which decrease the labor participation rate because there are less citizens participating on the work force. As you can see in the chart above, in 2006 the labor participation rate was around 66%, and while we continue to experience one of the longest economic expansions of all time, the labor participation rate is still lower now than it was prior to the beginning of the economic recovery. Remember we are in an expansion and it has dropped by about 3%. What do you think will happen when we hit the next recession? While the baby boomer generation has had an impact on these numbers as you can see based on the large percentage of that decrease attributed to an “aging population”. Traditionally when someone retires, the company will promote the person below them and then hire another person to fill there spot. As many of us know, that’s not how it works anymore. Now that key employee retires, the company promotes one person into their role, but instead of hiring a new employee they just redistribute the work to the current staff. If anything, the baby boomer generation moving into retirement has made this transition to “do more with less people” easier on companies because they don’t have to fire anyone.
Tax Reform Will Accelerate The Trend
If you combine tax reform with the current 4.1% employment rate, I would expect this to accelerate the development of artificial intelligence. Companies are going to have cash from the tax savings to reinvest into new technologies which includes artificial intelligence. If the economy continues to grow at its current 2% pace or accelerates, one would expect consumption to increase which increases the demand for products and services. With the unemployment rate at 4.1%, we are already at "full employment". There are not enough qualified workers for companies to hire to meet the increase in demand for their product or service. The answer, let's accelerate the development of artificial intelligence that will allow the company to enter Phase 2 which is "Do MORE with the SAME number of workers".
People Will Cheer
These advances in technology are potentially setting the stage for levels of profitability that companies have only dreamed of. Higher profits traditionally equal higher stock prices. Investors will cheer this!! It may even lead us to the longest economic expansion of all time. In the short term, investors may have a lot to be excited about but we may look back years from now and realize that we were unintentionally cheering for the end of the middle class as we know it.
Again, this article is not meant to be a “dark cloud” or a new conspiracy theory but rather to keep our readers aware of the world that is changing rapidly around us. Like many of the economic challenges that the U.S. economy has experienced in the past, the hazard was in plain view, but investors failed to see it because they got caught up in the moment. When investing, it’s ok to take advantage of short term gains but never lose sight of the big picture.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
A Lesson From Bitcoin
I'm not writing this article to predict whether Bitcoin is going to $0 or $50,000. I have no idea whether it's going to go up or down from here. But I have had countless conversations with clients and friends over the past few weeks which starts like this "What do you think about Bitcoin?"My response is, before you make any type of investment, you should
I'm not writing this article to predict whether Bitcoin is going to $0 or $50,000. I have no idea whether it's going to go up or down from here. But I have had countless conversations with clients and friends over the past few weeks which starts like this "What do you think about Bitcoin?"
My response is, before you make any type of investment, you should be able to answer the following questions. If you can't answer these questions with confidence, you probably should not be investing in it.
"Explain It To Me In 30 Seconds"
Investing is as much of an art as it is a science which is why you can ask three different investment advisors about the same investment and get three different answers. While the full analysis of an investment can be complex and require a thorough understanding of markets, equity analysis, and financial reports, seasoned veterans have mastered their craft and have a way of simplifying the process. One of the lessons that I learned from my mentor and that I continue to apply to selecting investments today is "If you can't explain it to me in less than 30 seconds, I don't want to have anything to do with it."Before investing in anything, you should:
Develop an investment thesis
Identify the risks
Identify competitors
Know at what price to sell at
Let's look at each of these items and how they apply to the Bitcoin situation.
Develop an investment thesis
An investment thesis answers the question, why are you committing money to that particular investment? When buying a stock, you try to identify companies that have strong management, good cash flow, a promising new product or service, expanding market share, and a competitive advantage with the expectation that the company will outperform a given benchmark.
“Because I think it will go up” is not an investment thesis. You have to include in your investment thesis items that can be measured. If for example, I decide to invest in a cell phone company because they are expected to expand into China, India, and increase their market share over the next 3 years by 50%. I have identified a clear and measurable reason why I have chosen to invest in that company.
Bitcoin poses a challenge in this sense. When you invest in a company, you are essentially investing in the future cash flow that is expected to be produced by that company. Which is why the price to earnings ratio is often used to determine if a company is “reasonably priced”. Bitcoin is a currency that does not produce future cash flow so what metrics can you build into an investment thesis that will allow you to measure your expected outcome? I have yet to hear a good answer to that question. An “expert” making a prediction that Bitcoin is going to $30,000 is not a great metric to use. Remember, price appreciation is a by product of the improvement of the underlying financial drivers of an investment. If you can’t identify what those financial drivers are, price is irrelevant.
Identify the risks
Before making any investment, you should be able to take out a sheet of paper and list of the risks to your investment thesis. If you don’t know the risks, how do you know when to get out of that investment? In my cell phone company example, I bought that stock because I expected that company to gain 50% of the cell phone market share in China & India over the next 3 years. What are the risks to that investment thesis?
Currency risk: The value of the U.S. dollar increases versus the local currency decreasing profits
Execution risk: They do not successfully execute their strategy. It takes 5 years instead of 3.
Political risk: The Chinese government assumes ownership of the company
Market risk: The global economy goes into a recession
Competitor risk: Another reputable cell phone company enters that market
Management risk: The current CEO leaves the company and the new CEO takes the company in a different direction
Cash flow risk: The company takes on too much debt trying to expand and has to scale back
While everyone goes into a new investment with the hopes and dreams that it is the next Apple, you have to be able to identify what could send your great investment tumbling to the ground.
Can you list all of the risks associated with Bitcoin? It could go to zero but that’s true of any investment. With many new technologies, services, currencies, and medical devices, you have too unfortunately accept the fact that all of the risks associated with that investment are probably not known. It does not necessarily mean it’s a bad investment since most breakthrough technology and products are met with resistance and then uniformly accepted by the masses down the road. But it does imply that the investment comes with a much higher level of risk because a greater number of unknowns exists and you have to be able to live with the fact that it has just as much of a chance of going up by 100% as it does going to zero. While this line of thinking may not completely deter you from making a particular investment, it will hopefully influence the amount that you decide to commit to riskier investments.
Identify Competitors
When identifying competitors, my first question is usually "how large are the barriers to entry into are particular product or market?" The larger the barriers to entry, the longer it takes competitors to catch up to the market leaders. It would seem in the case of Bitcoin, that the barriers to entry for cryptocurrencies are fairly low. I'm already starting to hear the buzz at holiday parties about "ICO's" which stands for Initial Coin Offering. If I were looking to invest in Bitcoin, I would be asking the questions:
Who are the other main stream cryptocurrencies?
Do they have a competitive advantage over Bitcoin?
What would entice someone to switch from Bitcoin to another cryptocurrency?
How large is the cyptocurrency market?
Will regulations eventually come into play and create barriers to entry?
How many people that invested in Bitcoin do you think can answer these questions? My guess is not many. That in itself is risky.
Knowing At What Price To Sell
Of all the investment criteria that I have listed so far, I think this one is the most problematic when it comes to Bitcoin. When making any investment, you have to be able to answer the question: “Based on all of the information that I have today, at what price should I sell it at?” If I own a rental property and it’s fair market value is $250,000 and I collect $15,000 per year in rent, if someone offered me $300,000 to buy my rental property should I sell it? To answer that question, I would map out all of the income that I expect to receive from that property over my lifetime and apply a reasonable appreciation rate of the property value itself. It’s a similar process in evaluating a stock. You are looking at the annual earnings of the company and what you expect those earnings to be in the future. Both of these examples, like most investments, generate future cash flow and have reasonable appreciation rates that can be applied. With Bitcoin, as I mentioned earlier, there is no future cash flow. It’s value right now is being set based on what the next person is willing to buy it for. If one day people wake up and decide I don’t want to buy your Bitcoin or provide you with any good or services in exchange for your Bitcoin, there is nothing there. There are no earnings, there are no products, there are no services, there are no brick and mortar buildings, it’s vapor. With traditional currency, like the U.S. dollar, you have the taxing power and the assets of the United States government confirming that the dollar bill in your hand is worth something
So if I decide to buy Bitcoin today at $14,000 per coin, at what dollar amount should I sell it because it has become overvalued? I have no idea how anyone answers that question at this point. That’s problematic because if I start to make money, the difficult decision is “when do I get out?” When investing, it’s very easy to sell investments that have lost money. It’s emotionally much more difficult to sell your winners. So again, if I buy Bitcoin today and it goes to $30,000, do I sell it? Does it keep going to $50,000? I have absolutely nothing to based that on and that’s a problem.
Remember The Tulips
The single most important take away from this articles is "make sure you understand what you are investing in". If you can't explain it in less than 30 seconds, you probably should not be investing in it. Specific to Bitcoin, I use the saying, history does not repeat itself but it does rhyme. Some of the rhyming took place in the 1600's in the form of the Tulip bubble. In the Netherlands, during the Tulip mania, the cost of a tulip equaled to the cost of a house. Don't believe it? Just take a stroll down history lane. Here's the article: Tulip Mania
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Watch These Two Market Indicators
While a roaring economy typically rewards equity investors, the GDP growth rate in the U.S. has continued to grow at that same 2.2% pace that we have seen since the recovery began in March 2009. When you compare that to the GDP growth rates of past economic expansions, some may classify the current growth rate as “sub par”. As in the tale of the
While a roaring economy typically rewards equity investors, the GDP growth rate in the U.S. has continued to grow at that same 2.2% pace that we have seen since the recovery began in March 2009. When you compare that to the GDP growth rates of past economic expansions, some may classify the current growth rate as “sub par”. As in the tale of the tortoise and the hare, sometimes slow and steady wins the race.
The number one questions on investor’s minds: “It’s been a great rally but are we close to the end?” Referencing the chart below, if you look at the length of the current economic expansion, going back to 1900 we are now witnessing the 3rd longest economic expansion on record which is making investors nervous because as we all know that markets work in cycles.
However, if you ignore the “length” of the rally for a moment and look at the “magnitude” of the rally it would seem that total GDP growth of the current economic expansion has been relatively tame compared to some of the economic recoveries in the past. See the chart below. The chart shows evidence that there have been economic rallies in the past that were shorter in duration but greater in magnitude. This may indicate that we still have further to go in the current economic expansion.
What causes big rallies to end?
Looking back at strong economic rallies in the past, the rallies did not die of old age but rather there was an event that triggered the next recession. So we have to be able identify trends within the economic data that would suggest that the economic expansion has ended and it will lead to the next recession.
Watch these two indicators
Two of the main indicators that we monitor to determine where we are in the current economic cycle are the Leading Indicators Index and the Yield Curve. History rarely repeats itself but it does rhyme. Look at the chart of the leading indicators index below. The leading indicators index is comprised of multiple economic indicators that are considered “forward looking”, like housing permits. If there are a lot of housing permits being issues, then demand for housing must be strong, and a strong housing market could lead to further economic growth. Look specifically at 2006. The leading indicators went negative in 2006, over a year before the stock market peaked in 2007. This indicator was telling us there was a problem before a majority of investors realized that we were on the doorstep of the recession.
Let’s look at the second key indicator, the yield curve. You will hear a lot about the “slope of the yield curve” in the media. In a healthy economy, long term interest rates are typically higher than short term rates which results in a “positively slopped” yield curve. In other words, when you go to the bank and you have the choice of buying a 2 year CD or a 10 year CD, you would expect to receive a higher interest rate on the 10 year CD because they are locking up your money for 10 years instead of 2.
There are periods of time where the interest rate on a 10 year government bond will drop below the interest rate on a 2 year government bond which is considered an “inverted yield curve”. Why does this happen and why would investors by that 10 year bond that is yielding less than the 2 year bond? This happens because bond investors are predicting an economic slowdown in the foreseeable future. They want to lock in the current 10 year interest rate knowing that if the economy goes into a recession that the Fed may begin to lower the Fed Funds Rate which has a more rapid impact on short term rates. It’s a bet that the 2 year bond rate will drop below the 10 year bond rate within the next few years.
If you look at the historical chart of the yield curve above, the yield curve inverted prior to the recession in the early 2000’s and prior to the 2008 recession.
Looking at where we sit today, within the last 6 months the leading indicators index has not only been positive but it’s accelerating and the yield curve is still positively sloped. While we realize that there is not a single indicator that accurately predicts the end of a market cycle, these particular economic indicators have historically been helpful in predicting danger ahead.
There will always be uncertainty in the world. Currently it has taken the form of U.S, politics, tax reforms, geopolitical events, and global monetary policy but it would seem that based on the hard economic data here in the U.S. that our economic expansion that began in March 2009 may still have further to go.
About Michael.........
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.