Planning for Healthcare Costs in Retirement: Why Medicare Isn’t Enough
Healthcare often becomes one of the largest and most underestimated retirement expenses. From Medicare premiums to prescription drugs and long-term care, this article from Greenbush Financial Group explains why healthcare planning is critical—and how to prepare before and after age 65.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
When most people picture retirement, they imagine travel, hobbies, and more free time—not skyrocketing healthcare bills. Yet, one of the biggest financial surprises retirees face is how much they’ll actually spend on medical expenses.
Many retirees dramatically underestimate their healthcare costs in retirement, even though this is the stage of life when most people access the healthcare system the most. While it’s common to pay off your mortgage leading up to retirement, it’s not uncommon for healthcare costs to replace your mortgage payment in retirement.
In this article, we’ll cover:
Why Medicare isn’t free—and what parts you’ll still need to pay for.
What to consider if you retire before age 65 and don’t yet qualify for Medicare.
The difference between Medicare Advantage and Medicare Supplement plans.
How prescription drug costs can take retirees by surprise.
The reality of long-term care expenses and how to plan for them.
Planning for Healthcare Before Age 65
For those who plan to retire before age 65, healthcare planning becomes significantly more complicated—and expensive. Since Medicare doesn’t begin until age 65, retirees need to bridge the coverage gap between when they stop working and when Medicare starts.
If your former employer offers retiree health coverage, that’s a tremendous benefit. However, it’s critical to understand exactly what that coverage includes:
Does it cover just the employee, or both the employee and their spouse?
What portion of the premium does the employer pay, and how much is the retiree responsible for?
What out-of-pocket costs (deductibles, copays, coinsurance) remain?
If you don’t have retiree health coverage, you’ll need to explore other options:
COBRA coverage through your former employer can extend your workplace insurance for up to 18 months, but it’s often very expensive since you’re paying the full premium plus administrative fees.
ACA marketplace plans (available through your state’s health insurance exchange) may be an alternative, but premiums and deductibles can vary widely depending on your age, income, and coverage level.
In many cases, healthcare costs for retirees under 65 can be substantially higher than both Medicare premiums and the coverage they had while working. This makes it especially important to build early healthcare costs into your retirement budget if you plan to leave the workforce before age 65.
Medicare Is Not Free
At age 65, most retirees become eligible for Medicare, which provides a valuable foundation of healthcare coverage. But it’s a common misconception that Medicare is free—it’s not.
Here’s how it breaks down:
Part A (Hospital Insurance): Usually free if you’ve paid into Social Security for at least 10 years.
Part B (Medical Insurance): Covers doctor visits, outpatient care, and other services—but it has a monthly premium based on your income.
Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage): Also carries a monthly premium that varies by plan and income level.
Example:
Let’s say you and your spouse both enroll in Medicare at 65 and each qualify for the base Part B and Part D premiums.
In 2025, the standard Part B premium is approximately $185 per month per person.
A basic Part D plan might average around $36 per month per person.
Together, that’s about $220 per person, or $440 per month for a couple—just for basic Medicare coverage. And this doesn’t include supplemental or out-of-pocket costs for things Medicare doesn’t cover.
NOTE: Some public sector or state plans even provide Medicare Part B premium reimbursement once you reach 65—a feature that can be extremely valuable in retirement.
Medicare Advantage and Medicare Supplement Plans
While Medicare provides essential coverage, it doesn’t cover everything. Most retirees need to choose between two main options to fill in the gaps:
Medicare Advantage (Part C) plans, offered by private insurers, bundle Parts A, B, and often D into one plan. These plans usually have lower premiums but can come with higher out-of-pocket costs and limited provider networks.
Medicare Supplement (Medigap) plans, which work alongside traditional Medicare, help pay for deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance.
It’s important not to simply choose the lowest-cost plan. A retiree’s prescription needs, frequency of care, and preferred doctors should all factor into the decision. Choosing the cheapest plan could lead to much higher out-of-pocket expenses in the long run if the plan doesn’t align with your actual healthcare needs.
Prescription Drug Costs: A Hidden Retirement Expense
Prescription drug coverage is one of the biggest cost surprises for retirees. Even with Medicare Part D, out-of-pocket expenses can add up quickly depending on the medications you need.
Medicare Part D plans categorize drugs into tiers:
Tier 1: Generic drugs (lowest cost)
Tier 2: Preferred brand-name drugs (moderate cost)
Tier 3: Specialty drugs (highest cost, often with no generic alternatives)
If you’re prescribed specialty or non-generic medications, you could spend hundreds—or even thousands—per month despite having coverage.
To help, some states offer programs to reduce these costs. For example, New York’s EPIC program helps qualifying seniors pay for prescription drugs by supplementing their Medicare Part D coverage. It’s worth checking if your state offers a similar benefit.
Planning for Long-Term Care
One of the most misunderstood aspects of Medicare is long-term care coverage—or rather, the lack of it.
Medicare only covers a limited number of days in a skilled nursing facility following a hospital stay. Beyond that, the costs become the retiree’s responsibility. Considering that long-term care can easily exceed $120,000 per year, this can be a major financial burden.
Planning ahead is essential. Options include:
Purchasing a long-term care insurance policy to offset future costs.
Self-insuring, by setting aside savings or investments for potential care needs.
Planning to qualify for Medicaid through strategic trust planning
Whichever route you choose, addressing long-term care early is key to protecting both your assets and your peace of mind.
Final Thoughts
Healthcare is one of the largest—and most underestimated—expenses in retirement. While Medicare provides a foundation, retirees need to plan for premiums, prescription costs, supplemental coverage, and potential long-term care needs.
If you plan to retire before 65, early planning becomes even more critical to bridge the gap until Medicare begins. By taking the time to understand your options and budget accordingly, you can enter retirement with confidence—knowing that your healthcare needs and your financial future are both protected.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why isn’t Medicare enough to cover all healthcare costs in retirement?
While Medicare provides a solid foundation of coverage starting at age 65, it doesn’t pay for everything. Retirees are still responsible for premiums, deductibles, copays, prescription drugs, and long-term care—expenses that can add up significantly over time.
What should I do for healthcare coverage if I retire before age 65?
If you retire before Medicare eligibility, you’ll need to bridge the gap with options like COBRA, ACA marketplace plans, or employer-sponsored retiree coverage. These plans can be costly, so it’s important to factor early healthcare premiums and out-of-pocket expenses into your retirement budget.
What are the key differences between Medicare Advantage and Medicare Supplement plans?
Medicare Advantage (Part C) plans combine Parts A, B, and often D, offering convenience but limited provider networks. Medicare Supplement (Medigap) plans work alongside traditional Medicare to reduce out-of-pocket costs. The right choice depends on your budget, health needs, and preferred doctors.
How much should retirees expect to pay for Medicare premiums?
In 2025, the standard Medicare Part B premium is around $185 per month, while a basic Part D plan averages about $36 monthly. For a married couple, that’s roughly $440 per month for both—before adding supplemental coverage or out-of-pocket expenses. These costs should be built into your retirement spending plan.
Why are prescription drugs such a major expense in retirement?
Even with Medicare Part D, out-of-pocket drug costs can vary widely based on your prescriptions. Specialty and brand-name medications often carry high copays. Programs like New York’s EPIC can help eligible seniors manage these costs by supplementing Medicare coverage.
Does Medicare cover long-term care expenses?
Medicare only covers limited skilled nursing care following a hospital stay and does not pay for most long-term care needs. Since extended care can exceed $120,000 per year, retirees should explore options like long-term care insurance, Medicaid planning, or setting aside savings to self-insure.
How can a financial advisor help plan for healthcare costs in retirement?
A financial advisor can estimate future healthcare expenses, evaluate Medicare and supplemental plan options, and build these costs into your retirement income plan. At Greenbush Financial Group, we help retirees design strategies that balance healthcare needs with long-term financial goals.
Special Tax Considerations in Retirement
Retirement doesn’t always simplify your taxes. With multiple income sources—Social Security, pensions, IRAs, brokerage accounts—comes added complexity and opportunity. This guide from Greenbush Financial Group explains how to manage taxes strategically and preserve more of your retirement income.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
You might think that once you stop working, your tax situation becomes simpler — after all, no more paychecks! But for many retirees, taxes actually become more complex. That’s because retirement often comes with multiple income sources — Social Security, pensions, pre-tax retirement accounts, brokerage accounts, cash, and more.
At the same time, retirement can present unique tax-planning opportunities. Once the paychecks stop, retirees often have more control over which tax bracket they fall into by strategically deciding which accounts to pull income from.
In this article, we’ll cover:
How Social Security benefits are taxed
Pension income rules (and how they vary by state)
Taxation of pre-tax retirement accounts like IRAs and 401(k)s
Developing an efficient distribution strategy
Special tax deductions and tax credits for retirees
Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) planning
Charitable giving strategies, including QCDs and donor-advised funds
How Social Security Is Taxed
Social Security benefits may be tax-free, partially taxed, or mostly taxed — depending on your provisional income. Provisional income is calculated as:
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) + Nontaxable Interest + ½ of Your Social Security Benefits.
Here’s a quick summary of how benefits are taxed at the federal level:
While Social Security is taxed at the federal level, most states do not tax these benefits. However, a handful of states — including Colorado, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, Rhode Island, Utah, and Vermont — do impose some form of state tax on Social Security income.
Pension Income
If you’re fortunate to receive a state pension, your state of residence plays a big role in determining how that income is taxed.
If you have a state pension and continue living in the same state where you earned the pension, many states exclude that income from state tax.
However, with state pensions, if you move to another state, and that state has income taxation at the stateve level, your pension may become taxable in your new state of domicile.
If you have a pension with a private sector employer, often times those pension payment are full taxable at both the federal and state level.
Some states also provide preferential treatment for private pensions or IRA income. For example, New York excludes up to $20,000 per person in pension or IRA distributions from state income tax each year — a significant benefit for retirees managing taxable income.
Taxation of Pre-Tax Retirement Accounts
Pre-tax retirement accounts — including Traditional IRAs, 401(k)s, 403(b)s, and inherited IRAs — are typically taxed as ordinary income when distributions are made.
However, the tax treatment at the state level varies:
Some states (like New York) exclude a set amount – for example New York excludes the first $20,000 per person per year — from state taxation.
Others tax all pre-tax distributions in full.
A few states offer income-based exemptions or reduced rates for lower-income retirees.
Because these rules differ so widely, it’s important to research your state’s tax laws.
Developing a Tax-Efficient Distribution Strategy
A well-designed distribution strategy can make a big difference in how much tax you pay throughout retirement.
Many retirees have income spread across:
Pre-tax accounts (401(k), IRA)
After-tax brokerage accounts
Roth IRAs
Social Security
Let’s say you need $70,000 per year to maintain your lifestyle. Some of that may come from Social Security, but you’ll need to decide where to withdraw the rest.
With smart planning, you can blend withdrawals from different accounts to minimize your overall tax liability and control your tax bracket year by year. The goal isn’t just to reduce taxes today — it’s to manage them over your lifetime.
Special Deductions and Credits in Retirement
Your Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) or Modified AGI doesn’t just determine your tax bracket — it also affects which deductions and credits you can claim.
A few important highlights:
The Big Beautiful Tax Bill that just passed in 2025 introduces a new Age 65+ tax deduction of $6,000 per person over and above the existing standard deduction.
Certain deductions and credits, however, phase out once income exceeds specific thresholds.
Your income level also affects Medicare premiums for Parts B and D, which increase if your income surpasses the IRMAA thresholds (Income-Related Monthly Adjustment Amount).
Managing your taxable income through careful distribution planning can therefore help preserve deductions and keep Medicare premiums lower.
Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) Planning
Once you reach age 73 or 75 (depending on your birth year), you must begin taking Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) from your pre-tax retirement accounts — even if you don’t need the money.
These RMDs can significantly increase your taxable income, especially when stacked on top of Social Security and other income sources.
A proactive strategy is to take controlled distributions or perform Roth conversions before RMD age. Doing so can reduce the size of your future RMDs and potentially lower your lifetime tax bill by spreading taxable income across more favorable tax years.
Charitable Giving Strategies
Many retirees are charitably inclined, but since most take the standard deduction, they don’t receive an additional tax benefit for their donations.
There are two primary strategies to consider:
Donor-Advised Funds (DAFs) – You can “bunch” several years’ worth of charitable giving into one tax year to exceed the standard deduction, then direct the funds to charities over time.
Qualified Charitable Distributions (QCDs) – Once you reach age 70½, you can donate directly from your IRA to a qualified charity. These QCDs are excluded from taxable income and count toward your RMD once those begin.
Final Thoughts
Retirement opens up new opportunities — and new complexities — when it comes to managing taxes. Understanding how your various income sources interact and planning your distributions strategically can help you:
Reduce taxes over your lifetime
Preserve more of your retirement income
Maintain flexibility and control over your financial future
As always, it’s wise to coordinate with a financial advisor and tax professional to ensure your retirement tax strategy aligns with your goals, income sources, and state tax rules.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How are Social Security benefits taxed in retirement?
Depending on your provisional income, up to 85% of your Social Security benefits may be subject to federal income tax. Most states don’t tax these benefits, though a few—including Colorado, Minnesota, and Utah—do.
How is pension income taxed, and does it vary by state?
Pension income is typically taxable at the federal level, but state rules differ. Some states exclude public pensions from taxation or offer partial exemptions—like New York’s $20,000 per person exclusion for pension or IRA income. If you move to another state in retirement, your pension’s tax treatment could change.
What taxes apply to withdrawals from pre-tax retirement accounts?
Distributions from Traditional IRAs, 401(k)s, and similar pre-tax accounts are taxed as ordinary income. Some states offer exclusions or partial deductions, while others tax these withdrawals in full. Understanding your state’s rules is essential for accurate tax planning.
What is a tax-efficient withdrawal strategy in retirement?
A tax-efficient strategy blends withdrawals from different account types—pre-tax, Roth, and after-tax—to control your annual tax bracket. The goal is not just to lower taxes today but to reduce lifetime taxes by managing income across multiple years and minimizing required minimum distributions later.
What new tax deductions or credits are available for retirees?
The 2025 tax law introduced an additional $6,000 deduction per person age 65 and older, in addition to the standard deduction. Keeping taxable income lower through smart planning can also help retirees preserve deductions and avoid higher Medicare IRMAA surcharges.
How do Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs) impact taxes?
Starting at age 73 or 75 (depending on birth year), retirees must withdraw minimum amounts from pre-tax retirement accounts, which increases taxable income. Performing partial Roth conversions or strategic withdrawals before RMD age can help reduce future tax exposure.
What are Qualified Charitable Distributions (QCDs) and how do they work?
QCDs allow individuals age 70½ or older to donate directly from an IRA to a qualified charity, satisfying all or part of their RMD while excluding the amount from taxable income. This strategy helps maximize charitable impact while reducing taxes in retirement.
Special Rules for S-Corps with Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans
Missing a Required Minimum Distribution can feel overwhelming, but the rules have changed under SECURE Act 2.0. In this article, we explain how to correct a missed RMD, reduce IRS penalties, and file the right tax forms to stay compliant.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
S-Corporations can be an excellent structure for small business owners, especially from a tax perspective. But when it comes to retirement plans—such as 401(k)s and profit-sharing plans—S-Corps play by a slightly different set of rules compared to other business entities. Understanding these differences is critical for maximizing retirement savings and avoiding unpleasant surprises.
In this article, we’ll cover:
How compensation is defined for S-Corp owners in a retirement plan
Why relying too heavily on distributions can limit retirement savings
The impact of employer contributions for S-Corp owners with staff
Timing considerations for employee deferrals in S-Corps versus pass-through entities
A practical example that shows how these rules work in real life
W-2 Wages Drive Retirement Contributions for S-Corp Owners
Here’s the key difference:
Partnerships and sole proprietorships – Contributions are based on total pass-through earnings from the business.
S-Corporations – Contributions are based only on W-2 wages paid to the owner.
This matters because many S-Corp owners try to minimize their W-2 salary and take more of their income in shareholder distributions. Distributions avoid payroll taxes, which can be a big tax advantage. But retirement plans only look at W-2 wages when calculating contribution limits.
Example: High Income, Low W-2
Suppose an S-Corp owner earns $500,000 total income, but only pays themselves $100,000 in W-2 wages.
Maximum employer contribution = 25% of W-2 wages = $25,000
Add employee salary deferral = up to $23,500 (2025 limit, or $31,000 if age 50+)
Total = roughly $48,500 (or $56,000 with catch-up)
That’s far below the 2025 annual addition limit of $70,000 ($77,500 with catch-up). By keeping W-2 wages artificially low, the owner unintentionally caps their retirement contributions.
The Ripple Effect on Employees
If the owner sets their employer contribution at 25% of W-2 compensation, that percentage generally applies to eligible employees as well.
In our example, if the owner receives a 25% contribution on $100,000 ($25,000), employees may also need to receive a large employer contribution for the plan to pass testing.
For a company with multiple employees, this can become a very expensive retirement plan design.
Timing of Deferrals: Another S-Corp Quirk
Another important difference involves the timing of employee salary deferrals:
S-Corp owners are on payroll, so any employee deferrals must be processed through payroll no later than the final paycheck in December. If you wait until after year-end, it’s too late to make employee deferrals for that tax year.
Partnership or sole proprietor owners may have more flexibility, since contributions can often be made up to the tax filing deadline (with extensions) and still count toward the prior year.
Translation: If you’re an S-Corp owner, don’t wait until tax season to think about retirement contributions. Deferrals need to be in place before December 31st.
Key Takeaways for S-Corp Owners
Only W-2 wages count toward retirement contributions, not shareholder distributions.
Keeping W-2 wages too low may limit your ability to maximize contributions.
Large employer contributions for the owner can trigger equally large contributions for employees.
Employee salary deferrals must run through payroll and be completed by the last December paycheck.
Careful planning throughout the year—not just at tax time—is essential.
If you’re an S-Corp owner considering a retirement plan, make sure your payroll and compensation strategy aligns with your retirement savings goals. The right plan design can help you strike a balance between tax efficiency today and meaningful retirement wealth in the future.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How do retirement plan contributions work for S-Corporation owners?
For S-Corp owners, retirement contributions are based only on W-2 wages—not total business income or shareholder distributions. This makes salary decisions especially important for maximizing 401(k) or profit-sharing plan contributions.
Why can keeping W-2 wages low hurt retirement savings for S-Corp owners?
While taking more income as shareholder distributions can reduce payroll taxes, it also limits how much you can contribute to a retirement plan. Employer contributions are capped at 25% of W-2 wages, so a lower salary means smaller allowable contributions.
How do employer contributions for owners affect employees in an S-Corp retirement plan?
If an owner contributes a high percentage of their W-2 income (such as 25%), nondiscrimination testing may require giving the same percentage to eligible employees. This can significantly increase plan costs for businesses with multiple staff members.
When must S-Corp owners make 401(k) salary deferrals?
Employee deferrals must be processed through payroll no later than the final paycheck of the year. Unlike partnerships or sole proprietors, S-Corp owners cannot make deferrals after December 31 for the prior tax year.
Can S-Corp owners include distributions when calculating 401(k) contributions?
No. Only W-2 wages qualify for retirement plan contribution calculations. Distributions from the S-Corp are not considered “earned income” for 401(k) or profit-sharing purposes.
What steps should S-Corp owners take to maximize retirement contributions?
Plan ahead by setting a reasonable W-2 salary that supports both tax efficiency and contribution goals. Coordinate payroll timing, plan design, and employee testing requirements with your tax advisor and retirement plan administrator early in the year.
How to Correct Missed Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs)
Missing a Required Minimum Distribution can feel overwhelming, but the rules have changed under SECURE Act 2.0. In this article, we explain how to correct a missed RMD, reduce IRS penalties, and file the right tax forms to stay compliant.
By Michael Ruger, CFP®
Partner and Chief Investment Officer at Greenbush Financial Group
Missing a Required Minimum Distribution (RMD) can cause a lot of stress, especially when you hear the words IRS excise tax. Fortunately, the rules around missed RMDs were updated under the SECURE Act 2.0, which provides some relief compared to the old law. In this article, we’ll break down:
What happens if you miss an RMD and how to correct it
The updated excise tax penalties under SECURE Act 2.0
The “first year” April 1st rule and why you may need to take two RMDs in one year
The new IRS guidance for beneficiaries who inherit retirement accounts
What tax forms need to be filed if you miss an RMD
A quick before-and-after look at the old rules versus SECURE Act 2.0
What Happens if You Miss an RMD?
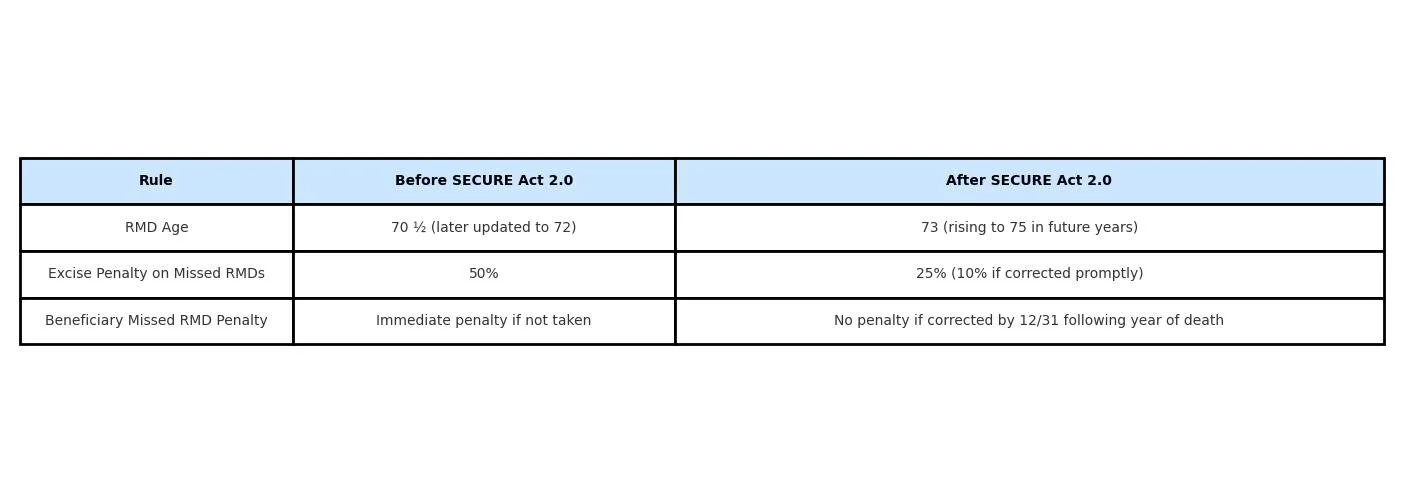
If you forget to take an RMD, the IRS assesses an excise tax penalty on the amount you should have withdrawn. Under the old law, that penalty was steep—50% of the missed RMD.
Under SECURE Act 2.0, the penalty was reduced to a much more manageable amount:
25% penalty on the missed distribution.
If corrected quickly (by taking the missed RMD and filing the proper paperwork), the penalty may be further reduced to 10%.
Example: If you missed a $10,000 RMD:
Old rule: You owed $5,000 in penalties.
New rule: You may owe only $1,000 (if corrected promptly).
The First-Year April 1st Rule
When you reach RMD age (currently age 73 under SECURE Act 2.0), your very first required distribution doesn’t have to be taken in that calendar year. Instead, you can delay it until April 1st of the following year.
But here’s the catch: if you delay your first RMD, you’ll still need to take two RMDs in that next year—the delayed one (by April 1st) plus the regular one (by December 31st).
Example:
Jane turns 73 in 2025.
She can delay her first RMD until April 1, 2026.
If she does, she must also take her 2026 RMD by December 31, 2026—meaning two taxable distributions in one year.
IRS Relief for Inherited Accounts (New Guidance)
For beneficiaries of inherited IRAs or retirement accounts, the IRS just issued new guidance under SECURE Act 2.0.
If a decedent had an RMD due in the year of their death and it wasn’t taken, the beneficiary must still withdraw it. However, the IRS has clarified that as long as the missed RMD is taken by December 31st of the year following the decedent’s death, no excise penalty will be assessed.
This is a significant update and provides more flexibility for beneficiaries who may be navigating a difficult time.
Before SECURE Act 2.0 vs. After
Filing Tax Forms for Missed RMDs
If you missed an RMD, you need to do two things:
Take the missed distribution as soon as possible.
File Form 5329 with your federal tax return to report the missed RMD and calculate the excise penalty.
If you qualify for the reduced 10% penalty, you’ll indicate this on Form 5329.
The actual RMD amount you withdraw will be reported on your Form 1099-R and included in your taxable income for the year you take it.
In some cases, the IRS has historically waived penalties if you can show “reasonable cause” for missing the RMD and that you’ve corrected the mistake. While SECURE Act 2.0 made the penalties less severe, requesting a waiver may still be an option worth considering with your tax professional.
Key Takeaways
SECURE Act 2.0 lowered the penalty for missed RMDs from 50% down to 25% (or 10% if fixed promptly).
The first-year April 1st rule gives you some flexibility but may cause two RMDs in one year.
Beneficiaries now have until December 31st of the year following the decedent’s death to take missed RMDs without penalty.
File Form 5329 to report missed RMDs and claim reduced penalties.
Missing an RMD isn’t ideal, but it’s not the end of the world—especially under the updated SECURE Act 2.0 rules. The most important step is to correct it quickly and make sure you file the proper paperwork with your tax return.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What happens if you miss a Required Minimum Distribution (RMD)?
If you miss an RMD, the IRS may assess an excise tax penalty on the amount that should have been withdrawn. Under SECURE Act 2.0, the penalty is now 25% of the missed amount, reduced to 10% if you correct the mistake promptly by taking the distribution and filing the appropriate tax form.
How did SECURE Act 2.0 change the penalties for missed RMDs?
Previously, missing an RMD triggered a 50% penalty on the shortfall. SECURE Act 2.0 lowered this to 25%, with a further reduction to 10% if the missed distribution is corrected in a timely manner. This change provides much-needed relief for retirees who make honest errors.
What is the April 1st rule for first-year RMDs?
When you first reach RMD age (currently 73), you can delay your initial withdrawal until April 1st of the following year. However, doing so means you must take two RMDs that year—the delayed one and the new year’s required amount—potentially increasing your taxable income.
What are the new IRS rules for inherited IRAs and missed RMDs?
If a deceased account owner had an RMD due in the year of death, the beneficiary must still take that distribution. Under new guidance, if the missed RMD is taken by December 31st of the year following the death, no excise penalty will apply.
What should you do if you missed an RMD?
Take the missed distribution as soon as possible and file IRS Form 5329 with your tax return to report the oversight and calculate any applicable penalty. Your financial or tax advisor can help determine if you qualify for the reduced 10% penalty or a possible waiver.
Can the IRS waive the RMD penalty entirely?
Yes. The IRS may waive the penalty if you can demonstrate reasonable cause for missing the RMD and show that you corrected the issue promptly. While SECURE Act 2.0 reduced the penalties, requesting a waiver may still be worthwhile in some cases.
Beneficiaries May Need To Take An RMD From A Decedent’s IRA In The Year They Pass Away
A common mistake that beneficiaries of retirement accounts make when they inherit either a Traditional IRA or 401(k) account is not knowing that if the decedent was required to take an RMD (required minimum distribution) for the year but did not distribute the full amount before they passed, the beneficiaries are then required to withdrawal that amount from the retirement account prior to December 31st of the year they passed away. Not taking the RMDs prior to December 31st could trigger IRS penalties unless an exception applies.
A common mistake that beneficiaries of retirement accounts make when they inherit either a Traditional IRA or 401(k) account is not knowing that if the decedent was required to take an RMD (required minimum distribution) for the year but did not distribute the full amount before they passed, the beneficiaries are then required to withdrawal that amount from the retirement account prior to December 31st of the year they passed away. Not taking the RMDs prior to December 31st could trigger IRS penalties unless an exception applies.
The RMD Requirement for the Decedent
Once you reach a specific age, the IRS requires taxpayers to begin taking mandatory annual distributions from their pre-tax retirement account each year. These mandatory annual distributions are called RMDs or required minimum distributions. The age at which an individual is required to begin taking RMDs is also referred to as the “Required Beginning Date” (RBD). The Required Beginning Date is based on your date of birth:
Born 1950 or earlier: Age 72
Born 1951 – 1959: Age 73
Born 1960 or later: Age 75
Example: If Jim was born in 1951 and turns age 73 this year, and Jim has a Traditional IRA with a $500,000 balance, in 2024, Jim would be required to withdraw $18,867 from his IRA as his annual RMD and pay tax on the distribution.
Undistributed RMD Amount When Someone Passes Away
It’s a common situation for an individual who has reached their Required Beginning Date for RMDs to pass away prior to distributing the required amount from their IRA account for that calendar year.
Example: Jen is age 81; she passed away in February 2024 with a $300,000 balance in her Traditional IRA. Her RMD amount for 2024 would be $15,463. If Jen only distributed $3,000 from her IRA prior to passing away in February, the beneficiary or beneficiaries of Jen’s IRA would be required to withdraw the remaining amount of her RMD, $12,463, prior to December 31, 2024, otherwise the beneficiaries will be faced with a 10% to 25% excise tax on the amount of the RMD that was not withdrawn prior to December 31st.
A Single Beneficiary
If there is only one beneficiary that is inheriting the entire account balance, the process is easy: determine the remaining amount of the decedent’s RMD, and then process the remaining RMD amount from the IRA account prior to December 31st of the year that they passed away.
Multiple Beneficiaries
When there are multiple beneficiaries of a pre-tax retirement account, the IRS recently released new regulations clarifying a question that has been in existence for a very long time.
The question has been, “If there are multiple beneficiaries of a retirement account, does EACH beneficiary need to distribute an equal share of the decedent’s remaining RMD amount OR do they collectively just have to make sure the remaining RMD amount was distributed but it does not have to be in equal shares?”
I’ll show you why this matters in an example:
Susan passed away before taking her $20,000 RMD for the year. She has a $200,000 balance in her Traditional IRA, and her two kids, Scott and Wanda, are both 50% primary beneficiaries on her account. The kids set up separate inherited IRAs and transfer their $100,000 shares into their respective accounts. Scott intends to take a $50,000 distribution from his Inherited IRA, pay the tax, and buy a boat, but Wanda, who is a high-income earner, wants to avoid taking taxable distributions from her Inherited IRA until after she retires.
Since Scott took enough out of his Inherited IRA to cover Susan’s full $20,000 undistributed RMD in the year she passed, is Wanda relieved of having to take an RMD from her account in the year that Susan passed, or does she still need to distribute her $10,000 share of the $20,000 RMD?
The new IRS regulations state that the decedent’s undistributed RMD amount is allowed to be satisfied by “any beneficiary” in the year that they pass away. Meaning the RMD does not have to be distributed in equal amounts to each beneficiary, as long as the total remaining RMD amount is distributed by one or more of the beneficiaries of the decedent.
In the example above, if Scott processed $50,000 from his inherited IRA in the year that Susan passed, Wanda would not be required to take a distribution from her inherited IRA that year because Susan’s $20,000 remaining RMD amount is deemed to be fulfilled.
A Decedent With Multiple IRAs
It’s not uncommon for an individual to have more than one Traditional IRA account when they pass away. The question becomes if they have multiple IRAs and each of those IRAs has an undistributed RMD amount at the time the decedent passes away, can the beneficiaries total up all of the undistributed RMD amounts and take the full amount from one single IRA account OR do they have to take the undistributed RMD amount from each IRA account?
The answer is “it depends”. It depends on whether the beneficiaries are the same or different for each of their IRA accounts.
Multiple IRAs – Same Beneficiaries
If the decedent has multiple IRAs but the beneficiaries are exactly the same as all of their IRAs, then the beneficiaries are allowed to aggregate the undistributed RMD amounts together and distribute that amount from any IRA or IRAs that they choose before the end of the year.
Multiple IRAs – Different Beneficiaries
However, in the instance that the decedent has multiple IRAs but has different beneficiaries listed amongst the different IRA accounts, then the decedent’s undistributed RMD amount needs to be taken from each IRA account.
Privacy Issue with Multiple Beneficiaries
I have been a financial planner long enough to know that not all family members get along after someone passes away. If the decedent had an undistributed RMD amount in the year that they passed and the beneficiaries are not openly sharing their plans regarding how much they plan to withdraw out of their inherited IRA in the year the decedent passed away, it may be impossible to coordinate the disproportionate distributions between the multiple beneficiaries defaulting the beneficiary to taking their equal share of the undistributed RMD amount.
IRS Penalty For Missing RMD
If the beneficiaries fail to distribute the decedent’s remaining RMD amount before December 31st of the year that they pass away, then the IRS will assess a 25% penalty against the amount that was not timely distributed from the IRA account.
Special Note: The IRS penalty is reduced to 10% if corrected in a timely fashion.
Automatic Waiver of the RMD Penalty
The final regulations released by the IRS in 2024 granted a very favorable automatic waiver of the missed RMD penalty that did not exist prior to July 2024. The automatic waiver originally stemmed from the common scenario that if the decedent passed away in December and had not yet satisfied their RMD amount for the year, it was often difficult for the beneficiaries to work with the custodians of the IRA to get those distributions processed prior to December 31st. However, the IRS, being oddly gracious, now provides beneficiaries with an automatic waiver of the missed RMD penalty, specifically for undistributed RMD amounts for a decedent, up until December 31st of the year AFTER the decedent’s death to satisfy the RMD requirement.
When Is No RMD Required?
I have gone through numerous scenarios without stating the obvious. If the decedent either died before their Required Beginning Date for RMDs or if they died AFTER their Required Beginning Date but distributed their full RMD amount prior to passing away, the beneficiaries are not required to distribute anything from the decedent’s IRA prior to December 31st in the year that they passed away.
Also, if the Decedent had a Roth IRA, Roth IRAs do not have an RMD requirement, so the beneficiaries of the Roth IRA would not be required to take an RMD prior to December 31st in the year the decedent passes away.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What happens if someone dies before taking their full RMD for the year?
If a person passes away without taking their full required minimum distribution (RMD), their beneficiaries must withdraw the remaining amount by December 31 of that same year. Failing to do so can result in IRS penalties unless an exception or waiver applies.
How can beneficiaries determine if the decedent had an RMD requirement?
The RMD obligation depends on the decedent’s age and date of birth. The Required Beginning Date (RBD) is age 72 for those born in 1950 or earlier, 73 for those born between 1951 and 1959, and 75 for those born in 1960 or later. If the decedent was past their RBD, the RMD rule applies.
If there are multiple beneficiaries, does each person need to take part of the RMD?
No. The IRS clarified in 2024 that any one or more beneficiaries can collectively satisfy the decedent’s remaining RMD. As long as the total required amount is withdrawn from the inherited accounts before year-end, it doesn’t need to be split evenly among beneficiaries.
How are RMDs handled if the decedent had multiple IRA accounts?
If all IRAs have the same beneficiaries, the total RMD amount can be aggregated and taken from any one or more accounts. However, if the IRAs have different beneficiaries, each account’s undistributed RMD must be withdrawn separately from that account.
What are the penalties for missing a decedent’s RMD?
The IRS can impose a 25% excise tax on any undistributed RMD amount not withdrawn by year-end. If corrected promptly, the penalty may be reduced to 10%.
Did the IRS change the RMD penalty rules recently?
Yes. Under final regulations released in 2024, beneficiaries now have an automatic waiver of the missed RMD penalty if they take the decedent’s remaining RMD by December 31 of the year after the death. This provides flexibility in situations where distributions are delayed.
When are beneficiaries not required to take a decedent’s RMD?
No RMD is required if the decedent passed away before reaching their Required Beginning Date or had already completed their RMD for the year. In addition, Roth IRAs are exempt from RMD requirements, so beneficiaries of Roth accounts do not need to take year-of-death distributions.
The Final Rules For Non-spouse Beneficiary Inherited IRAs Has Been Released: The 10-Year Rule, Annual RMD Requirement, Tax Strategies, New 401(k) Roth Rules, and More…….
In July 2024, the IRS released its long-awaited final regulations clarifying the annual RMD (required minimum distribution) rules for non-spouse beneficiaries of retirement accounts that are subject to the new 10-year rule. But like most IRS regulations, it’s anything but simple and straightforward.
In July 2024, the IRS released its long-awaited final regulations clarifying the annual RMD (required minimum distribution) rules for non-spouse beneficiaries of retirement accounts that are subject to the new 10-year rule. But like most IRS regulations, it’s anything but simple and straightforward. The short answer is for non-spouse beneficiaries that are subject to the 10-year rule; some beneficiaries will be required to begin taking annual RMDs starting in 2025 while others will not. In this article, we will review:
The RMD requirement for non-spouse beneficiaries
RMD start date
IRS penalty relief for missed RMDs
Are one-time distributions required for missed RMDs 2020 - 2024?
Different RMD rules for Traditional IRAs versus Roth IRAs
Different RMD rules for Roth 401(k) versus Roth IRAs
Common RMD mistake for stretch rule beneficiaries
In addition to covering the topics above related to the new RMD rules, we want this article to be a “one-stop shop” for non-spouse beneficiaries to understand how these non-spouse inherited IRAs work from start to finish, so we will start this article by covering:
How Inherited IRA work for non-spouse beneficiaries
Rules for a decedent that pass either before or after 2019
The new 10-year Rule
Beneficiaries that are granted an exception to the new 10-year rule
Required minimum distributions (RMDs)
Taxation of distributions from inherited IRAs
Tax strategies and Pitfalls associated with Inherited IRA accounts
Special rules for minor children with Inherited IRAs
(If you are reading this just for the new RMD rules, you can skip to the second half of the article)
Non-spouse Beneficiaries of Retirement Accounts
When you inherit a retirement account, there are different options available to you depending on whether you are a “spouse beneficiary” or a “non-spouse beneficiary”. In this article, we are going to be focusing on the options available to a non-spouse beneficiary.
Non-spouse Beneficiary Rules Prior to 2020
In 2019, the SECURE Act 1.0 was passed, which greatly limited the inherited IRA options that were available to non-spouse beneficiaries of IRAs, 401(k)’s, and other types of employer-sponsored retirement plans. Under the old rules, if someone passed away prior to January 1, 2020, you as a non-spouse beneficiary, were allowed to move the balance of that IRA into an inherited IRA in your name, avoid any immediate tax implications, and you only had to take small distributions each year called RMDs (required minimum distributions) based on IRS life expectancy table. This was called the “stretch rule” which allowed a non-spouse beneficiary to stretch the distributions over their lifetime.
If you wanted to take more out of the account, you could, since it’s an inherited IRA, even if you were under the age of 59 ½, you avoided the 10% early withdrawal penalty and either had to pay income tax on a pre-tax retirement account or avoided tax altogether on Roth inherited IRA accounts. These beneficiaries had a lot of flexibility with this option with minimal emergency tax planning needed.
For individuals in this camp who inherited a retirement account from someone who passed away prior to January 1, 2020, the good news is you are grandfathered in under the old rules, and none of the changes that we are going to cover in this article apply to you. You still have access to the stretch provision.
Non-spouse Beneficiary of Decedent That Passed After December 31, 2019
SECURE Act 1.0, which passed in 2019, took away the “stretch option” for most non-spouse beneficiaries and replaced it with a much more restrictive “10-Year Rule,” which requires a non-spouse beneficiary to fully deplete the account balance of that inherited retirement account within 10 years start the year after the decedent passed away. If you inherited a retirement account from someone who passed away AFTER December 31, 2019, and you are non-spouse beneficiaries, you are subject to the new 10-Year Rule UNLESS you meet one of the exceptions. Non-spouse beneficiaries that qualify for an exception to the 10-year rule are referred to as “Eligible Designated Beneficiaries” in the new tax regulations if you choose to read the 260 pages that were just released by the IRS.
Here is the list of beneficiaries that are exempt from the new 10-year rule and still have the stretch option available to them:
Surviving spouse
Person less than 10 years younger than the decedent
Minor children
Disabled person
Chronically ill person
Some See-Through Trusts benefitting someone on this exception list
Non-Spouse Beneficiary Not More Than 10 Years Younger Than The Decedent
I wanted to highlight this exception because it’s the most common exception to the 10-rule for non-spouse beneficiaries that we see amongst our clients. If you are a non-spouse beneficiary of a retirement account from someone that was not more than 10 years younger than you like a sibling or a cousin, the new 10-year distribution rule does not apply to you. You are allowed to roll over the balance to your own inherited IRA and stretch annual RMDs over your lifetime.
Example: Tim passes away at the age of 55 and his sister Susan age 58 is the 100% primary beneficiary of his Traditional IRA account, since Susan is a non-spouse beneficiary, she normally would be subject to the 10-year rule requiring her to fully distribute and pay tax on Tim’s IRA balance within a 10 year period. However, since Tim was less than 10 years younger than Susan, she qualifies for the exception to the 10-year rule. She can rollover Tim’s IRA balance into an Inherited IRA in her name, and she would only be required to take small required minimum distributions each year starting the year after Tim passed away.
Minor Children As Beneficiary of Retirement Accounts
The minor child exception is a little tricker. If a minor child is the beneficiary of a retirement account, and they inherited the retirement account from their parents, they are only required to take those small annual RMDs until they reach age 21, but then as soon as they turn 21, they switch over to the 10-Year Rule. If they inherited the retirement account from someone other than their parent, then the 10-year period begins the year after the decedent passes away like the rest of the non-spouse beneficiaries.
Example: Josh is age 12 and his mother unexpectedly passes away and Josh is listed as the primary beneficiary on his mother’s 401(K) account at work. Josh, as a non-spouse beneficiary, would not immediately be subject to the 10-year rule, but instead, he would be temporarily allowed to use the stretch provision; he would be required to take annual RMDs each year from the retirement account until he reaches age 21. Once Josh reaches age 21, he will then be subject to the 10-year rule, and he will be required to fully distribute the retirement account 10 years following when he turns age 21.
Age of Majority: Normally the “age of majority” is defined by the state that the minor lives in. For some states, it’s age 18, and in other states, it’s age 21. The new IRS regulations addressed this issue and stated that regardless of the age of majority for the state that the minor lives in and regardless of whether or not the child is a student past the age of 18, the age of majority for purposes of triggering the 10-year rule for non-spouse beneficiaries will be age 21.
Non-Spouse Beneficiary Subject To The 10-Year Rule
If you are a non-spouse beneficiary who inherited a retirement account from someone who passed away AFTER December 31, 2019, and you DO NOT qualify for one of the exceptions previously listed, then you are subject to the new “10-Year Rule”. The 10-Year Rule requires a non-spouse beneficiary to fully deplete the inherited retirement account balance no later than 10 years following the year after the decedent passes away.
The 10-Year Rule Applies to Both Pre-Tax and Roth Retirement Accounts
Regardless of whether you inherited a pre-tax retirement account like a Traditional IRA, SEP IRA, or 401(k) account or a Roth retirement account like a Roth IRA or Roth 401(k), the 10-year rule applies.
Example: Sarah’s father just passed away in February 2024, and she was the 100% primary beneficiary of his Traditional IRA account with a balance of $300,000. Sarah is age 60. Sarah, as a non-spouse beneficiary, would be subject to the 10-year rule and would be required to fully distribute and pay tax on the full $300,000 before December 31, 2034, which is 10 years following the year after her father passed away.
The RMD Mystery
When the 10-Year Rule first came into being in 2020, it was assumed that this 10-year rule was an extension of the previous “5-year rule”, which only required the beneficiary to deplete the account balance within 5 years but there was no annual RMDs requirement during that 5-year period. The IRS just simply eliminated the “stretch option” and extended the 5-year rule to a 10-year rule.
But then, two after the IRS passed SECURE Act 1.0 with this new 10-year rule, the IRS came out with new proposed regulations that basically said, “Whoops, I know we wrote it that way, but that’s not what we meant.”
In the proposed regulations that the IRS released in February 2022, the IRS clarified that what they meant to say was that certain non-spouse beneficiaries that are subject to the new 10-year rule would ALSO be required to take annual RMDs during that 10-year period. This was not welcome news for many non-spouse beneficiaries, and it created a lot of confusion since a few years had already gone by since the new 10-year rule was signed into law.
The New RMD Rules for Inherited IRA for Non-spouse Beneficiaries
The finalized IRS regulations that were just released in July 2024 made their stance official. Whether or not a non-spouse beneficiary will be subject to BOTH the 10-Year Rule and annual RMDs will be dependent on two factors:
The age of the decedent when they passed away
The type of retirement account that the beneficiary inherited (Pre-tax or Roth)
RMD Requirement Based on Age of Decedent
If you are the original owner of a retirement account (Traditional IRA, 401(k), etc.), once you reach a specific age, the IRS requires you to start taking small distributions from that pre-tax account each year, which are called required minimum distributions (RMDs).
The age at which you are required to begin taking RMDs is called your Required Beginning Date (“RBD”), not to be confused with the “RMD”. There are too many acronyms in the finance world “The IRS wants you to take your RMD by your RBD ASAP so they can collect their TAX.”
The date at which RMDs are required to begin varies based on your date of birth:
Born 1950 or earlier: Age 72
Born 1951 – 1959: Age 73
Born 1960 or later: Age 75
Someone that is born in 1956 would be required to start taking RMDs from their pre-tax retirement accounts at age 73. Why is this relevant to non-spouse beneficiaries? Because whether or not the decedent died before or after their Required Beginning Date for RMDs will determine whether or not you, as the non-spouse beneficiary, are required to take annual RMDs during the 10-Year Rule period.
The Decedent Passes Away Prior to Their RMD Required Beginning Date
If the decedent passed away prior to their Required Beginning Date, then you, as the non-spouse beneficiary, are subject to the 10-Year Rule, but you ARE NOT REQUIRED to take annual RMDs during the 10-year period. You simply have to deplete the account balance prior to the end of the 10 years.
Example: Brad’s father passes away at age 68 and Brad is the 100% beneficiary of his Traditional IRA. Brad’s father was born in 1956, making his RMD start at age 73. Since Brad’s father passed away prior to reaching age 73 (RBD), Brad would be subject to the 10-year rule but would not be required to take annual RMDs during that 10-year period.
The Decedent Passes Away After Their RMD Required Beginning Date
If the decedent passes away AFTER their Required Beginning Date for RMDs, then the non-spouse beneficiary is subject to BOTH the 10-year rule AND is required to take annual RMDs during that 10-year period.
Example: Dave’s father passed away at age 80, and he had been taking RMDs for many years since he was beyond his Required Beginning Date. When Dave inherits his father’s Traditional IRA, he will not only be subject to the 10-year rule as a non-spouse beneficiary, but he will also be required to distribute annual RMDs every year from the Inherited IRA account since his father had already begun receiving RMDs for his account.
RMDs Not Required Until 2025
Since the IRS just released the final regulation in July 2024, for non-spouse beneficiaries that are subject to both the 10-Year Rule and annual RMDs, RMDs are not required to begin until 2025.
Good news: For non-spouse beneficiaries subject to the 10-year rule, the IRS has waived all penalties for the “missed RMDs” between 2020 and 2024, and they are not requiring these non-spouse beneficiaries to “make up” for missed RMDs for years leading up to 2025. The RMDs will be calculated in 2025 like everything has been working smoothly since Day 1.
No Reset of the 10-Year Depletion Timeline
It’s important to note that even though the IRS took 4 years to clarify the RMD rules associated with the new 10-year rule, it does not reset the 10-year clock for the depletion of the inherited retirement account.
Example: Jessica’s uncle passed away in 2020 at the age of 82. Jessica, as a non-spouse beneficiary, would be subject to the 10-year rule requiring her to fully deplete the Traditional IRA by December 31, 2030. Since her uncle was past his Required Beginning Date for RMDs, Jessica would be required to take annual RMD in the years 2025 – 2030. (Note that the 2021 – 2024 RMDs were waived due to the IRS delay). Even though her first RMD will not be until 2025, she is still required to deplete the Traditional IRA account by December 31, 2030.
Annual RMD Rules
Many of these examples incorporate the delay in annual RMDs due to the delay in the IRS regulations being released. However, if someone passes away in 2024 and has a non-spouse beneficiary listed on their pre-tax retirement account, the 10-year timeline and the first annual RMD calendar would begin in 2025, which is the year following the decedent’s date of death.
The first RMD is required to be taken by a non-spouse beneficiary by December 31st of the year following the decedent's death.
Inherited Roth IRAs – No RMD Requirement
You will notice in most of my examples that I specifically use a “Traditional IRA” or “Pre-tax Retirement Account.” That is because only pre-tax retirement accounts have the RMD requirement. If you are the original owner of a Roth IRA, Roth IRAs do not require you to take an RMD regardless of your age. So, under the new rules, if you inherit a Roth IRA, since the decedent would not have been required to take an RMD from a Roth IRA at any age, they never had a “Required Beginning Date”. This makes the non-spouse beneficiary subject to the 10-year rule, but no annual RMDs would be required from an inherited Roth IRA.
Note: If you inherit a Roth IRA and you are eligible for the stretch options, annual RMDs are then required from you Inherited Roth IRA account.
Roth 401(k)s Are Different
While typically, Roth IRAs and Roth 401(k)s have the same rules, the IRS included a weird rule for Roth 401(k)s in the final regulations regarding the RMD requirement. If you inherit a 401(k) plan, it’s possible that there are both Pre-tax and Roth monies within that same account since most 401(k) plans allow plan participants to make either pre-tax deferrals or Roth deferrals to the plan.
Normally I would have thought if a 401(k) account contains both Pre-tax and Roth dollars, as a non-spouse beneficiary, you would have the 10-year rule for the full account balance, but you could ignore the RMD requirement for the Roth dollars, but the annual RMDs on the pre-tax portion of the account would depend on whether or not the decedent passed away before or after their Required Beginning Date for RMDs. Assuming this, I would have been correct for the pre-tax portion of the 401(k) account but potentially wrong about no annual RMDs for the Roth portion of the 401(k) account.
The final regulations state that if the 401(k) account contains ONLY Roth dollars, no pre-tax dollars within the account, then a non-spouse beneficiary is subject to the 10-year rule but DOES NOT have to take annual RMDs during that 10-year period.
However, if the 401(k) account contains both Roth and any other type of pre-tax source, like employee pre-tax deferrals, employer match, and employer profit sharing, which is much more common for 401(k) plans, then the ENTIRE BALANCE in the 401(k) plan, INCLUDING THE ROTH SOURCE, is subject to the annual RMD requirement during the 10-year period. Yuck!!!
This new rule will encourage individuals who have a Roth source within their employer-sponsored retirement plans to roll over their Roth monies within the plan to a Roth IRA before they pass away. By removing that Roth source from the employer-sponsored retirement plans and moving it into a Roth IRA, now when the non-spouse beneficiary inherits the Roth IRA, they are allowed to accumulate those Roth dollars longer within the 10-year period since they are not required to take annual RMDs from a Roth IRA account.
Note: The pre-tax sources within a 401(k) works the same way as inheriting a Traditional IRA. A non-spouse beneficiary would be subject to the 10-year rule and may or may not have to take RMDs during the 10-year period depending on whether or not the decedent dies before or after their Required Beginning Date for RMDs.
Non-Spouse Beneficiaries Eligible For The Stretch Rule Only Had An RMD Waiver for 2020
In 2020, part of the COVID relief packages was the ability to waive taking an RMD during that calendar year. I have run into a few cases where non-spouse beneficiaries that were grandfathered in under the “stretch rules” requiring them to take an annual RMD each year, are getting confused with the delay in the RMD requirement for non-spouse beneficiaries that are subject to the new 10-year rule after December 2019. The delay in the annual RMDs until 2025 for non-spouse beneficiaries ONLY applies to individuals subject to the 10-year rule. If you inherited a retirement account from someone who passed away prior to 2020 or you qualify for one of the exceptions to the 10-Year Rule as a non-spouse beneficiary, you are grandfathered in under the old “Stretch Rule,” which requires the owner of that Inherited IRA to take annual RMD’s from that account each year starting in the calendar year following the decedent’s date of death.
In summary, if you are a stretch rule non-spouse beneficiary, the only year you were allowed to skip your RMD was 2020 per the COVID relief; you should have restarted your annual RMDs in 2021 and taken an RMD for 2021, 2022, and 2023, and subsequent years. If you missed this, the good news is the Secure Act 2.0 also lowered the IRS penalty amount for missed RMDs, from 50% to 25% and even lower to 10% if timely corrected.
Non-Spouse Inherited IRA Tax Strategies
We will be writing a separate article that contains all of the advanced tax strategies that we implement for clients who are non-spouse beneficiaries subject to the 10-year rule since there are a number of them, but here is some of the standard guidance that we provide to our clients.
If you inherit a Roth IRA, that is an ideal situation because even though you are subject to the 10-year rule as a non-spouse beneficiary, all of the accumulation in an Inherited Roth IRA can be withdrawn tax-free.
Example: John inherits a $200,000 Roth IRA from his mother in 2024. John, as a non-spouse beneficiary, will be subject to the 10-year rule, so the account has to be depleted by 2034, but he is not required to take annual RMDs because it’s a Roth IRA account. If John invests the $200,000 wisely and receives an 8% annual rate of return, at the end of 10-year the $200,000 has grown to $431,785 within that Inherited Roth IRA, and the full balance will be distributed to him ALL TAX-FREE.
For this reason, we have a lot more clients processing Roth Conversions in retirement to push more of their net worth from the pre-tax bucket over to the Roth bucket, which is much more favorable for non-spouse beneficiaries when they inherit the account.
For clients that inherit larger pre-tax retirement accounts that are subject to the 10-year rule, we have to develop a detailed tax plan for the next 10 years since we know all of that money will need to be distributed and taxed within the next 10 years, which could cause the money to be taxed at a higher tax rate, increased Medicare premiums, lower financial aid awards for parents with kids in college, have their social security taxed at a higher rate, lose tax deductions, or other negative consequences for showing too much income in a single year.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What did the IRS clarify about non-spouse beneficiary RMDs in 2024?
In July 2024, the IRS issued final regulations confirming that some non-spouse beneficiaries subject to the 10-year rule must begin taking annual required minimum distributions (RMDs) starting in 2025. Whether annual RMDs are required depends on the decedent’s age at death and the type of retirement account inherited.
Who must take annual RMDs under the 10-year rule?
If the decedent passed away after reaching their Required Beginning Date (the age at which RMDs must begin), the non-spouse beneficiary must take annual RMDs during the 10-year depletion period. If the decedent passed before reaching that age, the beneficiary is only required to deplete the account by the end of the 10 years—no annual RMDs are needed.
What are the new RMD start dates for non-spouse beneficiaries?
The IRS delayed required RMDs for non-spouse beneficiaries until 2025. Any missed RMDs for the years 2020–2024 are waived, and beneficiaries are not required to make catch-up distributions for those years.
Does the 10-year rule clock reset under the new regulations?
No. Even though the IRS delayed annual RMDs until 2025, the 10-year period to deplete the inherited account still begins the year after the decedent’s death. Beneficiaries must empty the account by the original deadline.
Do Roth IRAs have RMD requirements for non-spouse beneficiaries?
No. Inherited Roth IRAs are subject to the 10-year rule, but they do not require annual RMDs since Roth owners are never required to take RMDs during their lifetimes. Beneficiaries can let the Roth IRA grow tax-free for the full 10 years before withdrawing the balance.
Are Roth 401(k)s treated differently?
Yes. If a Roth 401(k) contains only Roth dollars, no annual RMDs are required during the 10-year period. However, if the account also contains any pre-tax sources—such as employer matches—the entire balance, including the Roth portion, becomes subject to annual RMDs. Rolling Roth 401(k) funds into a Roth IRA before death can avoid this issue.
What happens to non-spouse beneficiaries who still qualify for the stretch rule?
Those grandfathered under the old stretch rule must continue taking annual RMDs each year. Only 2020 distributions were waived under COVID relief. Any missed RMDs after 2020 may trigger penalties unless corrected under the new reduced penalty rules.
What are key tax considerations for non-spouse beneficiaries?
Inherited Roth IRAs are generally ideal since withdrawals are tax-free. Beneficiaries of large pre-tax accounts should work with a tax professional to spread distributions over several years, minimizing the impact on income taxes, Medicare premiums, and financial aid eligibility.
2023 RMDs Waived for Non-spouse Beneficiaries Subject To The 10-Year Rule
There has been a lot of confusion surrounding the required minimum distribution (RMD) rules for non-spouse, beneficiaries that inherited IRAs and 401(k) accounts subject to the new 10 Year Rule. This has left many non-spouse beneficiaries questioning whether or not they are required to take an RMD from their inherited retirement account prior to December 31, 2023. Here is the timeline of events leading up to that answer
There has been a lot of confusion surrounding the required minimum distribution (RMD) rules for non-spouse beneficiaries who inherited IRAs and 401(k) accounts subject to the new 10-Year Rule. This has left many non-spouse beneficiaries questioning whether or not they are required to take an RMD from their inherited retirement account prior to December 31, 2023. Here is the timeline of events leading up to that answer:
December 2019: Secure Act 1.0
In December 2019, Congress passed the Secure Act 1.0 into law, which contained a major shift in the distribution options for non-spouse beneficiaries of retirement accounts. Prior to the passing of Secure Act 1.0, non-spouse beneficiaries were allowed to move these inherited retirement accounts into an inherited IRA in their name, and then take small, annual distributions over their lifetime. This was referred to as the “stretch option” since beneficiaries could keep the retirement account intact and stretch those small required minimum distributions over their lifetime.
Secure Act 1.0 eliminated the stretch option for non-spouse beneficiaries who inherited retirement accounts for anyone who passed away after December 31, 2019. The stretch option was replaced with a much less favorable 10-year distribution rule. This new 10-year rule required non-spouse beneficiaries to fully deplete the inherited retirement account 10 years following the original account owner’s death. However, it was originally interpreted as an extension of the existing 5-year rule, which would not require the non-spouse beneficiary to take annual RMD, but rather, the account balance just had to be fully distributed by the end of that 10-year period.
2022: The IRS Adds RMDs to the 10-Year Rule
In February 2022, the Treasury Department issued proposed regulations changing the interpretation of the 10-year rule. In the proposed regulations the IRS clarified that RMDs would be required for select non-spouse beneficiaries subject to the 10-year rule, depending on the decedent’s age when they passed away. Making some non-spouse beneficiaries subject to the 10-year rule with no RMDs and others subject to the 10-year rule with annual RMDs.
Why the change? The IRS has a rule within the current tax law that states that once required minimum distributions have begun for an owner of a retirement account the account must be depleted, at least as rapidly as a decedent would have, if they were still alive. The 10-year rule with no RMD requirement would then violate that current tax law because an account owner could be 80 years old, subject to annual RMDs, then they pass away, their non-spouse beneficiary inherits the account, and the beneficiary could voluntarily decide not to take any RMDs, and fully deplete the account in year 10 in accordance with the new 10-year rule. So, technically, stopping the RMDs would be a violation of the current tax law despite the account having to be fully depleted within 10 years.
In the proposed guidance, the IRS clarified, that if the account owner had already reached their “Required Beginning Date” (RBD) for required minimum distributions (RMD) while they were still alive, if a non-spouse beneficiary, inherits that retirement account, they would be subject to both the 10-year rule and the annual RMD requirement.
However, if the original owner of the IRA or 401k passes away prior to their Required Beginning Date for RMDs since the RMDs never began if a non-spouse beneficiary inherits the account, they would still be required to deplete the account within 10 years but would not be required to take annual RMDs from the account.
Let’s look at some examples. Jim is age 80 and has $400,000 in a traditional IRA, and his son Jason is the 100% primary beneficiary of the account. Jim passed away in May 2023. Since Jason is a non-spouse beneficiary, he would be subject to the 10-year rule, meaning he would have to fully deplete the account by year 10 following the year of Jim’s death. Since Jim was age 80, he would have already reached his RMD start date, requiring him to take an RMD each year while he was still alive, this in turn would then require Jason to continue those annual RMDs during that 10-year period. Jason’s first RMD from the inherited IRA account would need to be taken in 2024 which is the year following Jim’s death.
Now, let’s keep everything the same except for Jim’s age when he passes away. In this example, Jim passes away at age 63, which is prior to his RMD required beginning date. Now Jason inherits the IRA, he is still subject to the 10-year rule, but he is no longer required to take RMDs during that 10-year period since Jim had not reached his RMD required beginning date at the time that he passed.
As you can see in these examples, the determination as to whether or not a non-spouse beneficiary is subject to the mandatory RMD requirement during the 10-year period is the age of the decedent when they pass away.
No Final IRS Regs Until 2024
The scenario that I just described is in the proposed regulations from the IRS but “proposed regulations” do not become law until the IRS issues final regulations. This is why we advised our clients to wait for the IRS to issue final regulations before applying this new RMD requirement to inherited retirement accounts subject to the 10-year rule.
The IRS initially said they anticipated issuing final regulations in the first half of 2023. Not only did that not happen, but they officially came out on July 14, 2023, and stated that they would not issue final regulations until at least 2024, which means non-spouse beneficiaries of retirement accounts subject to the 10-year rule will not face a penalty for not taking an RMD for 2023, regardless of when the decedent passed away.
Heading into 2024 we will once again have to wait and see if the IRS comes forward with the final regulations to implement the new RMDs rules outlined in their proposed regs.
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Secure Act 2.0: RMD Start Age Pushed Back to 73 Starting in 2023
On December 23, 2022, Congress passed the Secure Act 2.0, which moved the required minimum distribution (RMD) age from the current age of 72 out to age 73 starting in 2023. They also went one step further and included in the new law bill an automatic increase in the RMD beginning in 2033, extending the RMD start age to 75.
On December 23, 2022, Congress passed the Secure Act 2.0, which moved the required minimum distribution (RMD) age from the current age of 72 out to age 73 starting in 2023. They also went one step further and included in the new law bill an automatic increase in the RMD beginning in 2033, extending the RMD start age to 75.
This is the second time within the past 3 years that Congress has changed the start date for required minimum distributions from IRAs and employer-sponsored retirement plans. Here is the history and the future timeline of the RMD start dates:
1986 – 2019: Age 70½
2020 – 2022: Age 72
2023 – 2032: Age 73
2033+: Age 75
You can also determine your RMD start age based on your birth year:
1950 or Earlier: RMD starts at age 72
1951 – 1959: RMD starts at age 73
1960 or later: RMD starts at age 75
What Is An RMD?
An RMD is a required minimum distribution. Once you hit a certain age, the IRS requires you to start taking a distribution each year from your various retirement accounts (IRA, 401(K), 403(b), Simple IRA, etc.) because they want you to begin paying tax on a portion of your tax-deferred assets whether you need them or not.
What If You Turned Age 72 In 2022?
If you turned age 72 anytime in 2022, the new Secure Act 2.0 does not change the fact that you would have been required to take an RMD for 2022. This is true even if you decided to delay your first RMD until April 1, 2023, for the 2022 tax year.
If you are turning 72 in 2023, under the old rules, you would have been required to take an RMD for 2023; under the new rules, you will not have to take your first RMD until 2024, when you turn age 73.
Planning Opportunities
By pushing the RMD start date from age 72 out to 73, and eventually to 75 in 2033, it creates more tax planning opportunities for individuals that do need to take distributions out of their IRAs to supplement this income. Since these distributions from your retirement account represent taxable income, by delaying that mandatory income could allow individuals the opportunity to process larger Roth conversions during the retirement years, which can be an excellent tax and wealth-building strategy.
Delaying your RMD can also provide you with the following benefits:
Reduce the amount of your Medicare premiums
Reduce the percentage of your social security benefit that is taxed
Make you eligible for tax credits or deductions that you would have phased out of
Potentially allow you to realize a 0% tax rate on long-term capital gains
Continue to keep your pre-tax retirement dollars invested and growing
Additional Secure Act 2.0 Articles
About Michael……...
Hi, I’m Michael Ruger. I’m the managing partner of Greenbush Financial Group and the creator of the nationally recognized Money Smart Board blog . I created the blog because there are a lot of events in life that require important financial decisions. The goal is to help our readers avoid big financial missteps, discover financial solutions that they were not aware of, and to optimize their financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
What is the new RMD age under the Secure Act 2.0?
Starting in 2023, the required minimum distribution (RMD) age increased from 72 to 73. Beginning in 2033, the RMD age will rise again to 75.
How does the new RMD timeline compare to previous rules?
Before 2020, RMDs began at age 70½. The Secure Act of 2019 moved it to age 72, and Secure Act 2.0 now increases it to age 73 in 2023 and age 75 starting in 2033.
How do you determine your RMD start age based on birth year?
If you were born in 1950 or earlier, your RMD started at 72. Those born between 1951 and 1959 begin at 73, and anyone born in 1960 or later will start at 75.
What if I turned 72 in 2022?
If you reached age 72 in 2022, you are still required to take your first RMD for that tax year, even if you delayed it until April 1, 2023. The new rule applies only to individuals turning 72 in 2023 or later.
What are the benefits of delaying RMDs?
Delaying RMDs can create valuable tax planning opportunities, including the ability to complete larger Roth conversions, reduce taxable income, lower Medicare premiums, and minimize taxes on Social Security benefits.
Can delaying RMDs impact long-term investment growth?
Yes. By postponing mandatory withdrawals, your tax-deferred savings can remain invested and continue to grow, potentially increasing your retirement assets over time.